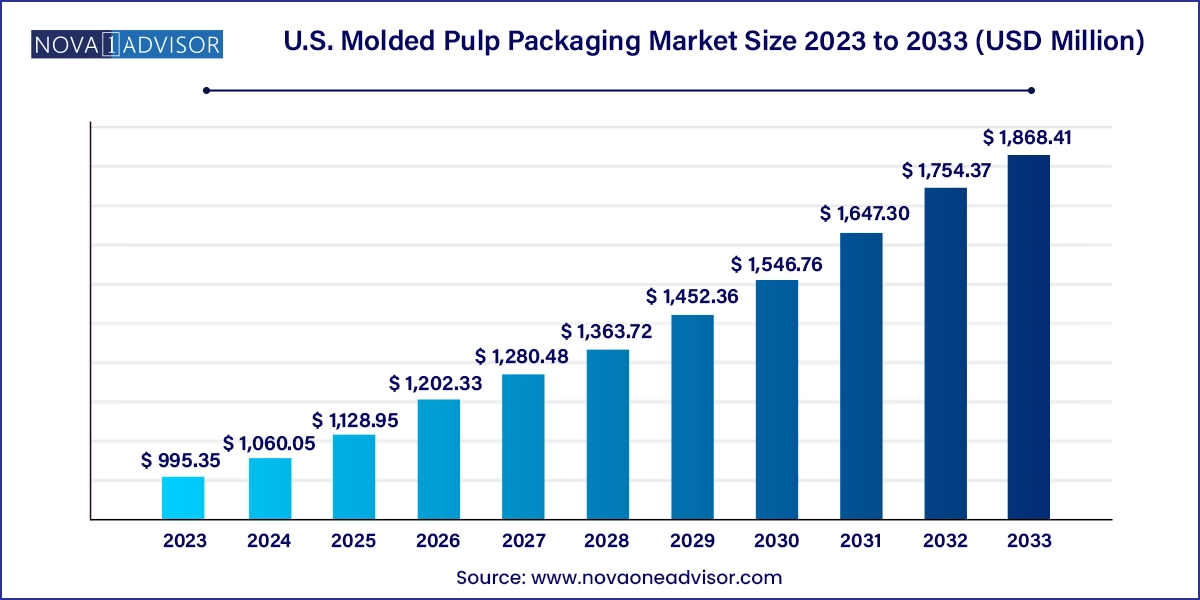
The U.S. molded pulp packaging market size was exhibited at USD 995.35 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 1,868.41 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. molded pulp packaging market has rapidly evolved into a cornerstone of the sustainable packaging industry. Molded pulp, derived from recycled paper, wood pulp, or non-wood fibers, is increasingly preferred for its biodegradability, cost-effectiveness, and eco-conscious profile. In an era where environmental responsibility drives consumer behavior and regulatory compliance, molded pulp packaging presents a compelling alternative to traditional plastic, Styrofoam, and other synthetic materials.
Across the U.S., businesses in industries ranging from food service and healthcare to electronics and industrial goods are pivoting toward sustainable packaging materials. Molded pulp is used to manufacture a variety of protective and display-oriented packaging solutions such as trays, clamshells, cups, plates, and protective end caps. Its natural resilience and ability to be custom-formed into complex shapes make it ideal for cushioning delicate items and presenting consumer-facing products.
Several key factors underpin the market’s growth: increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging, escalating bans and restrictions on single-use plastics, and widespread corporate sustainability goals. For example, major quick-service restaurants (QSRs) in the U.S. have announced plans to eliminate polystyrene containers in favor of molded pulp alternatives. Simultaneously, technology companies are investing in fiber-based packaging solutions for devices like smartphones, wearables, and accessories.
With technological advancements enabling better aesthetics, moisture resistance, and printability, the application scope of molded pulp packaging continues to expand. As the U.S. transitions toward a circular economy, molded pulp is positioned not merely as an alternative but as a mainstream packaging solution.
Shift from plastic and Styrofoam to fiber-based, compostable molded pulp solutions.
Adoption of thermoformed molded pulp for high-precision retail and electronics packaging.
Expansion of QSR chains using molded pulp clamshells, trays, and drink carriers.
Growth in use of non-wood pulps like bamboo and bagasse for premium sustainable appeal.
Integration of digital printing and embossing in molded pulp packaging for branding.
Investment in automation and robotics for high-speed molded pulp production in the U.S.
Increasing collaboration between packaging startups and major food delivery platforms.
Customized molded pulp used in ecommerce packaging to reduce plastic void fillers.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1,060.05 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 1,868.41 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 6.5% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Source, Product, Molded Type, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Sonoco Products Company; Smurfit Kapp; Western Pulp Products Company; Huhtamaki Group; DS Smith; Hartmann; Novolex; Omni-Pac Group; Pulp-Tec Ltd.; Eco-Products, Inc. |
One of the most compelling drivers of the U.S. molded pulp packaging market is the combined effect of regulatory mandates and rising consumer environmental consciousness. A wave of state and city-level bans on single-use plastic and polystyrene packaging—seen in jurisdictions such as California, New York, and Washington D.C.—has spurred widespread demand for alternatives. Molded pulp, being biodegradable and recyclable, fits seamlessly into this shift.
