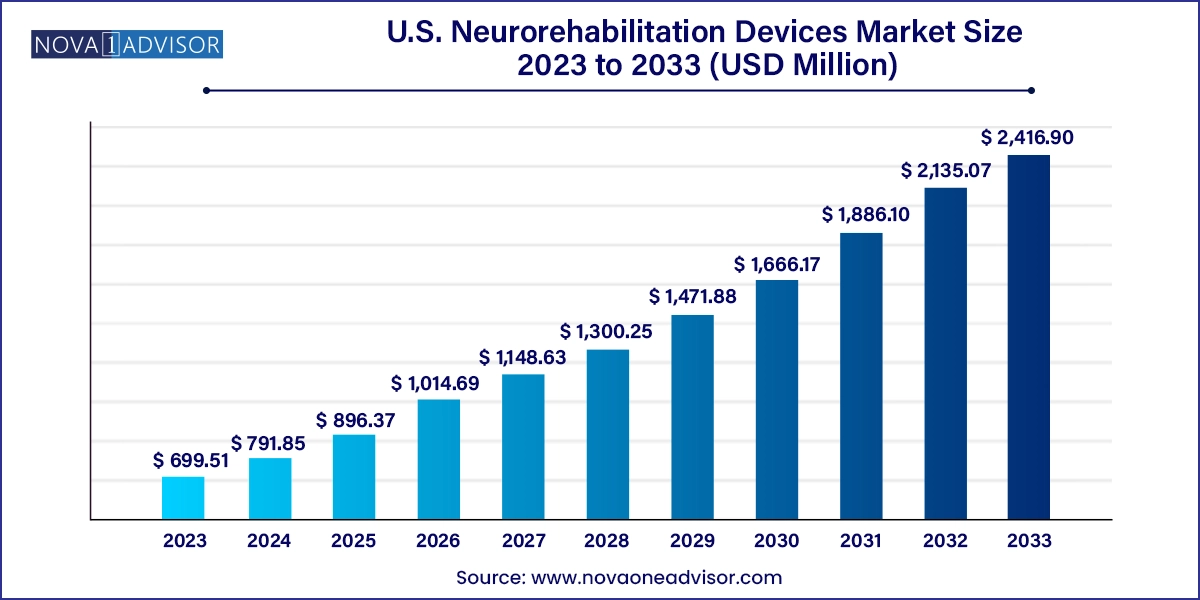
The U.S. neurorehabilitation devices market size was exhibited at USD 699.51 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 2,416.90 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 13.2% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. neurorehabilitation devices market is gaining substantial traction as the nation grapples with rising incidences of neurological disorders and increasing awareness about early intervention strategies. Neurorehabilitation involves the use of specialized therapeutic tools and technologies to help patients recover or compensate for the loss of neurological functions caused by conditions such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, and spinal cord injuries. This growing market segment is an intersection of medical innovation, robotics, neuroengineering, and digital health.
As the aging population in the U.S. grows—coupled with sedentary lifestyles, stress, and chronic diseases—the prevalence of neurological disorders has surged. According to the CDC, stroke alone affects nearly 800,000 Americans annually, with many survivors experiencing lasting motor and cognitive impairments. Similarly, over 1 million people in the U.S. are living with Parkinson’s disease, creating immense demand for continuous and targeted rehabilitation. This demographic shift, combined with clinical advancements, has led to the development and commercialization of innovative neurorehabilitation devices tailored to different stages of recovery.
These devices include neurorobotic exoskeletons, brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), wearable neurostimulation devices, and non-invasive stimulators, each addressing a unique aspect of neural function restoration. What was once limited to specialized hospital centers is now expanding to outpatient rehabilitation clinics, home healthcare settings, and tele-rehabilitation programs, thanks to technological miniaturization and digital connectivity. With continued support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Department of Veterans Affairs, and private investors, the U.S. neurorehabilitation market is projected to grow steadily over the next decade, transforming the future of neurological care and recovery.
Rise in Robotic-Assisted Rehabilitation: Robotic exoskeletons and assistive devices are being increasingly adopted in both hospital and outpatient settings to support motor recovery in stroke and spinal cord injury patients.
Adoption of Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs): BCIs are allowing patients to regain motor function and control prosthetics or assistive tools using neural signals.
Integration of Telehealth and Remote Monitoring: Neurorehabilitation is being extended into the home through wearable devices and remote software platforms, increasing access and adherence.
AI-Powered Adaptive Therapy Devices: Artificial intelligence is being used to personalize rehabilitation protocols in real-time based on patient performance and biofeedback.
