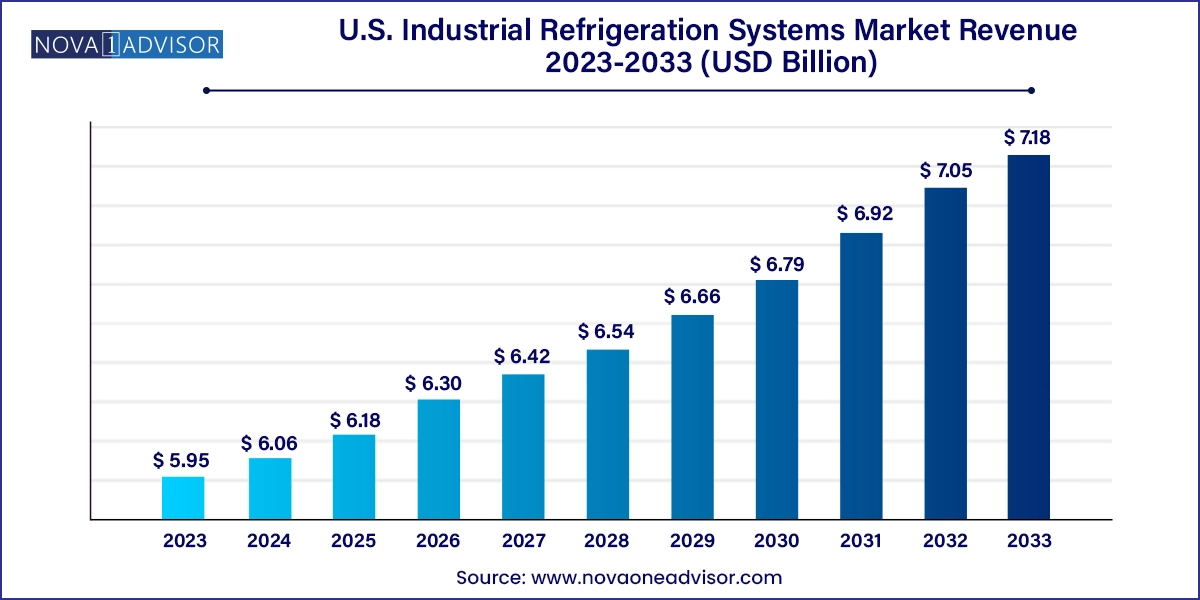
The U.S. industrial refrigeration systems market size was exhibited at USD 5.95 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 7.18 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 1.9% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. industrial refrigeration systems market is a mature but dynamically evolving sector critical to national supply chains for perishable goods, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and temperature-sensitive industrial processes. These systems are designed to handle large-scale cooling applications in environments such as food processing plants, refrigerated warehouses, beverage manufacturing, petrochemical complexes, and logistics operations involving cold chain storage and transport.
As the U.S. faces increased pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, decarbonize infrastructure, and support energy-efficient operations, the role of industrial refrigeration is undergoing a significant transformation. The transition away from high-global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants, integration of smart controls, and adoption of natural refrigerants like ammonia and CO₂ are shaping market behavior. Additionally, digitalization, automation, and Industry 4.0 frameworks are reshaping how refrigeration systems are monitored, maintained, and managed in large-scale facilities.
Heightened consumer expectations for food safety, stringent regulatory frameworks (such as EPA’s AIM Act, DOE efficiency standards, and FDA cold chain regulations), and increased demand for e-commerce-based grocery and pharmaceutical delivery are further reinforcing the need for robust, scalable, and compliant refrigeration solutions.
Growing Adoption of Natural Refrigerants: Ammonia and CO₂ are replacing synthetic refrigerants to meet sustainability and regulatory requirements.
Integration of IoT and Cloud-Based Control Systems: Intelligent systems enable predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and remote management of large-scale refrigeration networks.
Expansion of Cold Chain Infrastructure for Food and Pharma: Demand is rising for temperature-controlled logistics driven by grocery e-commerce and vaccine distribution.
Customization and Modularization of Refrigeration Plants: Modular refrigeration units offer scalability and faster installation in new or upgraded facilities.
Electrification and Decarbonization of Cooling Processes: Facilities are deploying energy-efficient compressors, waste heat recovery systems, and solar-powered refrigeration to reduce carbon footprints.
Stringent Compliance and Safety Mandates: Increasing safety regulations for ammonia systems and refrigerant leak detection are influencing system design and maintenance practices.