On the consumer side, eco-friendly packaging has evolved from a value-add to an expectation. According to surveys conducted across U.S. retailers, over 60% of consumers are more likely to purchase from brands that adopt sustainable packaging. This behavioral shift is encouraging large corporations to overhaul their packaging portfolios. Fast food giants like McDonald’s and Starbucks have piloted molded pulp containers in select markets, while electronics firms like Apple have moved to fiber-based trays for their retail boxes.
Molded pulp packaging not only satisfies compliance and consumer sentiment but also enables brands to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) benchmarks, making it a strategic driver in long-term planning.
Despite its many advantages, molded pulp packaging faces challenges related to performance limitations, particularly in moisture-sensitive applications. Unlike plastic or laminated paperboard, standard molded pulp can absorb moisture, which compromises structural integrity and aesthetics. This constraint limits its adoption in certain food service applications that involve wet or greasy foods unless additional coatings or treatments are applied.
However, coating molded pulp with barrier layers like PLA (polylactic acid) or paraffin often raises concerns about compostability and cost. Moreover, achieving precise surface smoothness and color consistency can be challenging, particularly when using recycled content, affecting the suitability for premium retail applications. These performance drawbacks necessitate trade-offs or investments in value-added processes, which may not be economically viable for smaller brands or operations with thin margins.
Therefore, while the market is expanding, performance limitations of molded pulp especially when compared to high-grade plastics or laminates remain a restraint for broader use across certain industries.
An exciting opportunity lies in the growth of thermoformed molded pulp packaging, a technology that allows for precise, sleek, and consumer-friendly designs. Unlike traditional molded pulp which has a rough texture and limited detail resolution, thermoformed pulp delivers a clean finish, intricate contours, and tight tolerances—making it ideal for retail packaging of electronics, cosmetics, and luxury goods.
Thermoformed molded pulp has gained traction as brands seek to elevate the unboxing experience while maintaining environmental credentials. For instance, high-end electronics companies in the U.S. have begun replacing plastic inlays and foams with sculpted fiber trays that offer equal protection and superior sustainability messaging. Moreover, companies in cosmetics and premium food packaging are exploring thermoformed designs that allow for embossed branding, color integration, and sealed compartments.
The expansion of thermoforming capabilities opens new market segments for molded pulp ones traditionally dominated by rigid plastics and polystyrene creating a significant growth frontier for U.S. manufacturers.
Wood pulp dominated the market, supported by the widespread availability and recyclability of paper-based inputs.
The majority of molded pulp packaging in the U.S. is currently derived from wood pulp, including recycled newspapers, cardboard, and virgin kraft. These materials are not only readily available but also cost-efficient and fully compatible with existing production equipment. They offer reliable structural properties and serve well across protective and disposable packaging needs. Wood pulp-based packaging is extensively used for egg cartons, cup carriers, end caps, and general food service trays, making it the backbone of the market.
However, non-wood pulp sources are growing rapidly, led by consumer preference for ‘alternative fiber’ packaging.
Non-wood pulps like bagasse (sugarcane fiber), wheat straw, and bamboo are gaining favor for their natural appeal and fast-growing, renewable profile. These materials are particularly prevalent in the food service sector, where compostability and ‘farm-to-table’ storytelling align well. Non-wood pulp also exhibits superior aesthetics and lower allergen risks, making it attractive in healthcare and premium packaging. Though currently costlier, increasing scale and technological investment are expected to boost this segment’s market share significantly.
Transfer molded pulp dominated due to its balance between structural performance and production scalability.
Transfer molded pulp is the most commonly used method in the U.S., responsible for mass-producing egg trays, cup carriers, and general protective packaging. It provides relatively smooth surfaces on one side and sufficient rigidity, making it ideal for both contact and cushioning applications. With automated lines capable of high-speed, low-cost production, transfer molding continues to be the workhorse of the molded pulp industry.
Thermoformed molded pulp is the fastest-growing type, driven by its application in high-definition packaging solutions.
As discussed earlier, thermoforming enables sleek, lightweight, and custom-contoured designs that are suitable for display packaging. U.S. manufacturers are investing in advanced molds and precision drying systems to cater to high-value industries like electronics, cosmetics, and wellness products. The technology is also allowing food service providers to upgrade from generic containers to more elegant, functional, and brandable designs, particularly for takeaway and delivery.
Trays remained the leading product segment, owing to their versatility and extensive use across industries.
Molded pulp trays are indispensable in industries such as food packaging, electronics, and healthcare. They are used to securely hold items during transport, ensure product separation, and reduce damage. Trays can be customized with compartments, drainage, and contours, making them highly adaptable. For instance, medical device companies use pulp trays to organize sterile surgical tools, while electronics firms use them for earbuds, cables, and adapters.
