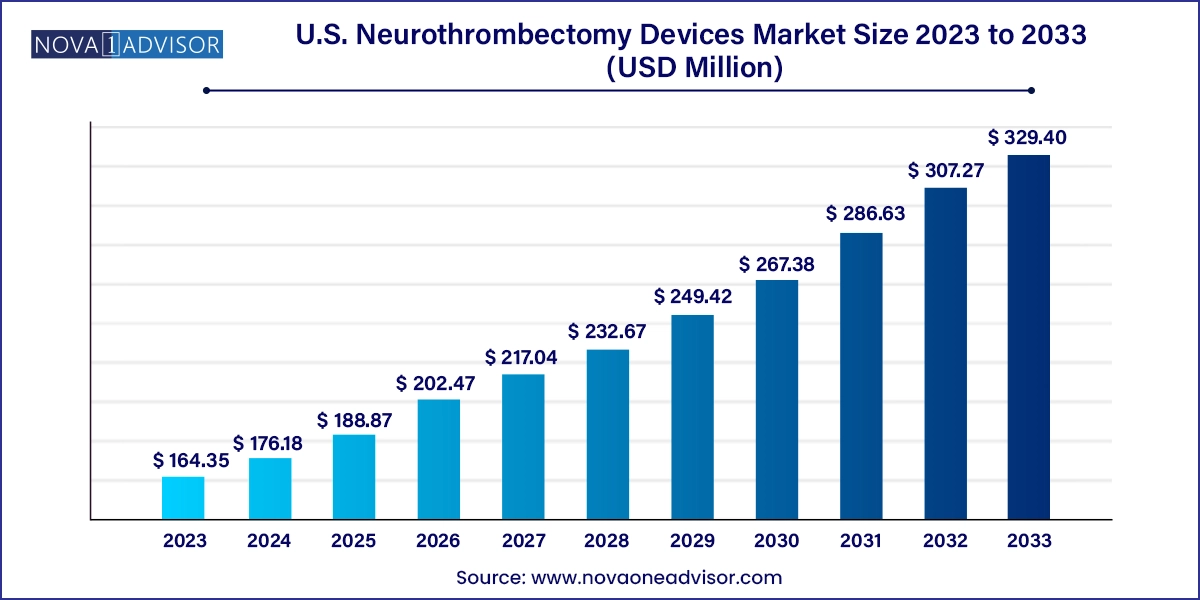
The U.S. neurothrombectomy devices market size was exhibited at USD 164.35 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 329.40 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. neurothrombectomy devices market is undergoing a significant transformation, largely propelled by the increasing burden of ischemic strokes and rapid advancements in interventional neurovascular technologies. Neurothrombectomy refers to the mechanical removal of blood clots from cerebral arteries, commonly performed in cases of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) to restore blood flow and prevent irreversible brain damage. With stroke remaining a leading cause of disability and death in the United States, early and effective intervention has become a national priority, positioning neurothrombectomy as a cornerstone of modern stroke management.
In the past, the standard of care for AIS largely depended on pharmacologic thrombolysis with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). However, with a narrow treatment window and risks of hemorrhagic complications, the limitations of tPA spurred demand for safer, more efficient mechanical interventions. Neurothrombectomy devices including clot retrievers, aspiration catheters, and vascular snares now offer a compelling alternative with quicker action, broader applicability, and superior clinical outcomes.
The U.S. market is witnessing steady procedural growth owing to improved emergency medical response, expanded use of advanced imaging tools in hospitals, and the growing expertise of neurointerventional surgeons. Public health awareness campaigns, guidelines from neurology societies, and improved reimbursement coverage have further encouraged adoption. With an increasing focus on time-to-treatment, healthcare systems are refining stroke care pathways to ensure neurothrombectomy devices are deployed within critical timeframes, thereby driving sustained demand and innovation in the market.
Growing popularity of stent retrievers that combine clot capture and vessel wall support during retrieval, reducing distal embolization risk.
Adoption of combined aspiration and stent retriever approaches to improve first-pass recanalization success.
Miniaturization and design optimization of devices for better access in distal or tortuous cerebral vessels.
Development of next-gen suction devices with improved lumen geometry and flow control for more efficient clot aspiration.
Rise in outpatient stroke care models, with ambulatory and emergency clinic settings adopting neurointervention capabilities.
Integration of AI-driven stroke triage software to identify eligible patients and prioritize neurothrombectomy faster.
Growing clinical emphasis on door-to-reperfusion time, driving hospital system investments in neurovascular tools.
