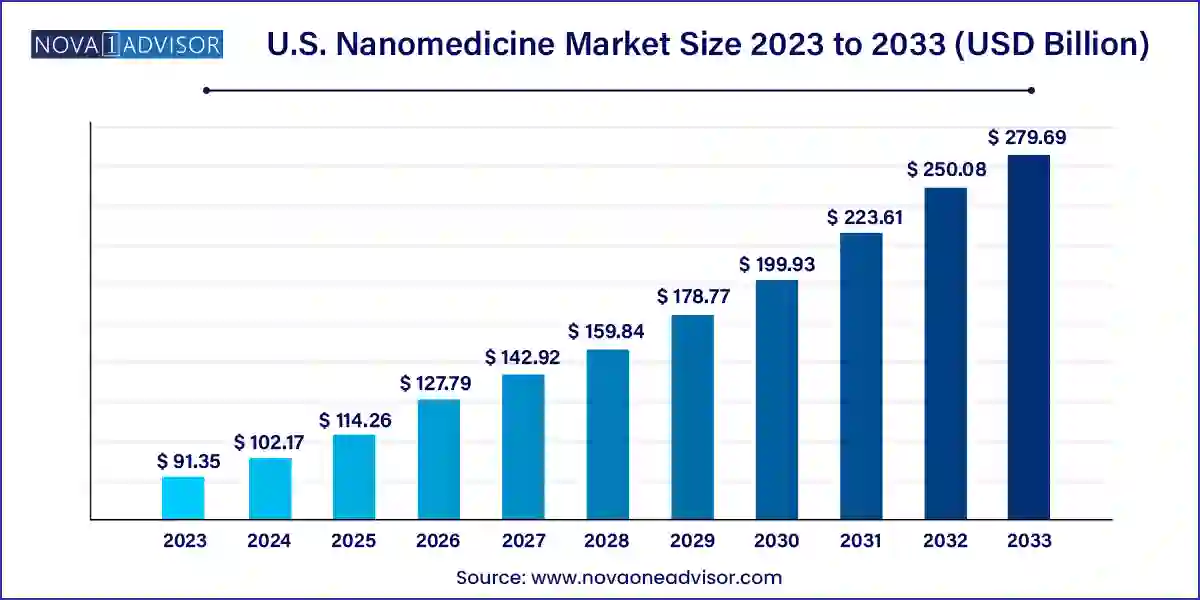
The U.S. nanomedicine market size was exhibited at USD 91.35 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 279.69 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11.84% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
Nanomedicine, an innovative subset of nanotechnology, refers to the application of nanotechnology in healthcare to diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases. In the United States, the nanomedicine market is rapidly evolving, driven by significant investments in research and development, an increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and the growing need for targeted drug delivery systems. Nanomedicine leverages nanoscale materials and tools, including nanoparticles, nanotubes, and nanoshells, to enhance the efficacy and precision of medical treatments. This includes areas such as drug delivery, imaging, diagnostics, and regenerative medicine.
The U.S. holds a leading position in the global nanomedicine landscape, supported by a robust healthcare infrastructure, world-renowned research institutions, and favorable regulatory frameworks. The convergence of biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and nanotechnology is opening up new therapeutic avenues and redefining conventional treatment protocols. According to market estimations, the U.S. nanomedicine market is anticipated to witness substantial growth in the coming decade, owing to increasing FDA approvals, rising demand for personalized medicine, and expanding investments from public and private stakeholders.
Nanomedicine, an innovative subset of nanotechnology, refers to the application of nanotechnology in healthcare to diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases. In the United States, the nanomedicine market is rapidly evolving, driven by significant investments in research and development, an increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and the growing need for targeted drug delivery systems. Nanomedicine leverages nanoscale materials and tools, including nanoparticles, nanotubes, and nanoshells, to enhance the efficacy and precision of medical treatments. This includes areas such as drug delivery, imaging, diagnostics, and regenerative medicine.
The U.S. holds a leading position in the global nanomedicine landscape, supported by a robust healthcare infrastructure, world-renowned research institutions, and favorable regulatory frameworks. The convergence of biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and nanotechnology is opening up new therapeutic avenues and redefining conventional treatment protocols. According to market estimations, the U.S. nanomedicine market is anticipated to witness substantial growth in the coming decade, owing to increasing FDA approvals, rising demand for personalized medicine, and expanding investments from public and private stakeholders.
Personalized Nanomedicine: Tailored treatment modalities based on a patient’s genetic profile using nanocarriers for drug delivery.
Advancements in Targeted Drug Delivery: Increasing adoption of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems that target specific cells, reducing systemic side effects.
Expansion of Nanotechnology in Diagnostics: Enhanced imaging techniques and in-vitro diagnostic tools using nanosensors for early disease detection.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning: Development of intelligent nanodevices and nanorobots guided by AI algorithms for real-time monitoring and drug administration.
