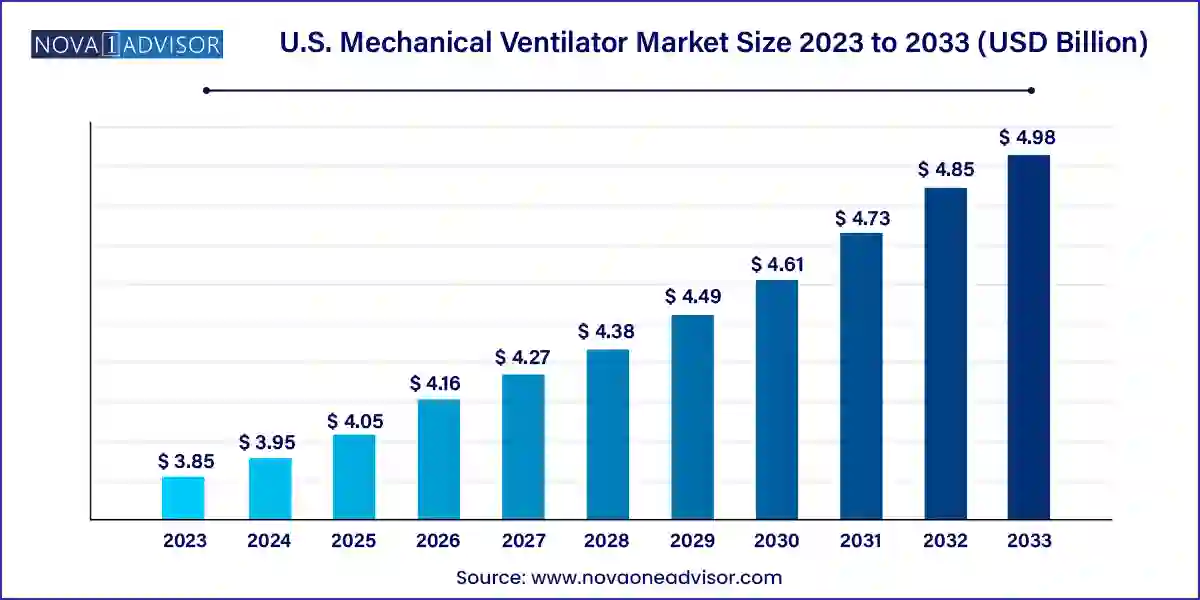
The U.S. mechanical ventilator market size was exhibited at USD 3.85 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 4.98 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 2.6% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. mechanical ventilator market continues to be a critical component of the nation’s healthcare infrastructure, playing a central role in the treatment of patients with respiratory disorders and emergency care needs. With rising incidences of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD), asthma, and other lung diseases, mechanical ventilators are increasingly becoming a necessity in hospitals, long-term care settings, and homecare environments. The COVID-19 pandemic further underlined the importance of robust ventilator supply chains and accelerated advancements in ventilator technology, ushering in an era of smart, compact, and more efficient systems.
Mechanical ventilators are life-saving machines that support or entirely assume breathing functions for patients who cannot breathe sufficiently on their own. These systems are integral to surgeries requiring anesthesia, treatment of patients in intensive care units (ICUs), and long-term respiratory support. In the U.S., with an aging population and rising healthcare expenditure, there is significant demand not only in urban hospitals but also in rural and mobile care units. Furthermore, the rise in chronic respiratory diseases and emergency respiratory failure cases in geriatric patients has pushed medical device manufacturers to enhance product capabilities and portability, while maintaining affordability and compliance with safety standards.
In addition, increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure, favorable reimbursement policies, and collaborations between government and private entities are augmenting the deployment of ventilator systems. The integration of IoT and AI in mechanical ventilators is expected to redefine patient monitoring and disease management, promoting both preventive and responsive care.
Shift Toward Portable and Transport Ventilators: The rising demand for ambulatory care and in-transit patient support is boosting the uptake of compact and lightweight ventilator systems.
Incorporation of AI and IoT in Mechanical Ventilators: Smart ventilators that can monitor patient responses and adjust airflow automatically are becoming increasingly common.
Remote Monitoring Capabilities: Especially post-COVID, healthcare facilities are adopting ventilators that allow remote patient monitoring to reduce hospital stay durations.
Expansion of Homecare Ventilation Use: Increasing geriatric population and chronic disease prevalence are driving demand for homecare-compatible ventilators.
Product Innovations for Neonatal Care: A growing focus on specialized ventilators for neonatal and pediatric applications to reduce ventilator-associated complications.
Environmental Sustainability and Green Ventilation Design: Manufacturers are prioritizing eco-friendly, reusable accessories and energy-efficient ventilators.