Wearable Neurostimulation Devices Gaining Ground: Compact, user-friendly stimulators for neuromuscular re-education and pain modulation are being adopted for daily home use.
Increased Pediatric and Veteran Use Cases: Devices tailored to pediatric patients and U.S. veterans are being developed to address the unique needs of these growing patient populations.
Public and Private Sector Funding Boost: Government grants and venture capital funding are fueling innovation and market entry for new startups in neurotechnology.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 791.85 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 2,416.90 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 13.2% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Therapy Area |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Bioventus; Ectron; Hocoma; Medtronic; Tyromotion Inc; Biometrics Ltd.; Bionik Laboratories Corp. (BNKL); BioXtreme Ltd.; Ekso Bionics; Kinestica; Kinova Inc.; Saebo, Inc.; Abbott |
One of the most prominent drivers for the U.S. neurorehabilitation devices market is the escalating incidence of neurological disorders, particularly stroke and Parkinson’s disease, which often require intensive and prolonged rehabilitation. As per the American Stroke Association, approximately 10% of stroke survivors recover completely, while over 40% experience moderate to severe impairments that require specialized therapy. This growing cohort of patients creates sustained demand for advanced rehabilitation tools capable of enhancing neuroplasticity and functional outcomes.
Moreover, conditions like multiple sclerosis and cerebral palsy, which manifest as progressive or lifelong motor challenges, further amplify the need for ongoing therapy supported by effective devices. The U.S. also has a significant aging population, with over 54 million Americans aged 65 and older, a demographic more susceptible to neurodegenerative conditions. Neurorehabilitation devices not only enable better functional outcomes but also reduce the long-term cost burden on healthcare systems by promoting independence and minimizing the need for full-time care. The synergy between clinical demand and technological capability is thus fueling significant market expansion.
Despite promising growth, a major restraint for the U.S. neurorehabilitation devices market is the high cost of advanced equipment and limited reimbursement policies. Many neurorobotic and BCI-based devices are priced in the range of tens of thousands of dollars, making them inaccessible to smaller rehabilitation clinics or underinsured patients. Additionally, while Medicare and Medicaid provide coverage for certain rehabilitation therapies, the inclusion of emerging neurorehabilitation technologies remains inconsistent across states and payers.
This financial burden limits market penetration, especially among low-income patients and rural populations. Furthermore, many facilities lack the specialized staff required to operate and integrate advanced technologies into clinical workflows. Without broader insurance coverage, training programs, and policy-level support, the adoption of these transformative devices may remain confined to large urban hospitals and elite institutions, curbing the potential market impact nationwide.
The rapid growth of home-based neurorehabilitation platforms presents a significant market opportunity. Driven by digital transformation, the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on in-person therapy, and a desire for convenience, many providers and patients are embracing remote rehabilitation. Wearable neurostimulation devices, lightweight robotic gloves, mobile apps, and cloud-based progress tracking tools now enable patients to continue therapy at home with minimal supervision.
Startups are capitalizing on this trend by offering device-as-a-service models, subscription-based platforms, and tele-rehab kits that can be shipped directly to the patient’s home. These solutions not only ensure therapy continuity but also allow clinicians to monitor progress and adapt treatment plans in real time. The expansion of remote care in neurorehabilitation holds the potential to reach underserved communities, improve patient adherence, and reduce hospital readmissions, creating a robust opportunity for growth and innovation in the U.S. market.
Neurorobotics dominated the product segment of the U.S. neurorehabilitation devices market. These include robotic exoskeletons, smart treadmills, and robotic arm supports used extensively in hospital rehabilitation departments. Devices like Ekso Bionics’ exosuits and ReWalk Robotics’ exoskeletons help patients relearn walking patterns after a stroke or spinal cord injury by simulating natural gait and providing feedback. These solutions promote neural rewiring through repetitive, precise motion—key to motor function recovery. Their adoption is highest in academic medical centers, VA hospitals, and advanced neurorehabilitation facilities.
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) are the fastest-growing product category, fueled by remarkable advancements in neural decoding and non-invasive brain signal capture. Companies like Neurable and NeuroPace are developing tools that allow patients with severe paralysis or motor disabilities to control external devices with their minds. BCIs hold immense promise for ALS patients, spinal cord injury survivors, and others with locked-in syndromes. Clinical trials and NIH-backed research into non-invasive BCIs have gained momentum, and successful outcomes could lead to broader commercialization across rehabilitation clinics and even consumer applications in the future.