Growth in Cancer Therapeutics: Increased utilization of nanomedicine in oncology for tumor targeting and improving the bioavailability of anticancer agents.
Rise in Nanomedicine Patents: Surge in patent filings related to nanopharmaceuticals and nano-formulations by U.S.-based biotech firms.
Emergence of Smart Nanodevices: Proliferation of implantable and wearable nanosystems for chronic disease monitoring.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 102.17 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 279.69 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 11.84% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Application, Indication, Molecule Type |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Abbott Laboratories; CombiMatrix Corporation; Celgene Corporation; Nanospectra Biosciences, Inc.; GE Healthcare; Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.; Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals; Merck & Co., Inc.; Pfizer, Inc.; Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.; Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
One of the primary drivers of the U.S. nanomedicine market is the escalating burden of chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, and neurodegenerative conditions. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), six in ten adults in the U.S. have a chronic disease, and four in ten adults have two or more. These diseases require continuous monitoring and long-term treatment regimens, which traditional therapies often fail to manage effectively due to limitations in drug bioavailability and specificity.
Nanomedicine offers a transformative approach by providing targeted, controlled, and sustained drug delivery systems. For example, liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil) is a nanoparticle formulation used for treating ovarian cancer and multiple myeloma, which enhances the drug’s efficacy while minimizing toxicity. Such breakthroughs are enhancing patient compliance and therapeutic outcomes, thus fueling the market's growth.
Despite its vast potential, the development of nanomedicine involves substantial financial investment due to the complexity of nanoparticle synthesis, characterization, and regulatory compliance. The cost of R&D in nanotechnology is significantly higher compared to conventional pharmaceuticals, often requiring specialized equipment and facilities. Moreover, stringent regulatory pathways for nano-drugs, including detailed safety assessments, add to the overall cost burden.
This high expenditure often translates into increased product pricing, posing affordability challenges for healthcare providers and patients. Startups and small biotech firms may also face hurdles in scaling operations or attracting funding, particularly in early development stages. Thus, the economic barriers to entry may slow down the commercialization of innovative nanotherapeutics.
The growing emphasis on personalized medicine, especially in oncology, presents a significant opportunity for the U.S. nanomedicine market. Personalized nanomedicine enables oncologists to design therapies based on individual genetic and molecular profiles. With the ability of nanoparticles to deliver drugs directly to tumor cells while sparing healthy tissues, treatment outcomes improve substantially.
Recent developments, such as the use of polymeric micelles and gold nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy, are revolutionizing how cancer is treated. Personalized nanomedicine also supports real-time imaging and monitoring, allowing for dynamic treatment adjustments. As genomic and proteomic technologies continue to advance, the integration of these insights with nanotechnology will unlock unprecedented therapeutic possibilities.
Therapeutics dominated the application segment due to the increasing number of nano-enabled drugs entering the U.S. market. Nanomedicine in therapeutics encompasses applications in cancer, cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, and infectious diseases. Liposomal and polymer-based nanoparticles are extensively used to improve drug solubility and bioavailability. One notable example is Abraxane (paclitaxel protein-bound particles), approved for breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer, which enhances the therapeutic index and reduces side effects.
Drug delivery is the fastest-growing application, driven by ongoing innovations in nanoparticle engineering. The development of multifunctional nanocarriers capable of simultaneous imaging and therapy (theranostics) is gaining traction. Companies are focusing on site-specific delivery platforms that respond to pH, temperature, or enzyme levels, ensuring that therapeutic payloads reach their intended target with minimal off-target effects. This precision reduces drug wastage, enhances treatment efficacy, and is particularly useful for chemotherapeutic agents.
Clinical oncology is the dominant indication, accounting for the largest revenue share in the U.S. nanomedicine market. The high incidence of cancer, coupled with the limitations of conventional treatments, has led to increased adoption of nanoparticle-based therapies. Nanocarriers like liposomes and dendrimers allow selective accumulation in tumor sites via the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. For instance, Onivyde, a liposomal irinotecan, is used in metastatic pancreatic cancer and showcases how nanomedicine can extend survival and reduce toxicity.
Infectious diseases are emerging as the fastest-growing indication, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the critical need for rapid and accurate diagnostics. Nanoparticles are being explored for delivering antiviral agents and vaccines. Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine, which uses lipid nanoparticles to deliver mRNA, exemplifies how nanomedicine is transforming infectious disease management. The success of such products is paving the way for broader adoption in diseases like HIV, influenza, and hepatitis.
