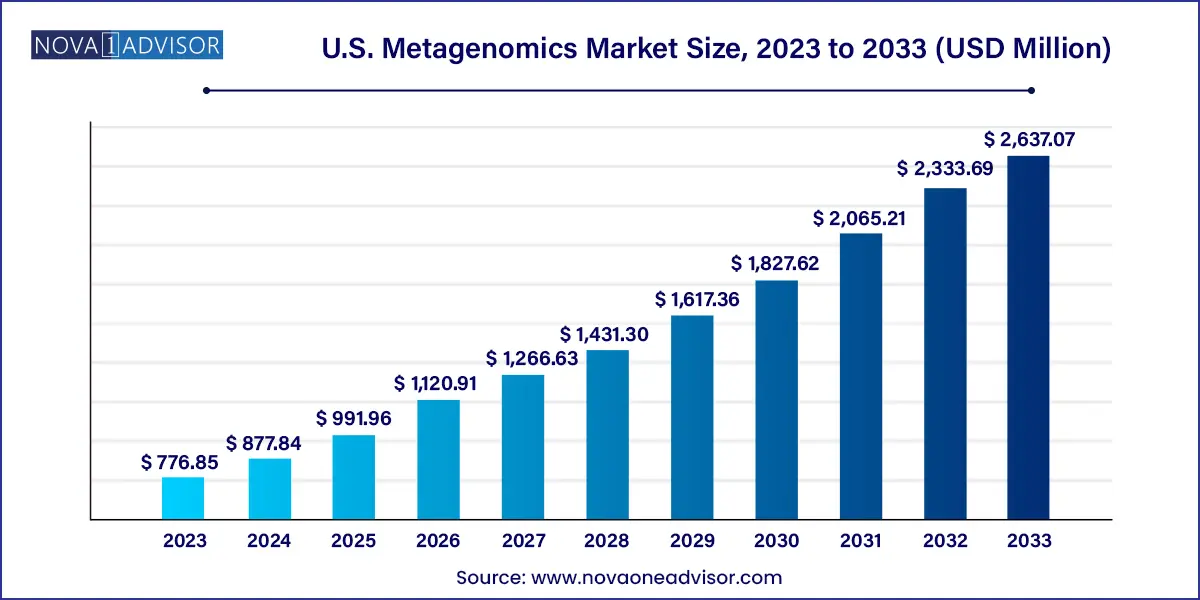
The U.S. metagenomics market size was exhibited at USD 776.85 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 2,637.07 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 13.0% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. metagenomics market is a fast-growing, technologically intensive segment within the broader genomics landscape. Metagenomics refers to the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples, enabling researchers to analyze microbial communities without the need for culturing. This approach has transformed our understanding of microbial diversity, functions, and their roles in health, disease, and the environment.
The market’s rapid growth is fueled by advancements in high-throughput sequencing technologies, reduced costs of genome analysis, and increasing applications across a diverse set of fields including clinical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, biotechnology, food safety, and drug discovery. Metagenomics has moved from academic research into practical and clinical realms, especially with growing interest in microbiome studies and pathogen surveillance. Institutions like the NIH have launched major initiatives focused on the human microbiome, while private-sector investments have proliferated around microbiome-based therapeutics and diagnostics.
One of the key drivers in the U.S. market is the increasing recognition of the human microbiome's role in diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, cancer, and mental health disorders. These revelations are pushing demand for metagenomic tools that can profile complex microbial communities and identify biomarkers of disease or therapeutic targets. Moreover, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of metagenomic sequencing for pathogen identification, prompting government and institutional funding to support rapid, accurate, and broad-spectrum microbial detection.
With the growing emphasis on precision medicine and one-health approaches that link human, animal, and environmental health, metagenomics is emerging as a critical enabler. The U.S. market is uniquely positioned due to the presence of leading technology providers, academic institutions, and an innovation-friendly regulatory framework.
Rising integration of AI and machine learning in metagenomic data interpretation: AI is helping decipher vast and complex datasets generated from sequencing to identify microbial signatures and disease links.
Expansion of microbiome-based diagnostics and therapeutics: Startups and major pharmaceutical firms are developing diagnostic kits and drugs based on microbiome manipulation.
Growth of long-read sequencing technologies: Platforms like Oxford Nanopore and PacBio are gaining traction due to their ability to resolve complex metagenomic assemblies.