Public-Private Partnerships for Emergency Stockpiling: The federal government has been building national ventilator stockpiles through partnerships with private manufacturers.
Rise in 3D Printing for Accessory Components: 3D printing is increasingly used to produce parts like flow sensors and breathing circuit sets with cost and time efficiency.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 3.95 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 4.98 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 2.6% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Getinge AB; Vyaire Medical Inc.; Medtronic; Drägerwerk AG & Co. KGaA; GE Healthcare; Koninklijke Philips N.V.; Smiths Group plc; Hamilton Medical; ResMed Inc.; Ventec Life Systems |
A key driver of the U.S. mechanical ventilator market is the escalating incidence of chronic respiratory conditions, such as COPD, asthma, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 16 million Americans suffer from COPD, a figure that likely underrepresents the total population with impaired lung function. This surge in respiratory ailments necessitates sustained and sophisticated ventilator support, especially in ICU settings. Additionally, increasing air pollution levels and high rates of smoking, particularly among older adults, have led to a higher demand for both acute and long-term respiratory assistance devices.
Ventilators are also indispensable in managing acute conditions such as pneumonia, which remains a leading cause of hospitalization in the U.S., particularly among the elderly. The capacity of modern ventilators to deliver tailored respiratory assistance with reduced risks of barotrauma or oxygen toxicity makes them essential for effective treatment and recovery. Moreover, the integration of these systems with hospital information systems ensures better patient monitoring and data analytics, further enhancing their clinical utility.
One of the most significant restraints in the U.S. mechanical ventilator market is the high acquisition and maintenance cost of modern ventilator systems. Advanced ventilators equipped with smart sensors, touchscreen interfaces, AI capabilities, and connectivity options can cost upwards of $25,000 per unit. This price point creates financial strain on smaller clinics, rural hospitals, and outpatient surgical centers, especially when factoring in the cost of disposable accessories, servicing, and training.
Furthermore, reimbursement gaps for home-based ventilation care often leave patients and caregivers burdened with out-of-pocket expenses. This limits the adoption of homecare ventilators, despite growing demand. Additionally, the FDA’s stringent approval process for ventilator systems and accessories, while ensuring safety and efficacy, adds to the time and cost associated with product development and launch.
The burgeoning home healthcare market presents a significant opportunity for mechanical ventilator manufacturers in the U.S. With the U.S. Census Bureau projecting that by 2030, all baby boomers will be older than 65, the country is expected to witness a rapid increase in patients requiring chronic respiratory support outside of hospital settings. Home mechanical ventilation not only reduces hospitalization costs but also enhances patient comfort and autonomy.
Manufacturers are investing in creating user-friendly, noise-free, and battery-operated ventilators that can seamlessly integrate into home settings. The development of wearable ventilation solutions, guided app support for caregivers, and compact designs are key trends aimed at tapping this opportunity. Companies offering bundled services ventilator equipment, telehealth monitoring, and 24/7 support—are likely to see greater adoption rates among homecare providers and patients alike.
Critical care ventilators dominated the product segment in 2024, primarily driven by their indispensable role in hospital ICUs and emergency care departments. These ventilators offer high-performance functionality, accommodating diverse modes of ventilation, precise oxygen delivery, and sophisticated monitoring systems. Given their use in complex cases involving comatose or intubated patients, these systems are commonly found in tertiary care hospitals. Additionally, the persistent influx of respiratory patients—both during pandemics and routine seasonal outbreaks—keeps critical care ventilators in continuous demand. Major manufacturers in the segment focus on technological improvements like adaptive ventilation and automatic leak compensation to boost efficacy and safety.
Transport and portable ventilators are expected to grow at the fastest rate during the forecast period due to increased demand for mobile emergency medical services, ambulances, and homecare settings. Their compact size, battery backup, and compatibility with various breathing circuits make them suitable for patients in transit or in remote areas. Post-COVID-19, many hospitals and care facilities are maintaining mobile ICU units equipped with portable ventilators for emergency preparedness. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) also supports mobile care initiatives with infrastructure and equipment funding, further boosting the segment’s growth potential.
Hospitals continue to dominate the end-use segment due to their comprehensive infrastructure, skilled personnel, and high volume of critical care cases. Ventilators are widely used in ICU wards, emergency departments, operating rooms, and post-surgical care units. Hospitals also serve as the primary location for ventilator-dependent patients requiring tracheostomy care or those undergoing treatment for ARDS or COPD exacerbations. Moreover, the presence of in-house biomedical teams enables regular maintenance and calibration of sophisticated ventilator systems, ensuring continuous functionality.
