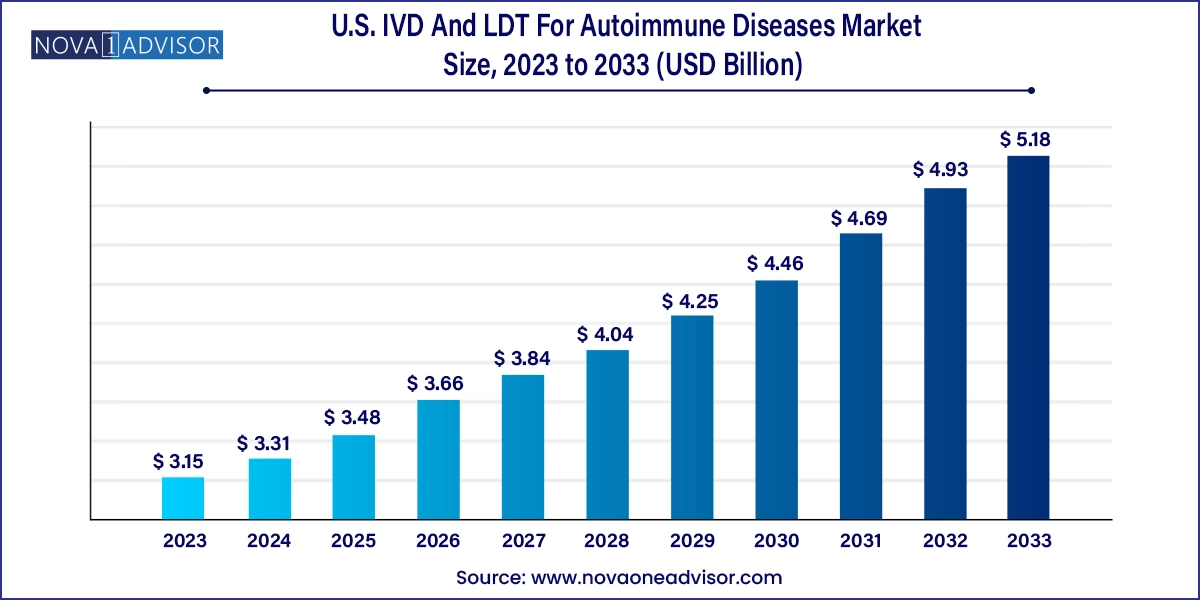
The U.S. IVD and LDT for autoimmune diseases market size was exhibited at USD 3.15 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 5.18 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.1% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. IVD (In Vitro Diagnostics) and LDT (Laboratory Developed Tests) for Autoimmune Diseases Market has emerged as a critical component in the country’s diagnostic and personalized medicine landscape. Autoimmune diseases—conditions where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue—affect more than 50 million Americans, with prevalence steadily rising, particularly among women. Early and accurate diagnosis of autoimmune conditions is crucial, not only to initiate appropriate therapies but also to prevent long-term damage, disability, and life-threatening complications.
IVD and LDTs serve as cornerstone diagnostic platforms for identifying biomarkers, antibodies, and genetic markers associated with autoimmune pathologies. These tests are essential for diagnosing a wide range of conditions, including systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and more. While IVD tests are developed by commercial manufacturers and regulated by the FDA, LDTs are designed, validated, and used within specific laboratories—often offering enhanced flexibility and customization for rare or complex autoimmune diseases.
The U.S. market is characterized by a robust ecosystem of clinical laboratories, diagnostic companies, academic research institutions, and regulatory oversight. Advances in molecular diagnostics, immunoassays, and multiplex platforms are enabling earlier detection and more precise disease monitoring. Simultaneously, patient demand for personalized care, the growing role of precision medicine, and enhanced payer reimbursement models are driving increased test utilization.
Furthermore, rising awareness of autoimmune disease burden, evolving testing technologies, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into diagnostics are transforming the landscape. With autoimmune diseases often mimicking each other clinically, sophisticated and accurate diagnostics—offered by both IVD and LDT platforms—are more important than ever. The market is poised for substantial growth through 2034 as it evolves to meet the demands of precision healthcare and chronic disease management.
Rise of Multiplex Autoantibody Panels: Multi-marker assays are gaining popularity for simultaneous testing of several autoimmune markers, improving diagnostic efficiency.
Growing Preference for Molecular Diagnostics: Molecular tools, including PCR and next-generation sequencing (NGS), are being adopted for better disease subtyping and genetic profiling.
