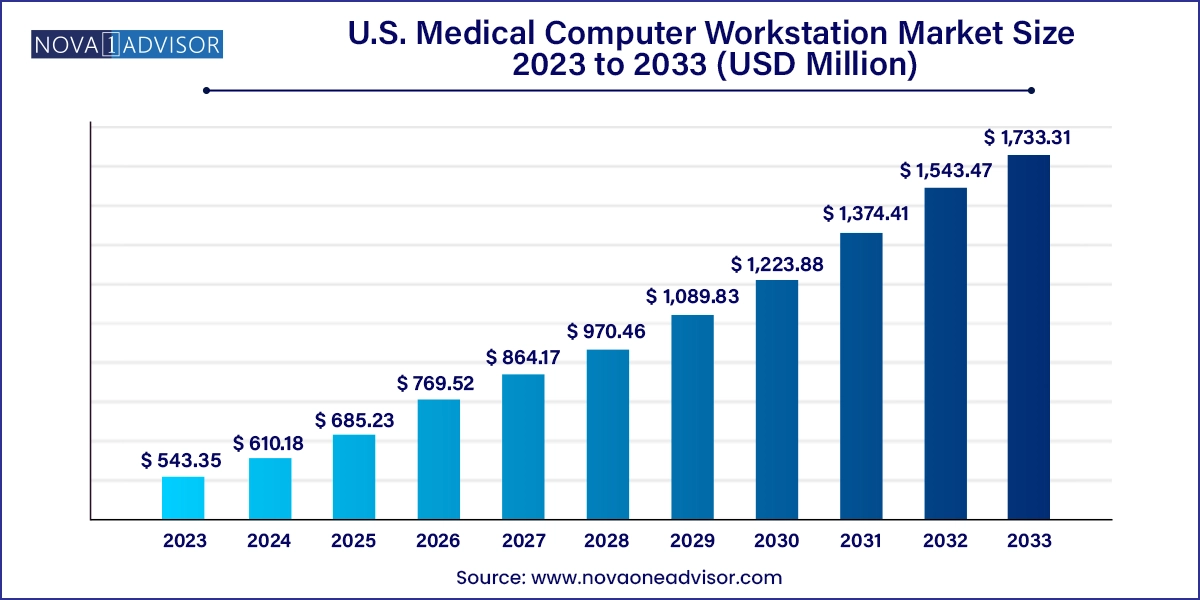
The U.S. medical computer workstation market size was exhibited at USD 543.35 Million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 1,733.31 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.3% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. medical computer workstation market represents a critical and rapidly evolving segment of the healthcare IT infrastructure landscape. Medical computer workstations are specialized platforms designed to support healthcare professionals in a variety of clinical settings offering computing capabilities alongside essential storage, documentation, and medical equipment integration. These workstations, configured as mobile carts, wall-mounted systems, or stationary units, play a pivotal role in modern patient care delivery by enabling real-time data access, patient documentation, medication management, and telehealth interactions.
The transition toward electronic health records (EHRs), driven by both government mandates and the pursuit of operational efficiency, has been a key factor in expanding the adoption of medical computer workstations across hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs), clinics, and long-term care facilities. These devices enhance clinical workflows by integrating computing hardware, power systems, adjustable work surfaces, secure storage, and accessories that support various healthcare applications. From medication delivery carts in emergency departments to documentation carts used in ICUs, medical workstations are now indispensable for optimizing clinical tasks and improving patient outcomes.
In the U.S., healthcare institutions continue to invest in digital transformation initiatives, including expanding the use of mobile workstations to reduce errors, support bedside charting, and streamline nurse-patient interactions. This is particularly important in large hospitals where clinicians require mobility and connectivity to update patient records in real-time across multiple departments. Simultaneously, advancements in telemedicine, especially post-pandemic, have prompted demand for telehealth workstations, providing the audiovisual and diagnostic support required for remote consultations.
Overall, the U.S. medical computer workstation market is benefiting from a confluence of factors: growing patient volumes, the need for workflow standardization, the expansion of outpatient care models, and the increasing reliance on digital tools to support decision-making and regulatory compliance.
