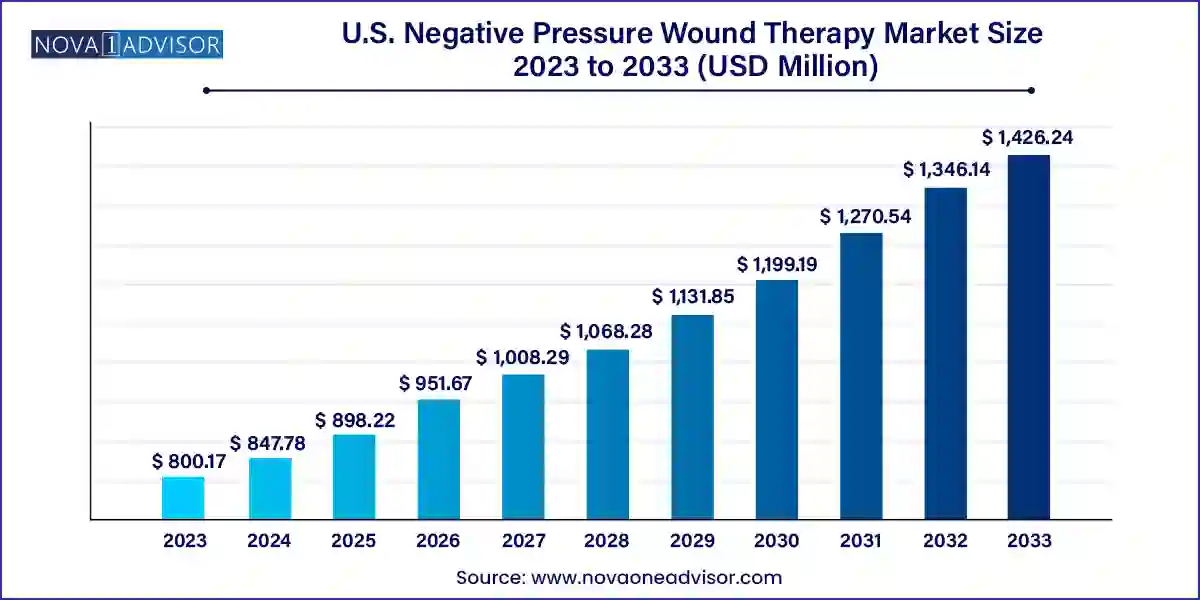
The U.S. negative pressure wound therapy market size was exhibited at USD 800.17 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 1,426.24 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.95% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) market represents a critical sector of the broader wound management landscape, playing a pivotal role in the treatment of complex, non-healing wounds. NPWT involves the application of sub-atmospheric pressure to a wound site, using a sealed dressing and a vacuum pump to promote faster healing, reduce infection risks, and facilitate granulation tissue formation. The therapy is widely utilized in both acute and chronic wound settings, especially for patients with diabetic foot ulcers, pressure sores, surgical site infections, and traumatic injuries.
As the population ages and the incidence of chronic diseases like diabetes and peripheral vascular disorders increases, the U.S. healthcare system is witnessing a surge in demand for advanced wound care modalities. NPWT systems are no longer confined to intensive care units or surgical wards; instead, they are increasingly being deployed in outpatient facilities, long-term care centers, and home healthcare settings. The availability of portable and single-use NPWT devices has expanded the therapy's reach, making it more accessible and convenient for both clinicians and patients.
The U.S. is home to several leading players in the NPWT space, including 3M (KCI), Smith & Nephew, Cardinal Health, Medela, Mölnlycke, and ConvaTec. These companies are continuously investing in product innovation, clinical research, and digital integration to enhance patient outcomes and reduce the cost burden on healthcare systems. The favorable reimbursement environment, coupled with strong clinical support for NPWT, continues to fuel growth across the market.
Increasing shift toward single-use and portable NPWT devices for outpatient and home care.
Rising prevalence of chronic wounds, especially diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers.