Shift Toward Home and Point-of-Care Testing: The expansion of self-collected sample kits and near-patient diagnostics is influencing LDT business models.
Increased Adoption of AI-Driven Algorithms: AI and machine learning are being applied to interpret complex autoantibody patterns and patient data.
Regulatory Shifts Affecting LDTs: Anticipated FDA oversight and policy reforms may reshape the development and deployment of laboratory-developed autoimmune diagnostics.
Integration of Companion Diagnostics in Autoimmune Therapy: As biologics and targeted therapies proliferate, companion diagnostics are being embedded into treatment workflows.
Rising Demand for Early Diagnosis Tools: Increased public and clinical awareness is pushing demand for high-sensitivity IVDs that detect diseases before symptom onset.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 3.31 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 5.18 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 5.1% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Type, Technology, and Application |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Key Companies Profiled | Adaptive Biotechnologies Corporation; Agilent Technologies Inc., Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., bioMerieux, Inc., Corgenix, Inc., Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc., Microbix Biosystems Inc., PerkinElmer, Inc., SQI Diagnostics Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. |
A key driver of the U.S. IVD and LDT for autoimmune diseases market is the rising prevalence of autoimmune diseases across the population. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, type 1 diabetes, and multiple sclerosis are on the rise, attributed to a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. The American Autoimmune Related Diseases Association (AARDA) estimates that autoimmune diseases are among the leading causes of morbidity in women under 65.
Many autoimmune diseases have overlapping symptoms, including fatigue, joint pain, and inflammation, which complicates diagnosis. This scenario increases the clinical reliance on precise, validated diagnostics to distinguish among conditions and rule out infections, cancers, and other differential diagnoses. Both IVDs and LDTs play a critical role in this setting—enabling earlier detection, confirming diagnoses, and monitoring disease activity. As awareness grows among healthcare providers and patients, the demand for advanced diagnostics is expected to surge.
A notable restraint in this market is the regulatory ambiguity surrounding Laboratory Developed Tests (LDTs). LDTs have historically been regulated under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) program, with minimal direct oversight from the FDA. However, recent policy discussions and legislative proposals such as the VALID Act have signaled a shift toward more stringent FDA regulation of LDTs.
This evolving landscape creates uncertainty for laboratories, especially those that specialize in rare autoimmune diagnostics, as compliance with FDA standards may require significant investment in infrastructure, documentation, and post-market surveillance. Smaller labs may struggle with these requirements, potentially reducing test availability or innovation. Until clear, standardized regulatory pathways are established, LDT developers and healthcare providers may face compliance risks and slowdowns in test adoption.
A transformative opportunity in the U.S. IVD and LDT autoimmune market lies in the expanding role of precision medicine in autoimmune disease management. Personalized medicine, which tailors therapy based on individual genetic and biomarker profiles, is increasingly being adopted in autoimmune care, especially in diseases with heterogeneous presentations like lupus or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
IVD and LDT platforms are essential to this shift, enabling targeted diagnosis and supporting treatment decisions based on autoantibody profiles, cytokine signatures, and HLA genotyping. For example, patients with rheumatoid arthritis who test positive for anti-CCP antibodies are more likely to respond to certain biologic therapies. Similarly, molecular tests are being developed to predict disease flares, therapeutic response, and risk of comorbidities.
As more autoimmune therapies come to market with diagnostic-linked indications, companion diagnostics will become integral to clinical workflows. This convergence of diagnostics and therapeutics presents a compelling growth opportunity for diagnostic manufacturers, laboratory networks, and health systems.
IVD accounted for the largest market revenue share in 2023. owing to its widespread clinical adoption, FDA clearance pathways, and broad test menu available across hospitals, reference labs, and point-of-care settings. IVD platforms provide high-throughput, standardized testing for common autoimmune markers such as ANA (antinuclear antibodies), rheumatoid factor, and anti-dsDNA. These tests are crucial for the initial screening and diagnosis of autoimmune disorders.
Commercially developed IVD kits benefit from extensive clinical validation, quality control, and manufacturer support, which makes them preferred in large hospital and commercial labs. The ease of integration into automated analyzers and LIS (Laboratory Information Systems) also supports high testing volumes and rapid turnaround times.
LDTs are experiencing the fastest growth, driven by the need for customized, high-sensitivity tests for complex or rare autoimmune conditions. LDTs are often developed by academic medical centers and specialty reference labs to meet specific clinical needs not addressed by commercially available IVDs. Examples include multiplex panels for systemic sclerosis or neuro-autoimmune conditions like autoimmune encephalitis.