Greater focus on one-health and zoonotic disease surveillance: Public health agencies are funding projects using metagenomics to monitor pathogens in animal and environmental reservoirs.
Personalized nutrition and wellness applications: Consumer genomics and wellness brands are offering gut microbiome tests for dietary recommendations based on metagenomic profiling.
Standardization of workflows and databases: Efforts are underway to establish standardized reference databases and pipelines to reduce variability in metagenomic analyses.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 877.84 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 2,637.07 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 13.0% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Technology, Workflow, Application |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Illumina, Inc., PerkinElmer, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Novogene Co., Ltd., Promega Corporation, QIAGEN, Takara Bio, Inc., Oxford Nanopore Technologies, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd |
A powerful driver of the U.S. metagenomics market is the burgeoning interest in the human microbiome and its implications for human health. Research over the past decade has shown that the trillions of microbes residing in the human body are not just passive inhabitants but active participants in metabolic processes, immune modulation, and even neurological functions. Metagenomic sequencing enables scientists to investigate this microbial universe without needing to isolate or culture each organism, which is especially useful given that many microbes are unculturable with traditional techniques.
Clinical studies have increasingly linked microbiome imbalances with a range of conditions, including autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders, depression, and even response to cancer immunotherapies. This has led to the development of microbiome-based diagnostic tests and therapeutics, especially fecal microbiota transplants and probiotic interventions. Metagenomics plays a foundational role in identifying microbial dysbiosis and understanding how interventions shift microbial populations. In response, healthcare institutions, biotech companies, and nutrition brands are investing in metagenomic platforms to offer personalized solutions—further accelerating market growth.
While technological advances have reduced the cost and increased the speed of metagenomic sequencing, one of the most persistent barriers in the U.S. market remains the complexity of data analysis. A typical metagenomic sequencing run generates gigabytes to terabytes of raw data that must be processed, filtered, assembled, and annotated before actionable insights can be derived. The bioinformatics expertise required for such analysis remains a bottleneck for many clinical and environmental labs.
Compounding the challenge is the lack of standardized reference genomes and taxonomies across databases. Results from different metagenomic pipelines can vary significantly, leading to reproducibility concerns and complicating clinical adoption. Moreover, many users lack the computational infrastructure or software platforms that can handle the scale and complexity of metagenomic data efficiently. While cloud-based tools and user-friendly interfaces are becoming more common, they are not yet universally adopted. These limitations hinder the scalability of metagenomics in clinical diagnostics and industrial workflows, especially among small and medium enterprises.
A promising opportunity in the U.S. metagenomics market lies in the clinical diagnosis of infectious diseases, especially those caused by rare, novel, or fast-mutating pathogens. Traditional diagnostic techniques often rely on culture-based methods or targeted PCR assays, which can be time-consuming and limited in scope. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS), by contrast, offers an unbiased approach capable of detecting all microbial DNA or RNA present in a sample including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
This technology is particularly valuable in cases of encephalitis, sepsis, and respiratory infections with unknown causes, where traditional methods fail. Clinical labs like UCSF’s Center for Next-Gen Precision Diagnostics are already using mNGS to identify pathogens in critically ill patients. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated investments in mNGS for variant surveillance and environmental testing. With continued regulatory progress and advances in data interpretation software, mNGS is poised to become a routine tool in infectious disease diagnostics. Companies that can offer turnkey solutions integrating wet lab and informatics capabilities will be best positioned to capture this emerging opportunity.
Kits & reagents dominated the U.S. metagenomics market, driven by their essential role in DNA extraction, library preparation, and amplification. These products are core components in both clinical and research workflows and are frequently optimized for different sample types—such as fecal, environmental, or water samples. Companies like QIAGEN and Zymo Research offer pre-validated kits that ensure reproducibility and compatibility with a wide range of sequencing platforms. The rising number of metagenomic studies and the growing trend toward at-home microbiome testing have further spurred demand for high-throughput, automation-friendly kits.
Sequencing and data analytics services are emerging as the fastest-growing segment, primarily due to the specialized expertise and infrastructure required. Many research and clinical labs lack in-house sequencing capabilities or the bioinformatics bandwidth to analyze complex datasets. As a result, companies offering end-to-end metagenomic services—from sample processing to interpretation—are gaining popularity. Firms like Illumina and Thermo Fisher Scientific, along with newer players like CosmosID, are expanding their service portfolios to cater to these needs, especially among small and mid-size biotechs and academic centers.