Integration of smart sensors and connectivity in NPWT systems for remote monitoring.
Growing preference for disposable components to reduce infection risks.
Adoption of NPWT in ambulatory surgical centers and specialty wound clinics.
Expansion of clinical studies validating NPWT for off-label and complex wound types.
Healthcare providers emphasizing cost-effective, long-duration NPWT solutions.
Collaborations between manufacturers and home care service providers to enhance at-home therapy.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 847.78 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 1,426.24 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 5.95% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Wound Type, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | 3M; DeRoyal Industries; Cardinal Health; Ethicon; Medline; Baxter; Organogenesis; Integra Lifesciences; MiMedx.; Pensar Medical; Guard Medical; Infusystem Holdings Inc |
Conventional NPWT devices dominate the U.S. market, especially in inpatient and critical care settings. These reusable, high-powered systems are commonly used for deep, exudating wounds that require long-term negative pressure support. Hospitals and surgical centers rely heavily on conventional NPWT systems for post-operative wound management and complex trauma cases. Devices from KCI (now part of 3M) and Smith & Nephew offer customizable therapy modes, dual-lumen tubing, and versatile dressing options to handle diverse wound anatomies.
Single-use NPWT devices are the fastest-growing product segment, gaining momentum in outpatient surgery centers, rehabilitation clinics, and home care. These disposable systems are pre-set, portable, and lightweight, making them ideal for low-to-moderate exudating wounds. Brands like PICO (Smith & Nephew) and Prevena (3M) have witnessed strong uptake due to their ease of use and effectiveness in post-operative incision management. Single-use NPWT reduces infection risk, eliminates equipment cleaning needs, and ensures convenience particularly in fast-discharge models and mobile wound care programs.
Chronic wounds dominate the wound type segment, driven by the high incidence of diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure sores in elderly and diabetic populations. Chronic wounds are notoriously slow to heal and often complicated by infection, biofilm formation, or poor perfusion. NPWT has proven efficacy in stimulating angiogenesis, managing exudate, and promoting granulation in chronic wound environments. Hospital wound care teams and home care nurses increasingly rely on NPWT to manage these long-standing wounds, especially when conventional dressings fail to deliver adequate results.
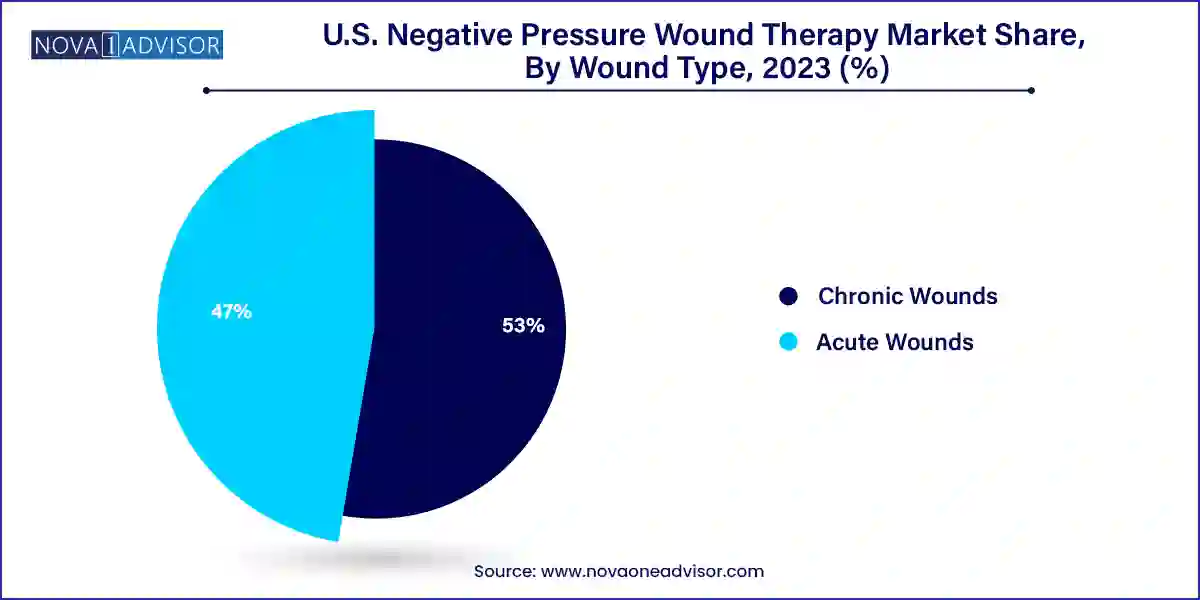
Acute wounds are the fastest-growing application, particularly surgical site and traumatic wounds. Surgical incision management is a key area where NPWT is gaining traction due to its ability to reduce surgical site infections (SSIs), dehiscence, and hematoma formation. With hospitals aiming to reduce postoperative complications and length of stay, NPWT is being adopted as a prophylactic tool in orthopedics, cardiovascular surgery, and reconstructive procedures. Burns, lacerations, and crush injuries also benefit from NPWT, especially when traditional closure is not feasible. Emerging clinical guidelines are supporting earlier NPWT adoption in acute trauma settings.