Clamshells are growing quickly as consumer-focused packaging solutions, particularly in food and retail.
Clamshell-style containers are widely used in the U.S. food service sector, especially for carry-out and prepackaged meals. With increasing environmental scrutiny on plastic takeout containers, many restaurants and cafes are switching to molded pulp clamshells that can be composted. These products are also gaining use in fresh produce packaging, bakery goods, and deli items. Advanced clamshells with locking mechanisms and leak-resistant designs are further boosting adoption.
Food packaging led the market due to the surge in demand for sustainable alternatives to plastic and Styrofoam containers.
U.S. food manufacturers, grocery retailers, and delivery platforms are actively transitioning to molded pulp packaging for fresh produce, dairy, and baked goods. From apple trays to cup holders and dessert bowls, molded pulp offers a biodegradable, compostable solution that aligns with growing pressure to reduce plastic in the food chain. The surge in meal kit deliveries and organic food consumption has further increased reliance on fiber-based trays and inserts.
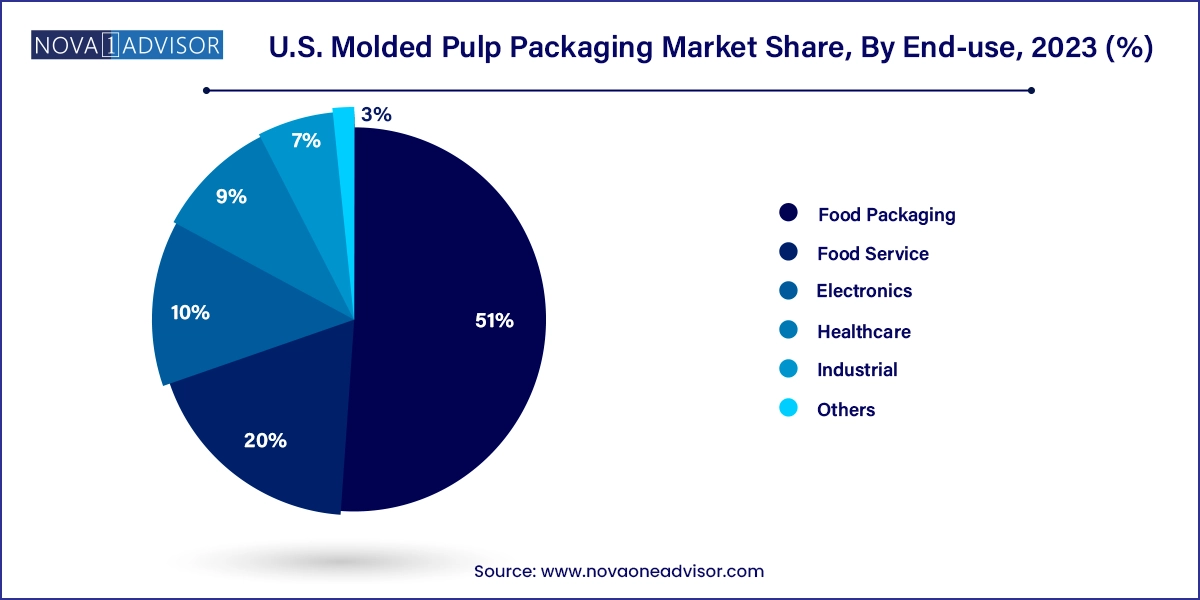
Healthcare is emerging as a fast-growing end-use segment as hospitals prioritize disposable and eco-safe packaging.
The pandemic amplified the need for sanitary, disposable, and cost-effective packaging in healthcare. Molded pulp is being used for single-use kidney trays, diagnostic test kits, and sterile packaging inserts. Unlike plastic, molded pulp is safe for incineration and can be made free of latex or other allergens. Hospitals and clinics, especially in the U.S. Northeast and Midwest, are shifting toward molded pulp to reduce waste management burdens and support sustainability mandates.
The United States leads global consumption and innovation in molded pulp packaging, driven by robust regulatory frameworks, consumer awareness, and corporate ESG commitments. Federal and state-level initiatives such as the Plastic Pollution Reduction Acts in California and New York are forcing businesses to re-evaluate packaging practices. The U.S. is also home to a highly developed waste management and recycling infrastructure, enabling the growth of recycled-content pulp products.
Major packaging clusters in states like California, Illinois, Georgia, and Texas are hubs for molded pulp manufacturing, powered by automation and skilled labor. Brands like Apple and Amazon are setting industry benchmarks by eliminating plastic from their packaging lines and switching to custom-formed fiber-based trays and inserts. Fast-food chains across the country have started to transition to molded pulp clamshells and trays, signaling large-volume adoption.
U.S. consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for sustainable packaging. In retail, grocery, and healthcare channels, molded pulp is gaining mainstream visibility as the industry pivots toward circular economy models.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. molded pulp packaging market
Source
Molded Type
Product
End-use