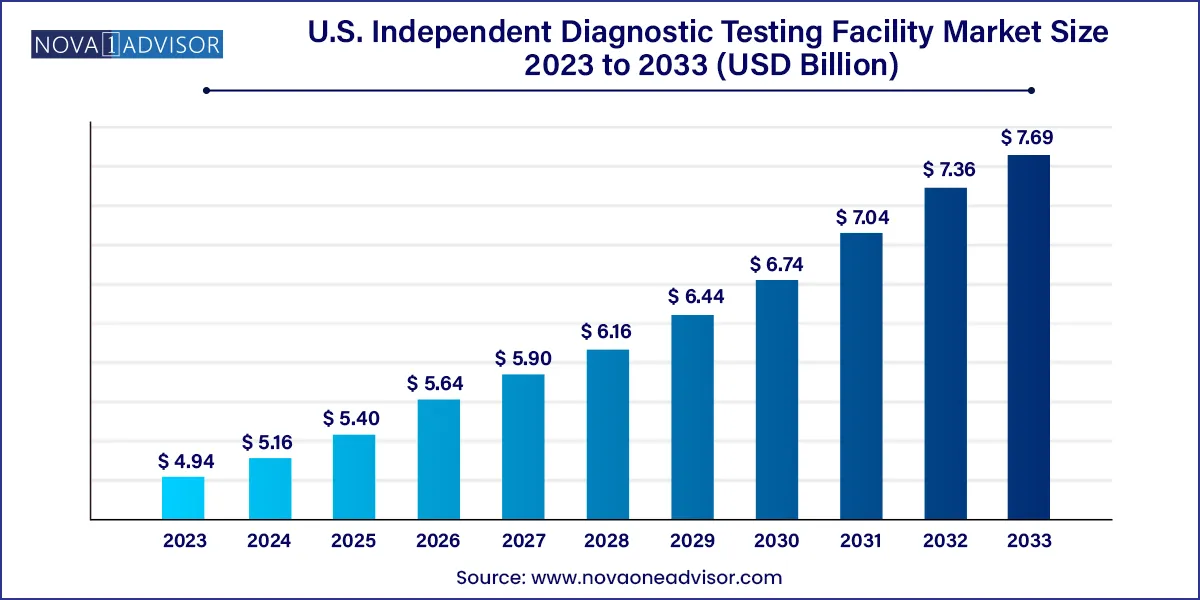
The U.S. independent diagnostic testing facility market size was exhibited at USD 4.94 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 7.69 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.53% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. Independent Diagnostic Testing Facility (IDTF) market plays a pivotal role in the healthcare ecosystem, providing specialized diagnostic services outside of traditional hospital settings. These facilities offer an array of non-invasive diagnostic tests that aid in disease detection, monitoring, and management. IDTFs are particularly valuable in serving outpatient needs and providing accessible, cost-effective, and high-quality diagnostic services to patients, especially those in underserved areas or rural regions.
The rise of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, and sleep apnea, has significantly increased the demand for diagnostic services. IDTFs help alleviate the burden on hospitals by offering these services in a more convenient and often more affordable environment. Their operational flexibility, quicker turnaround times, and dedicated diagnostic focus make them indispensable to primary care physicians, specialists, and patients alike.
With advancements in imaging technologies, digital health integration, and portable diagnostic equipment, IDTFs are evolving rapidly. These facilities offer services such as radiology (X-ray, MRI, CT scans), cardiac monitoring, and sleep studies—services that once required hospital infrastructure. IDTFs have gained regulatory recognition through Medicare and private insurers, making reimbursement easier and fueling their expansion.
Moreover, the market is benefitting from the push towards value-based care, where early diagnosis and preventive screenings are critical. This has heightened the role of IDTFs, which not only offer diagnostic testing but also serve as data hubs contributing to longitudinal patient health records. In an era where personalized care and real-time monitoring are becoming the norm, the strategic role of IDTFs in the U.S. healthcare system has never been more prominent.