These tests are tailored to detect emerging biomarkers, rare autoantibodies, or to stratify patients for clinical trials. As autoimmune diseases become more heterogenous in their diagnostic criteria, the flexibility and innovation potential of LDTs will continue to drive their expansion—especially in tertiary care settings and precision medicine programs.
Immunoassays are the leading diagnostic technology, widely used in both IVDs and LDTs for autoimmune testing. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), chemiluminescence immunoassays (CLIA), and radioimmunoassays are the gold standard for detecting autoantibodies. These techniques offer high specificity, scalability, and compatibility with automated laboratory workflows.
Clinicians rely heavily on immunoassays to identify ANA, anti-CCP, anti-Ro, and other markers associated with autoimmune pathologies. Moreover, advancements in multiplex immunoassays allow for the simultaneous detection of multiple markers in a single sample, reducing diagnostic time and increasing accuracy.
Molecular diagnostics is the fastest growing segment, fueled by the increasing use of genetic and RNA-based testing in autoimmune care. PCR, qPCR, and NGS technologies are enabling researchers and clinicians to delve deeper into the genetic predispositions and immunologic pathways associated with autoimmune conditions.
For instance, HLA genotyping helps identify patients at risk of type 1 diabetes, narcolepsy, and celiac disease. Molecular assays are also being developed to monitor treatment response and disease progression. As costs decline and clinical utility increases, molecular diagnostics will play an increasingly central role in autoimmune disease detection and management.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the dominant application segment, accounting for a significant share of diagnostic testing volumes in the autoimmune disease space. RA affects over 1.3 million people in the U.S. and requires prompt and accurate diagnosis to initiate disease-modifying therapies. Diagnostic panels typically include rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP), and inflammatory markers.
Widespread clinician familiarity with RA diagnostic criteria, coupled with well-established IVD kits and treatment protocols, contributes to the segment’s prominence. Additionally, ongoing development of biomarkers for disease activity and therapeutic response ensures sustained diagnostic testing needs in this area.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is the fastest growing application, driven by increasing awareness, advancements in biomarker research, and new targeted therapies entering the market. Lupus presents with diverse clinical manifestations and requires complex diagnostic workups, often involving multiple autoantibodies like anti-dsDNA, anti-Sm, anti-Ro, and anti-La.
The rise in precision medicine approaches in SLE, including B-cell targeting biologics, necessitates detailed serologic profiling for diagnosis, patient stratification, and treatment monitoring. Diagnostic innovation in this segment is accelerating rapidly, with LDTs playing a key role in detecting rare autoantibodies and novel biomarkers.
The United States remains the largest and most dynamic market for autoimmune IVD and LDTs, characterized by advanced healthcare infrastructure, a strong diagnostics industry, and an active research ecosystem. With autoimmune diseases affecting an estimated 15-20% of the U.S. population, there is strong demand for early and precise diagnostics.
The country hosts leading diagnostic companies, academic institutions, and specialty labs driving innovation in test development. Regulatory frameworks, including the FDA’s approval process for IVDs and CLIA oversight of LDTs, provide a structured, albeit evolving, environment. Additionally, organizations such as the American College of Rheumatology and NIH contribute to standardization and research funding.
Reimbursement by private insurers and Medicare for many autoimmune diagnostic tests has improved in recent years, although challenges persist for newer LDTs and niche panels. Health systems are increasingly incorporating autoimmune diagnostics into integrated care models and electronic health record platforms, further enhancing market penetration.
With ongoing R&D investment, expanding therapeutic options, and increasing autoimmune disease awareness, the U.S. market is positioned for strong and sustained growth through 2034.
In March 2025, Thermo Fisher Scientific launched a new multiplex immunoassay panel designed for early detection of systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disorders.
In January 2025, Labcorp expanded its autoimmune LDT offerings with a new neuro-autoimmune panel for diagnosing autoimmune encephalitis and paraneoplastic syndromes.
In November 2024, Quest Diagnostics partnered with the Lupus Foundation of America to enhance awareness and access to ANA and anti-dsDNA testing across underserved communities.
In September 2024, Roche Diagnostics received FDA approval for an anti-CCP immunoassay with enhanced specificity for early rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis.
In July 2024, Mayo Clinic Laboratories integrated AI-based interpretation into its autoimmune serology panels to assist physicians in evaluating complex cases.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. IVD and LDT for autoimmune diseases market
Type
Technology
Application