Stroke held the largest share by therapy area, representing the bulk of neurorehabilitation procedures in the U.S. Stroke patients commonly face hemiparesis, balance disorders, and cognitive deficits, necessitating structured rehabilitation protocols that include gait training, neuromuscular re-education, and cognitive retraining. Neurorobotic systems, such as robotic gait trainers and smart balance platforms, are frequently used in this context. With early intervention recognized as crucial to optimal recovery, stroke-focused rehab centers across the country are increasingly investing in advanced technologies to improve patient throughput and outcomes.
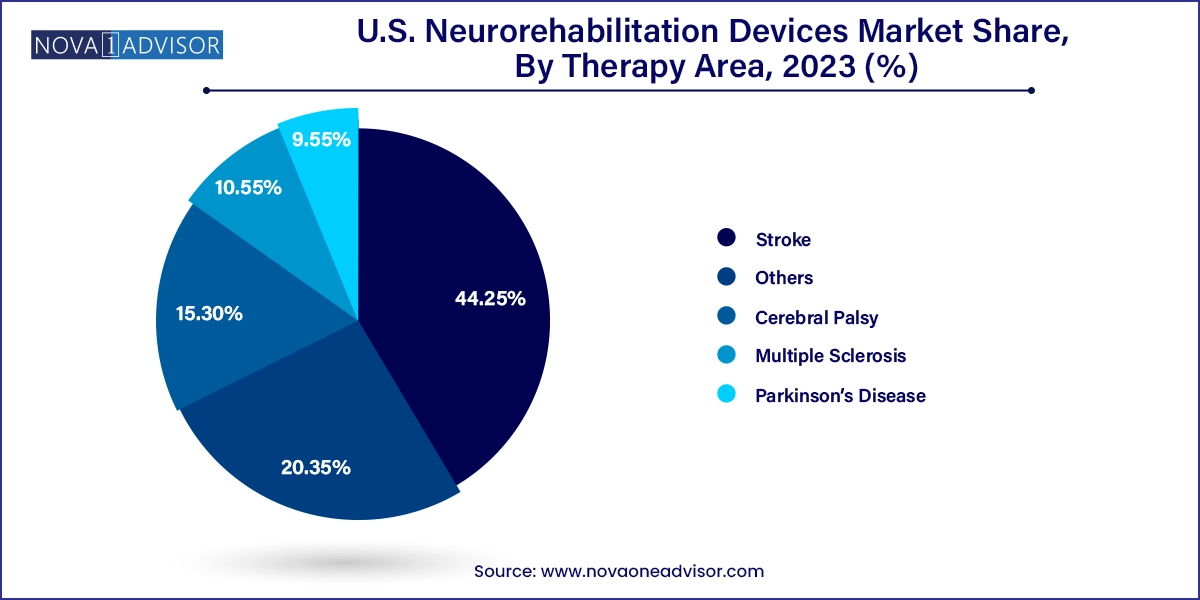
Parkinson’s disease is emerging as the fastest-growing therapy area, reflecting the rising number of diagnosed cases and advancements in targeted rehabilitation solutions. Patients with Parkinson’s often experience tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia, for which wearable stimulators and motion-tracking feedback systems have shown promise. Devices that deliver rhythmic auditory cues or wearable sensors that detect movement irregularities are being used to improve gait and prevent freezing episodes. With the American Parkinson Disease Association (APDA) actively funding innovation and patient support programs, this segment is expected to grow rapidly in clinical adoption and technology integration.
The U.S. neurorehabilitation devices market is shaped by demographic shifts, regional healthcare infrastructure, and innovation clusters. The Northeast region, home to institutions such as Massachusetts General Hospital, Johns Hopkins, and Columbia University Medical Center, dominates the market due to its concentration of academic hospitals, R&D funding, and early access to clinical trials. These facilities often serve as launchpads for new neurotechnology pilots and are among the first to adopt cutting-edge devices like neurorobotics and BCIs.
Meanwhile, the Southwest region, especially Texas and Arizona, is the fastest-growing area, driven by population aging, expanding veteran rehabilitation programs, and the rise of private neurorehab clinics. Texas, in particular, has invested significantly in rehabilitation infrastructure through partnerships between VA hospitals, state research institutes, and medtech startups. Additionally, the rise of remote and home-based rehabilitation services has enabled broader access in these less densely populated states, accelerating growth in patient volumes and device adoption.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. neurorehabilitation devices market
Product
Therapy Area