Surge in Outpatient and Preventive Care Services: A shift in healthcare delivery from inpatient to outpatient settings is driving the demand for diagnostic services at IDTFs.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning in Diagnostics: Automated interpretation tools and AI-powered imaging platforms are streamlining workflows in IDTFs.
Growth in Portable and Remote Diagnostic Devices: Miniaturization of imaging and monitoring technologies is making mobile IDTF services viable.
Rising Use of Telehealth and Teleradiology: Remote consultations and interpretations are expanding access to specialist diagnostic services.
Increased Medicare and Medicaid Support: Regulatory support through CMS has improved IDTF participation in publicly reimbursed healthcare programs.
Focus on Multimodal Diagnostic Offerings: IDTFs are increasingly combining radiology, cardiac, and sleep diagnostics to become one-stop diagnostic centers.
Expansion in Rural and Underserved Markets: IDTFs are bridging diagnostic gaps in areas lacking full-service hospitals.
Emphasis on Patient-centric Experience: Quicker appointment scheduling, shorter waiting times, and real-time result sharing are enhancing patient satisfaction.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 5.16 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 7.69 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 4.53% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Service |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | RadNet, Inc.; Equimed Corporation; Vitalistics; Breathe; Texas MRI; The Brookwood Diagnostic Center; ACS Diagnostics, Inc.; Houston MRI & Diagnostic Imaging; TestSmarter Inc.; Duke University and Duke University Health System; Covenant Health Diagnostics; AliveCor, Inc.; Advanced Cardio Services; Diagnostic Medical Testing Inc.; K & T Diagnostic, Inc.; Vestavia Diagnostic Center (VDC); Advanced Imaging Center |
A primary driver of the U.S. IDTF market is the escalating prevalence of chronic and lifestyle-related diseases, which necessitate frequent diagnostic evaluations. Conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and sleep apnea are on the rise due to sedentary lifestyles, poor diet, and aging demographics. According to the CDC, six in ten adults in the U.S. live with at least one chronic disease, and four in ten have two or more.
These conditions often require recurrent testing, including imaging, blood tests, cardiac monitoring, and sleep studies. IDTFs are particularly well-positioned to meet this need by offering high-quality diagnostic services outside traditional hospital environments. For instance, cardiac monitoring services such as Holter monitoring and event recorders provided by IDTFs have become standard tools for detecting arrhythmias in outpatient settings. Similarly, sleep study services are addressing the needs of the growing population diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea.
By providing easy access, faster service, and reduced costs, IDTFs support chronic disease management and reduce the likelihood of hospital readmissions. Their role becomes even more important as the healthcare model shifts toward proactive and preventive care, where early detection is the linchpin of effective treatment.
Despite their benefits, IDTFs face a significant challenge in the form of regulatory hurdles and inconsistent reimbursement policies. Medicare, which plays a major role in funding diagnostic services, has established stringent requirements for IDTF accreditation and billing compliance. These include limitations on the types of services offered, required documentation, and enrollment under specific CMS guidelines.
Moreover, reimbursement rates are often scrutinized or subject to budget cuts, creating financial unpredictability. Many IDTFs face audits, payment delays, or denials due to minor documentation discrepancies. Private insurers also vary widely in their reimbursement criteria, further complicating billing processes.
These complexities can hinder the scalability of IDTFs, particularly for small to medium-sized players who lack dedicated administrative resources. Additionally, ongoing changes in healthcare policies related to billing codes, provider qualifications, and telehealth usage can make long-term planning difficult for IDTFs.
The post-pandemic shift toward home healthcare has opened a vast opportunity for IDTFs to expand their reach through remote and home-based diagnostics. With patients increasingly seeking convenience, comfort, and safety, the demand for mobile imaging units, remote cardiac monitors, and at-home sleep test kits is rising sharply.
Companies are already developing portable ECG machines, wireless Holter monitors, and AI-powered sleep apnea detection devices that can be used at home with minimal setup. IDTFs that integrate these technologies can tap into a broader patient base, including those in rural and mobility-challenged populations.