Increased Adoption of Mobile Workstations: Hospitals and clinics are rapidly integrating mobile carts to facilitate point-of-care documentation, enhancing clinical mobility and efficiency.
Telehealth Integration: The growing use of telemedicine is driving demand for workstations configured with video conferencing tools, cameras, and secure access to remote monitoring platforms.
Battery and Power System Innovations: Manufacturers are focusing on longer battery life and fast-charging solutions to increase uptime and reduce cart downtime in busy environments.
Ergonomic and User-Centric Designs: Height-adjustable work surfaces, swivel monitors, and antimicrobial surfaces are being prioritized to enhance clinician comfort and reduce infection risk.
Hybrid Workstations: There is a rise in workstations that combine functionalities such as medication delivery and documentation into a single unit, minimizing the need for multiple devices per room.
Integration with EHR Platforms: Seamless compatibility with major EHR vendors (e.g., Epic, Cerner) is becoming a core purchasing criterion for healthcare providers.
Outpatient and Long-Term Care Expansion: Clinics and nursing homes are investing in cost-effective, non-powered and wall-mounted workstations as outpatient services expand.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 610.18 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 1,733.31 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 12.3% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Energy Source, Configuration, Application, Type, End-use, Distribution Channel |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Capsa Healthcare; Ergotron Inc.; Bytec Healthcare Ltd.; Midmark Corporation; Altus Inc.; AFC Industries Inc.; Newcastle Systems Inc.; Enovate Medical; GCX Corporation (Jaco Inc.) |
A central driver of the U.S. medical computer workstation market is the continued shift toward electronic documentation and the digital transformation of healthcare workflows. With the federal government promoting the adoption of electronic health records through programs like the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act and Meaningful Use incentives, healthcare facilities are increasingly digitizing patient data, lab results, imaging, and physician notes.
To support this transformation, medical computer workstations serve as critical points of access to EHR systems and are strategically positioned in hallways, operating rooms, nursing stations, and at the patient bedside. They allow clinicians to input and retrieve patient data in real-time, enhancing clinical decision-making and reducing the risk of transcription errors. By eliminating paper charts and supporting mobile documentation, these workstations also improve time management, reduce administrative burden, and facilitate multidisciplinary collaboration.
As digital tools like barcode medication administration (BCMA), computer physician order entry (CPOE), and clinical decision support systems become more embedded in daily routines, the demand for robust and ergonomic computer workstations will continue to rise.
One of the major restraints in the market is the significant upfront capital investment and ongoing maintenance requirements associated with medical computer workstations. High-quality powered mobile carts, which include lithium-ion batteries, integrated computers, and modular storage, can cost several thousand dollars per unit. For large hospital systems or networks planning mass deployment across multiple departments, these costs can quickly escalate.
Moreover, the complexity of these devices necessitates regular maintenance, software updates, battery replacements, and user training to ensure they function optimally. In busy environments, carts are subject to wear and tear, misuse, and technical malfunctions—often requiring dedicated IT support. The necessity of integrating these carts with other digital systems (EHR, medication dispensing software, etc.) adds another layer of complexity, occasionally leading to compatibility challenges.
For smaller clinics, outpatient centers, and nursing facilities operating under tight budgets, the cost-benefit analysis may delay adoption or result in preference for simpler, non-powered alternatives. Addressing cost barriers through leasing models, scalable modular designs, and service contracts may help expand the market in the future.
A significant opportunity in the U.S. medical computer workstation market lies in the expansion of telehealth-configured workstations across all levels of care. With the COVID-19 pandemic accelerating the acceptance and use of remote care services, healthcare providers are now investing in telehealth infrastructure not only for outpatient virtual visits but also for inpatient virtual rounding, remote specialist consultations, and even post-acute home monitoring.
Telehealth workstations are specifically configured with webcams, noise-canceling microphones, secure communication software, and high-resolution monitors to support clear and HIPAA-compliant virtual interactions. These carts are used in isolation rooms, long-term care facilities, and rural hospitals where on-site specialist access may be limited. The adoption of such carts facilitates not only clinical efficiency but also infection control and staff safety.