Emergence of Low-Charge Ammonia Systems: These systems balance ammonia’s high efficiency with reduced risk and smaller charge volumes for safer application in urban or indoor environments.
Increased M&A and Strategic Partnerships: Major players are acquiring smaller firms or entering strategic partnerships to gain market share and access proprietary technology.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 6.06 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 7.18 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 1.9% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Component, Capacity, Refrigerant, Application |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Johnson Control; Emerson Electric Co; Danfoss; DAIKIN Industries Ltd.; GEA Group Aktiengesellschaft; MAYEKAWA MFG Co. Ltd.; BITZER; EVAPCO Inc.; Guntner GmbH & Co. KG; and LU-VE S.P.A. |
One of the most significant drivers in the U.S. industrial refrigeration market is the expansion of cold chain logistics networks, especially to serve the food & beverage and pharmaceutical sectors. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed gaps in the U.S. cold chain infrastructure, leading to a surge in public and private investment in refrigerated warehousing and temperature-controlled distribution.
With growing consumer demand for frozen and ready-to-eat meals, online grocery platforms like Amazon Fresh, Walmart, and Instacart are expanding their footprint in cold chain-enabled warehouses. Moreover, pharmaceutical advancements, especially with biologics and temperature-sensitive vaccines, require precise and uninterrupted cold storage environments.
To meet these demands, manufacturers and logistics providers are increasingly deploying advanced refrigeration systems with remote monitoring, multi-temperature zones, and compliance with federal safety standards. This trend is projected to sustain high demand for refrigeration systems with integrated automation and sustainability features in the coming years.
Despite robust demand, one of the key restraints in the U.S. industrial refrigeration systems market remains the high capital investment associated with installing and maintaining advanced systems. Industrial refrigeration setups are complex, requiring precise engineering, safe installation practices (especially for ammonia), and ongoing technical support.
Costs can escalate further when incorporating state-of-the-art components such as variable speed compressors, multi-stage evaporators, and smart control interfaces. Moreover, strict compliance with regulatory requirements from OSHA, EPA, and ASHRAE often mandates additional safety equipment, leak detection sensors, and skilled labor for operation.
Smaller food processors, independent cold storage providers, and agricultural cooperatives may find these initial expenses prohibitive, leading to delayed upgrades or partial system retrofits. As such, balancing performance with affordability and scalability is an ongoing challenge for OEMs and integrators.
The increasing regulatory and corporate emphasis on reducing environmental impact presents a major opportunity for manufacturers and service providers in the U.S. industrial refrigeration market. The American Innovation and Manufacturing (AIM) Act aims to phase down hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), creating urgency and incentives for companies to invest in low-GWP systems.
This transition is creating strong demand for CO₂-based cascade systems, low-charge ammonia systems, and hybrid configurations that offer both efficiency and compliance. Simultaneously, energy efficiency improvements—such as variable-speed drives, heat recovery units, and advanced control software—enable facilities to reduce electricity consumption and operating costs.
Government programs offering tax credits, grants, and financing for green infrastructure, along with rising ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) commitments from corporations, are accelerating investment in future-ready refrigeration solutions. OEMs that can deliver modular, compliant, and eco-efficient systems are well-positioned to gain market share.
Systems in the 1000–5000kW range dominate the U.S. market, typically found in large refrigerated warehouses, food processing plants, and petrochemical facilities. These systems are capable of supporting centralized cooling networks and are essential for high-volume, continuous operation environments. Their robustness and ability to accommodate complex load profiles make them suitable for 24/7 operations where reliability and compliance are critical.