For example, Zio XT—a wearable cardiac monitor from iRhythm Technologies—enables remote cardiac rhythm monitoring and transmits data to centralized facilities for analysis. Such devices, when integrated into an IDTF’s offerings, dramatically enhance scalability and service diversification. These advancements can also facilitate participation in value-based care models, where continuous monitoring and data collection are critical for outcome-based reimbursements.
Radiology/Imaging services dominate the U.S. IDTF market, accounting for the largest share due to the extensive need for non-invasive diagnostic visualization across nearly all specialties. Among these, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans are highly utilized due to their superior imaging resolution and diagnostic accuracy. These services are essential in evaluating neurological, musculoskeletal, and oncological conditions, making them core offerings at most IDTFs.
MRI, in particular, is frequently used for brain scans, spinal diagnostics, and soft tissue assessments, while CT scans are preferred for bone injuries, internal bleeding, and lung disorders. The demand for advanced imaging modalities is also being fueled by the growing incidence of cancers, stroke, and traumatic injuries. The emergence of low-dose CT for lung cancer screening and whole-body MRI for early cancer detection is further elevating demand for imaging services.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans and mammography are among the fastest-growing services, driven by the emphasis on early cancer detection. PET scans are highly effective in identifying metabolic activity, often used in oncology, cardiology, and neurology. Mammography, critical in breast cancer screening, has seen widespread implementation under government initiatives like the CDC’s National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program.
Ultrasound services are also expanding due to their low cost, real-time results, and applicability in multiple diagnostic scenarios ranging from pregnancy monitoring to vascular assessments. The incorporation of AI-enabled image interpretation tools is allowing IDTFs to improve diagnostic turnaround time, efficiency, and accuracy.
In the United States, the role of IDTFs is gaining strategic prominence due to the healthcare system's shift toward cost-efficiency, early diagnosis, and outpatient management. The country’s aging population, high chronic disease burden, and technological leadership in diagnostics provide a fertile ground for IDTF expansion.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) play a crucial role in shaping the operational landscape for IDTFs. Regulations such as the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (PFS) and the Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS) affect reimbursement rates, influencing service adoption. Recently, CMS expanded telehealth eligibility and remote patient monitoring reimbursement, enabling IDTFs to integrate virtual diagnostics.
The U.S. is also witnessing a boom in ambulatory and stand-alone diagnostic centers. Urban areas are saturated with specialized IDTFs offering rapid diagnostics for orthopedic injuries, cancer screening, cardiac arrhythmias, and sleep disorders. In contrast, rural regions present significant opportunities for mobile and portable diagnostic services. Policy efforts like the Rural Health Care Program and incentives for deploying mobile diagnostic units are helping bridge access gaps.
Additionally, the U.S. market is highly competitive, with companies investing heavily in digital infrastructure. Many IDTFs are integrating PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems), EMRs (Electronic Medical Records), and AI algorithms to enhance workflow and compliance. As a result, the U.S. IDTF landscape is evolving into a more connected, agile, and patient-centered diagnostic network.
In March 2025, iRhythm Technologies announced the expansion of its Zio® cardiac monitoring service into more than 100 outpatient diagnostic centers across the U.S., reinforcing the adoption of remote arrhythmia monitoring.
In January 2025, RadNet Inc. introduced its new AI-powered mammography interpretation system, enhancing early breast cancer detection rates at its nationwide diagnostic centers.
In November 2024, BioTelemetry Inc., a Philips company, unveiled an upgrade to its remote cardiac telemetry platform, integrating real-time analytics and physician alerts.
In September 2024, Akumin Inc. launched a mobile imaging division to serve rural U.S. counties with limited access to advanced radiology services.
In July 2024, ResMed announced FDA approval of a new at-home sleep study system, which will be distributed through independent testing facilities across key U.S. markets.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. independent diagnostic testing facility market
Service