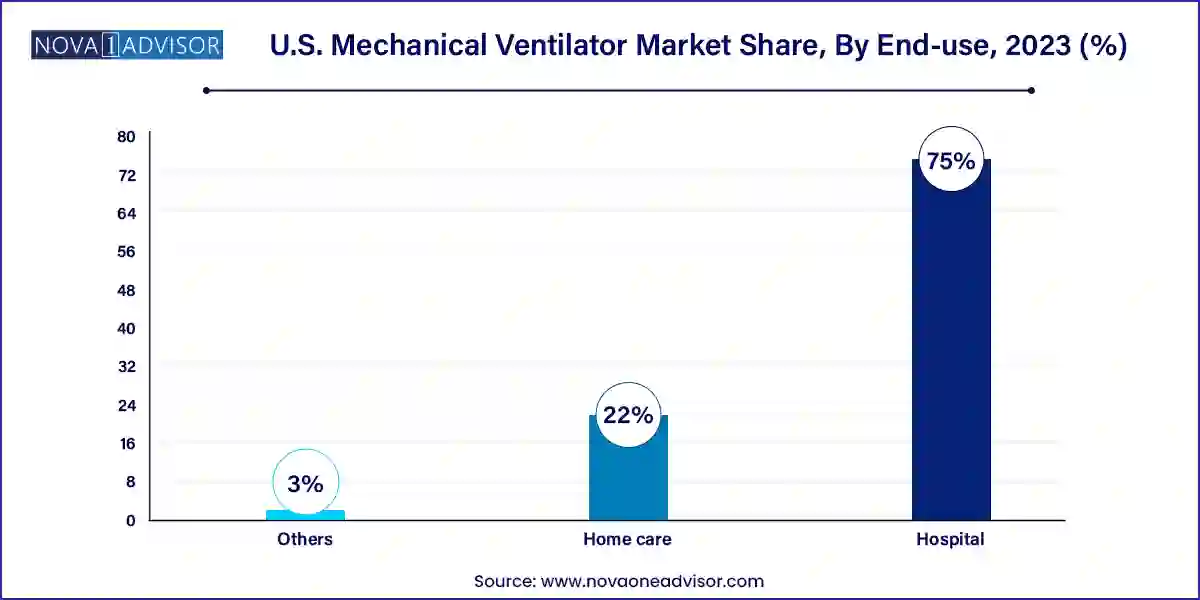
Homecare is expected to be the fastest-growing end-use segment, spurred by the growing trend of managing chronic conditions outside traditional healthcare settings. Ventilators designed for home use are increasingly feature-rich, offering sleep apnea support, portable humidification, and compatibility with telemonitoring systems. As more elderly individuals choose aging-in-place over institutional care, the need for safe and efficient mechanical ventilation at home is rising. Insurance providers and government programs like Medicare are also progressively covering durable medical equipment, including ventilators, which is further encouraging adoption.
In the United States, the mechanical ventilator market is witnessing robust innovation and policy support. Federal agencies like BARDA (Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority) and the Department of Defense have been instrumental in developing and stockpiling emergency-use ventilators post the COVID-19 crisis. States like California, New York, and Texas are the top users of ventilators owing to their dense population, large healthcare networks, and high number of respiratory illness cases. The U.S. Veterans Health Administration is also a key public sector purchaser of mechanical ventilators, especially for chronic care.
Healthcare providers across the Midwest and Southern regions are increasingly investing in mobile and transport ventilators to support rural and under-resourced areas. Additionally, regulatory agencies such as the FDA have introduced Emergency Use Authorizations (EUAs) to expedite the launch of innovative ventilator designs, ensuring rapid market penetration during public health emergencies. These favorable regulatory changes are expected to encourage more companies to introduce next-gen ventilator technologies in the U.S. market.
Philips Respironics (January 2025): Announced an expansion of its homecare ventilator product line with the launch of DreamStation Advanced Plus, featuring wireless connectivity and real-time patient data sharing for remote monitoring.
ResMed (February 2025): Entered a strategic partnership with Humana Inc. to deploy AI-enabled ventilator solutions in homecare for chronic disease patients, aiming to improve outcomes and reduce hospital readmissions.
Medtronic (December 2024): Released a new software upgrade for its Puritan Bennett 980 ventilator, enabling predictive alarms and early detection of ventilator-associated complications through machine learning algorithms.
GE HealthCare (November 2024): Rolled out a new portable ventilator—AireGoX—optimized for military and disaster response teams, featuring rugged design and cloud-based tracking.
Dräger (October 2024): Opened a new training center in Chicago to educate clinical staff on the latest mechanical ventilator technologies and emergency ventilation strategies.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2023 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. mechanical ventilator market
Product
End-use