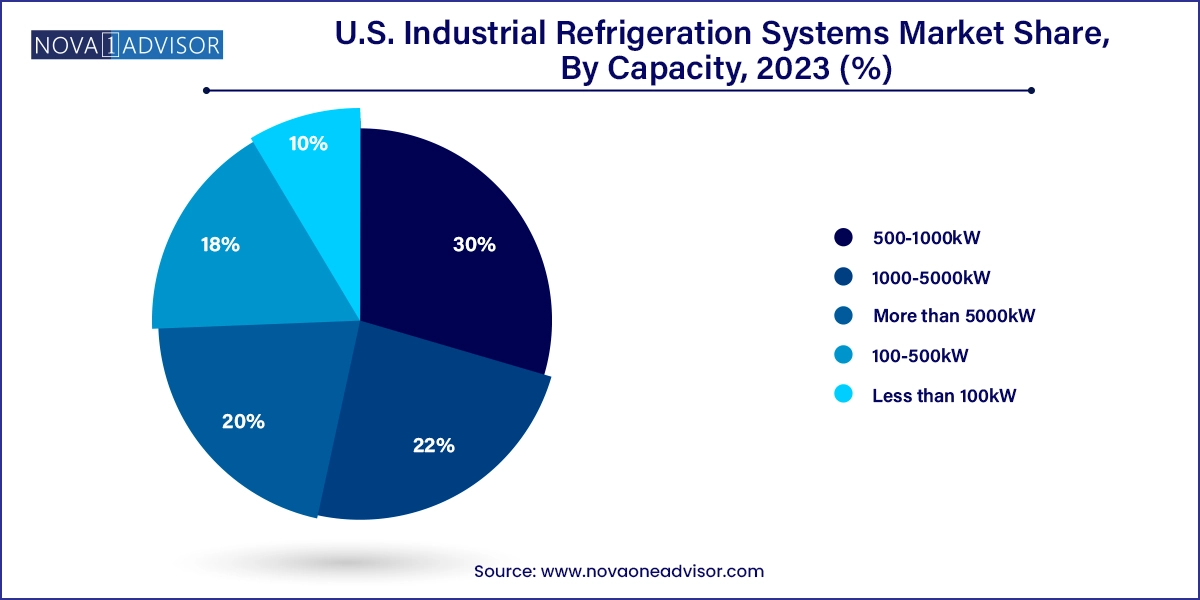
Systems below 100kW are growing the fastest, fueled by the increasing number of decentralized and specialized facilities like pharmaceutical storage units, boutique beverage plants, and urban distribution centers. These systems emphasize compactness, energy efficiency, and easy installation. The rise of modular refrigeration designs and low-charge systems is facilitating their deployment in retrofits and smaller-footprint warehouses, especially in densely populated urban centers where space and safety are key constraints.
Compressors dominated the U.S. industrial refrigeration systems market, serving as the critical component responsible for maintaining refrigeration cycles and driving system performance. Within this, rotary screw compressors are most commonly used due to their high reliability, continuous operation capabilities, and lower maintenance in large-scale applications such as food processing and chemical storage. These compressors are preferred in high-capacity systems that require stable operation and energy efficiency under variable load conditions.
Controls are the fastest-growing component, as industrial refrigeration systems evolve into smart, integrated assets within automated facilities. Advanced control systems offer features like adaptive setpoint management, load balancing, real-time fault detection, and cloud-based performance monitoring. With increased adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, facilities are investing in controls that interface with broader building management and enterprise systems to optimize uptime and energy use, especially in multi-unit installations and geographically distributed operations.
Refrigerated warehouses dominate the U.S. industrial refrigeration market, owing to the expansion of food storage, e-commerce logistics, and pharmaceutical cold chains. These facilities require multi-zone refrigeration, remote system diagnostics, and continuous temperature control. As more grocery and pharmaceutical retailers build or lease dedicated cold storage space, the demand for industrial-grade refrigeration with scalable capacity and compliance features continues to grow.
Refrigerated transportation is the fastest-growing application, supported by increased demand for last-mile cold delivery and pharmaceutical distribution. Trucks, trailers, and containers equipped with smart refrigeration units are essential to maintain product quality and regulatory compliance. Technological advancements in trailer refrigeration—like solar-assisted power, battery backup, and GPS-integrated systems—are revolutionizing how perishable goods are moved across the U.S.
The United States is both a high-demand market and a global innovator in industrial refrigeration systems. It houses leading OEMs, system integrators, and component manufacturers that serve a wide range of industries—food & beverage, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, logistics, and retail. The country’s large-scale cold chain network, advanced manufacturing ecosystem, and strong compliance culture make it an ideal landscape for both legacy and next-generation refrigeration technologies.
Federal regulations from OSHA and the EPA guide design standards, refrigerant usage, and operational safety, while the DOE enforces energy efficiency norms. State-level programs such as California’s refrigerant phase-out and New York’s Clean Cooling initiatives are also pushing innovation and early adoption of sustainable alternatives.
Infrastructure investments, reshoring of food production, and the rise of local distribution centers for e-grocery and healthcare are increasing regional demand for modular and flexible refrigeration systems. The U.S. also leads in R&D for next-gen cooling technologies, including magnetic refrigeration, phase-change materials, and AI-powered thermal management platforms.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. industrial refrigeration systems market
Component
Capacity
Refrigerant
Application