Shotgun sequencing held the largest market share, owing to its broad utility and ability to sequence entire genomes without amplification bias. This approach allows researchers to detect even low-abundance species and infer functional gene content, making it ideal for studies where taxonomic resolution and functional profiling are crucial. In environmental metagenomics, shotgun sequencing has enabled the discovery of novel antibiotic resistance genes and metabolic pathways.
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) is witnessing the fastest growth, driven by its ability to offer high-resolution insights into microbial evolution, virulence factors, and resistance genes. As sequencing costs decline and analysis tools become more accessible, WGS is increasingly being integrated into microbial surveillance and pathogen outbreak investigations. The approach is being adopted in public health labs, food safety agencies, and pharmaceutical companies involved in microbial engineering.
Sequencing is the dominant workflow stage, reflecting the central role of NGS platforms in metagenomics. High-throughput systems from companies like Illumina and Oxford Nanopore have reduced sequencing costs and increased read lengths, enhancing both qualitative and quantitative microbial profiling. The demand for sequencing reagents, flow cells, and instruments remains consistently high across academic, clinical, and commercial labs.
.webp)
Data analysis is the fastest-growing workflow segment, given the explosion of raw sequencing data and the critical need for accurate interpretation. Tools for quality control, taxonomic classification, metagenomic assembly, and functional annotation are in high demand. Companies and academic consortia are developing AI-driven pipelines and cloud-based platforms that allow users to upload data and receive comprehensive reports in a user-friendly format, accelerating adoption beyond bioinformatics specialists.
Clinical diagnostics emerged as the largest application area, spurred by the integration of metagenomics in pathogen detection, microbiome health assessments, and personalized medicine. Clinical institutions are using mNGS to diagnose atypical infections, understand microbial contributions to chronic disease, and inform therapeutic choices. In hospitals and reference labs, metagenomics is increasingly seen as a complement or alternative to targeted molecular diagnostics.
Drug discovery is the fastest-growing application segment, as pharmaceutical companies explore the microbiome’s role in drug metabolism, immune modulation, and therapeutic efficacy. Metagenomics provides a treasure trove of biosynthetic gene clusters and microbial enzymes that can be harnessed for novel drug leads. Additionally, companies are screening microbiome profiles to stratify patient populations and predict response to immunotherapy, particularly in oncology and autoimmune conditions.
The United States stands at the forefront of the global metagenomics industry, benefiting from its well-established genomics infrastructure, advanced sequencing capabilities, and a thriving ecosystem of academic research and biotech entrepreneurship. Leading institutions such as NIH, UCSF, Harvard, and MIT are pioneering microbiome research projects and deploying metagenomic tools in clinical trials and translational research.
The presence of major sequencing providers like Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Pacific Biosciences, all headquartered or strongly operating in the U.S., has provided domestic players with easier access to cutting-edge technology. The FDA and CDC have been proactive in exploring metagenomics for infectious disease tracking, antibiotic resistance surveillance, and food safety. Additionally, public-private partnerships such as those under the Precision Medicine Initiative are incorporating metagenomics to improve population-level healthcare outcomes.
From a commercial perspective, the country is seeing a rise in direct-to-consumer microbiome testing, personalized nutrition platforms, and microbiome-based clinical trials. This makes the U.S. a comprehensive market, encompassing the full spectrum from academic discovery to clinical application and consumer engagement.
April 2024 – Illumina launched NovaSeq X Plus, a new sequencing system tailored for large-scale metagenomic applications, boasting faster throughput and integrated cloud analytics for pathogen surveillance.
March 2024 – Thermo Fisher Scientific partnered with the CDC to deploy its metagenomic pathogen detection kits in five state public health laboratories, targeting antimicrobial resistance and emerging infectious threats.
February 2024 – Zymo Research released a next-generation Microbiome Standards Kit, aimed at improving the reproducibility and benchmarking of metagenomic workflows in academic and clinical settings.
January 2024 – QIAGEN announced the expansion of its QIAGEN Digital Insights platform with new metagenomic annotation tools powered by AI, aimed at enabling faster identification of microbial communities.
March 2024 – Oxford Nanopore Technologies launched VolTRAX-2, an automated sample prep device optimized for portable metagenomic sequencing in clinical and field settings.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. metagenomics market
Product
Technology
Workflow
Application