Hospitals are the primary end-users of NPWT, accounting for the largest share of market revenue. Hospitals manage high volumes of complex wounds, surgical cases, and trauma patients requiring continuous monitoring and high-intensity care. NPWT systems deployed in hospitals often include large-capacity canisters, multiple dressing options, and advanced interface features to handle a wide variety of wounds. These facilities typically operate under GPO contracts and use evidence-based protocols to integrate NPWT into patient recovery pathways.
Home healthcare is the fastest-growing end-use segment, aligned with the nationwide push for decentralizing care and reducing inpatient costs. Portable NPWT devices have enabled effective therapy continuation at home under nurse supervision or with telehealth integration. Patients with chronic wounds, post-operative incisions, or limited mobility increasingly prefer home-based treatment, and providers are responding by training visiting nurses and equipping them with single-use systems. The combination of patient satisfaction, cost-effectiveness, and technological advancement is making home healthcare a powerful growth driver in the NPWT ecosystem.
The United States has one of the most structured and innovation-driven markets for negative pressure wound therapy. The market benefits from an advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, strong reimbursement policies, and a large patient pool with chronic conditions. The prevalence of diabetes, which affects nearly 11% of the U.S. population, coupled with aging demographics and obesity rates, underscores a strong clinical need for NPWT in wound management.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and commercial insurers generally reimburse NPWT for approved indications, particularly when used in conjunction with certified wound care services. Leading hospitals have dedicated wound care teams and outpatient wound clinics that actively prescribe NPWT for both acute and chronic indications. Furthermore, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a critical role in regulating NPWT device approval, ensuring clinical safety and performance through robust evidence requirements. Innovation hubs in states like California, Texas, and Massachusetts continue to support startups and established companies developing next-gen NPWT platforms.
March 2024 – 3M Health Care announced the launch of a new advanced NPWT system in the U.S., incorporating smart dressing sensors and real-time healing analytics to support clinical decisions in hospital and home settings.
February 2024 – Smith & Nephew expanded the distribution of its PICO 7Y single-use NPWT system in ambulatory surgical centers, emphasizing incision management in orthopedic and colorectal procedures.
January 2024 – Cardinal Health initiated a partnership with a nationwide home healthcare provider to supply portable NPWT devices and consumables directly to patients’ homes, ensuring post-discharge care continuity.
December 2023 – Mölnlycke Health Care announced a U.S. clinical trial for its proprietary NPWT foam dressing that integrates antimicrobial silver ions, targeting wound sites with high infection risk.
November 2023 – Medela introduced a mobile app-enabled NPWT unit for home care patients, allowing them to log wound photos, monitor canister fill levels, and communicate with clinicians securely.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. negative pressure wound therapy market
Product
Wound Type
End-use