As payers and policymakers continue to reimburse telehealth at parity with in-person visits, and as rural and senior care populations grow, the demand for scalable, mobile, and multi-functional telehealth workstations is poised to increase sharply. Vendors that can offer turnkey solutions including hardware, software integration, and technical support stand to capitalize on this trend.
Powered workstations dominate the U.S. medical computer workstation market, especially in high-acuity settings like hospitals and emergency rooms where continuous operation is essential. These workstations typically include built-in rechargeable batteries, integrated power management systems, and uninterrupted power supply (UPS) functionalities, enabling clinicians to use them for extended periods without needing to plug in. Their utility in supporting mobile EHR access, barcode medication scanning, and patient monitoring is unmatched. Hospitals value powered carts for their mobility, reliability, and ability to host peripherals like label printers and vital sign monitors.
Non-powered workstations are the fastest-growing subsegment, particularly in budget-conscious outpatient and long-term care settings. These carts rely on external devices (such as tablets or laptops) and require manual charging but offer advantages in terms of cost, simplicity, and lower maintenance needs. Facilities that prioritize lightweight, ergonomic designs and do not need extended battery life often choose non-powered alternatives for documentation, teleconsultation, or light data entry tasks. With improvements in laptop battery life and increased cloud adoption, the usability of non-powered workstations is expanding.
Mobile workstations are the dominant configuration, reflecting their flexibility, portability, and critical role in point-of-care applications. These carts are deployed throughout hospital floors, allowing nurses and physicians to move seamlessly between rooms while maintaining real-time access to digital records. They reduce back-and-forth movement to centralized stations and improve patient safety by enabling tasks like medication administration and charting to occur at the bedside. Advances in lightweight materials, height-adjustable features, and antimicrobial surfaces have made mobile carts more clinician-friendly and infection-resistant.
Wall-mounted workstations are the fastest-growing configuration, particularly in compact clinical environments such as exam rooms, outpatient clinics, and imaging centers. These fixed units provide stable, space-saving solutions and are often positioned for quick access to computers during check-in or pre-examination procedures. With the increase in same-day surgical centers and physician office-based labs, wall-mounted workstations are increasingly preferred for their lower footprint and ergonomic advantages in constrained spaces. They are also being adopted in hallways and administrative areas to support nurses and clerical staff.
Medical documentation is the leading application, accounting for the largest share of demand. With the near-universal use of EHRs across U.S. healthcare institutions, clinicians require immediate access to documentation tools during rounds, procedures, and consultations. Medical workstations enable real-time entry of vitals, medications, and care notes—minimizing error and maximizing care continuity. Furthermore, documentation carts support barcode scanning, digital signatures, and lab result reviews, making them indispensable in multidisciplinary care environments.
Telehealth workstations are the fastest-growing application, buoyed by the national shift toward virtual care models. These workstations allow remote interaction between patients and providers and are increasingly used in ICUs, COVID-19 isolation rooms, and geriatric care settings. They facilitate specialist access in rural areas and help reduce patient transfer costs by enabling consults without moving the patient. Their use is also growing in behavioral health and chronic care management programs where virtual encounters improve adherence and engagement.
Emergency carts dominate the workstation type segment, especially in high-volume acute care settings. Designed for rapid response, these carts house emergency drugs, defibrillators, intubation tools, and monitoring equipment. Hospitals rely on emergency carts that include robust casters, secure compartments, and easy maneuverability for Code Blue situations.
Telehealth-specific carts and multipurpose carts are the fastest-growing types, as institutions seek flexibility to repurpose carts for different clinical needs. For example, some carts can be adapted from basic documentation to medication administration by swapping out storage modules. This modular design trend is making workstation investments more future-proof and attractive to procurement teams.
Hospitals are the dominant end users, representing the highest adoption rate of medical computer workstations across the U.S. They require comprehensive workstation fleets to serve inpatient wards, operating rooms, emergency departments, and intensive care units. Hospitals prioritize robust, battery-powered, modular systems that can integrate with EHR, barcode scanning, and lab systems. Large academic and teaching hospitals often have dedicated teams for cart maintenance and software support.