Nanoparticles, particularly liposomes and polymers & polymer-drug conjugates, dominate this segment due to their versatility, biocompatibility, and regulatory precedence. Liposomal formulations, like Doxil and AmBisome, are well-established in clinical practice and continue to inspire new innovations. Polymer-based nanocarriers are gaining attention for their ability to provide sustained release and reduce immunogenicity, essential for chronic disease management.
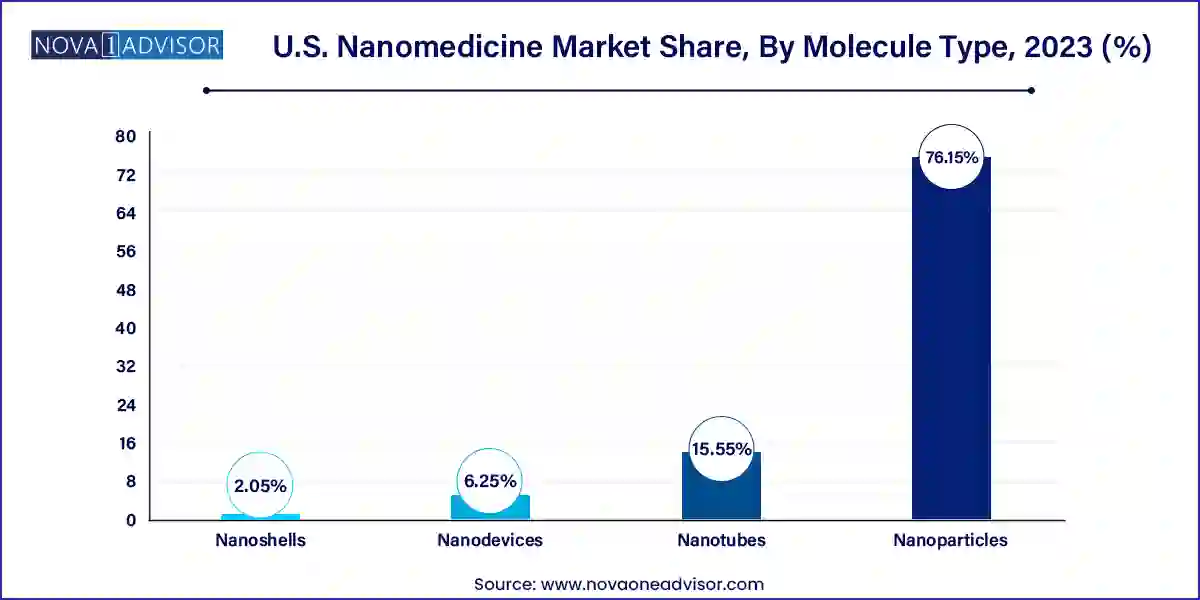
Hydrogel nanoparticles and dendrimers are among the fastest-growing molecule types, offering advanced drug loading capabilities and tunable surface functionalities. Hydrogel nanoparticles are highly hydrophilic, allowing for controlled drug release and high tissue compatibility. Meanwhile, dendrimers, with their branched architecture, are being explored for gene therapy and siRNA delivery. Their precision and ability to carry multiple therapeutic agents are propelling research efforts, particularly in neurodegenerative and autoimmune diseases.
The United States represents the epicenter of nanomedicine innovation and commercialization. Federal initiatives like the National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI) have bolstered R&D funding, facilitating groundbreaking discoveries. Furthermore, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has established specific guidance for nanotechnology-based products, which streamlines the regulatory pathway for nano-drugs.
Prominent U.S. cities, such as Boston, San Francisco, and San Diego, host a concentration of biotech clusters and academic institutions contributing to nanomedicine advancement. The U.S. market also benefits from strong intellectual property protections and an established ecosystem of venture capital firms ready to invest in nanotech startups. Collaborations between universities and pharmaceutical giants are also common, promoting translational research and expediting clinical adoption. The healthcare system’s focus on innovation, combined with high per capita healthcare expenditure, ensures a favorable environment for the growth of nanomedicine.
January 2025: Moderna Inc. announced the expansion of its mRNA pipeline to include oncology targets using its proprietary lipid nanoparticle technology, with clinical trials expected to begin in late 2025.
October 2024: Pfizer invested $250 million in a joint venture with a California-based nanotech firm to develop nanocarrier systems for targeted drug delivery in rare diseases.
August 2024: Johnson & Johnson published promising phase 2 results for a dendrimer-based drug candidate aimed at treating glioblastoma, marking a significant milestone in nanomedicine for CNS cancers.
May 2024: BioNTech opened a new R&D hub in Cambridge, Massachusetts, focusing on nanoparticle formulations for personalized vaccines in oncology.
March 2024: The U.S. FDA approved a novel liposomal formulation for rheumatoid arthritis developed by a Boston-based startup, further diversifying nanomedicine applications beyond oncology.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. nanomedicine market
Application Scope
Indication Scope
Molecule Type Scope