Ambulatory surgical centers and physician clinics are the fastest-growing end users, particularly as outpatient care continues to expand in the U.S. These facilities seek cost-effective, compact, and easy-to-clean workstations for patient documentation, pre-op screening, and post-op monitoring. With shorter lengths of stay and lower staff-to-patient ratios, these settings value user-friendly and low-maintenance devices that still integrate seamlessly with EHR systems.
IT/CDW/Value Added Resellers (VARs) dominate distribution, reflecting the technical nature of workstation procurement and the need for integration with healthcare IT systems. VARs often offer bundled solutions that include installation, warranty, software support, and training services, making them attractive to health systems that need turnkey deployments.
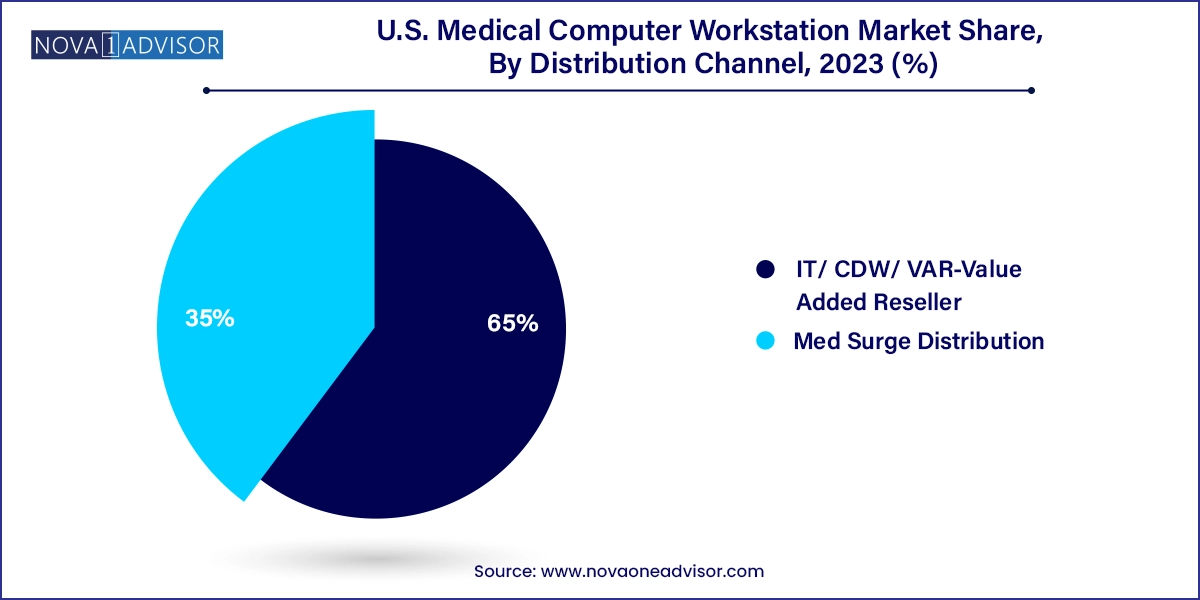
Med Surge distribution is growing fast, especially for simpler and more cost-sensitive workstation types used in nursing homes, rehab centers, and urgent care clinics. These distributors offer fast lead times, product variety, and procurement simplicity, often serving facilities without a large IT department.
The U.S. leads globally in the adoption of medical computer workstations, supported by high healthcare spending, extensive hospital networks, and a strong regulatory push for digital documentation. Government incentives and mandates have accelerated EHR adoption, leading to widespread use of mobile and fixed workstations across clinical settings. Hospitals are also increasingly investing in fleet management software for carts, ensuring uptime and performance optimization.
Long-term care and skilled nursing facilities are gradually catching up, especially as CMS reimbursement models encourage better documentation and care coordination. Additionally, telehealth's mainstream adoption during and after the pandemic has prompted rapid workstation deployment across rural health systems and integrated delivery networks (IDNs).
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. medical computer workstation market
Energy Source
Configuration
Application
Type
End-use
Distribution Channel