Emergence of training simulators and augmented reality tools for neurointerventional skill development.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 176.18 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 329.40 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 7.2% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Medtronic; Acandis GmbH; Phenox GmbH; Stryker; Penumbra, Inc.; Vesalio |
One of the primary drivers accelerating the U.S. neurothrombectomy devices market is the rising incidence of acute ischemic strokes across various age groups. While stroke is traditionally considered a disease of the elderly, lifestyle factors such as sedentary behavior, poor diet, smoking, and untreated hypertension have expanded the risk profile to include middle-aged and even younger adults.
What further amplifies the need for neurothrombectomy devices is the increased awareness and detection of large vessel occlusion (LVO) strokes an especially severe subtype of ischemic stroke that responds well to mechanical intervention. As emergency departments and first responders are increasingly equipped with stroke diagnostic protocols and mobile imaging tools, the diagnosis of LVOs is becoming more accurate and timely. This has created an environment in which neurothrombectomy procedures are not only more frequent but are being performed earlier in the care cycle, improving outcomes and driving consistent demand for device innovation and deployment.
Despite technological progress, the neurothrombectomy devices market faces a critical constraint the requirement of specialized infrastructure and trained personnel to perform these complex procedures. Neurothrombectomy is a time-sensitive, high-stakes intervention that demands a coordinated, multidisciplinary effort involving stroke neurologists, neurointerventionalists, radiologists, and critical care teams.
This limits the accessibility of neurothrombectomy devices to high-tier stroke centers, typically in urban regions. Rural and community hospitals may lack both the personnel and angiographic equipment to perform these procedures. While transfer protocols exist to route patients to comprehensive stroke centers, such delays often push patients beyond the therapeutic window. As a result, even in a technologically advanced country like the U.S., significant portions of the population remain underserved, limiting full market penetration and growth potential.
An emerging opportunity in the U.S. market is the potential expansion of neurothrombectomy capabilities into ambulatory and emergency clinic settings. With the shift toward decentralized, fast-response medical care, ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) and specialized stroke clinics are being upgraded with imaging and procedural tools to provide critical interventions in localized settings.
As neurothrombectomy devices become smaller, more flexible, and easier to deploy, the scope for their use outside of traditional hospital environments is increasing. This democratization of stroke care aligns with healthcare system goals of reducing ER burden, improving patient access, and lowering treatment costs. Moreover, the availability of real-time telemedicine support from major stroke centers allows trained clinicians at smaller facilities to initiate or assist in thrombectomy procedures with expert guidance unlocking new use cases for compact and rapid-deployment neurothrombectomy kits.
Clot retrievers are the cornerstone of the neurothrombectomy device segment, maintaining dominance due to their widespread clinical use, especially in cases involving large vessel occlusions. These devices, often designed as stent retrievers, operate by expanding within the clot to ensnare it, then carefully retracting it while maintaining vessel wall contact. This design enables high first-pass success rates essential in improving patient outcomes and minimizing procedural complications.
Moreover, manufacturers continue to refine clot retrievers with hydrophilic coatings, improved radial force, and better flexibility to enhance maneuverability through tortuous cerebral vasculature. As more neurologists are trained in their use and new training simulators proliferate, clot retrievers will likely retain their leading role in both routine and complex thrombectomy cases. Their integration with advanced catheter systems and imaging platforms also supports their long-term value proposition in the market.
Aspiration or suction-based thrombectomy devices are experiencing the fastest growth, largely due to the evolution of their tip designs, lumen diameter improvements, and ability to achieve rapid, atraumatic clot evacuation. These devices work by applying continuous or pulsatile suction to aspirate the clot directly into the catheter, offering a less complex alternative to stent retrievers.
Clinicians are increasingly using aspiration techniques either independently or in combination with retrievers, especially in scenarios where speed is paramount or vessel access is restricted. Furthermore, aspiration systems are being favored in outpatient and smaller center setups, where simpler device workflows and shorter procedural times are critical. As innovation focuses on optimizing vacuum efficiency and preventing clogging, aspiration systems are likely to outpace others in uptake, particularly in high-volume stroke centers.
Hospitals remain the leading end-use setting for neurothrombectomy devices due to their established surgical infrastructure, round-the-clock emergency capabilities, and in-house expertise. Most comprehensive stroke centers in the U.S. are located in large hospitals where advanced imaging, trained neurointerventionalists, and ICU support are readily available. These centers handle a high volume of stroke cases and are often the only facilities within their catchment areas capable of performing thrombectomy procedures.
Their access to capital for purchasing high-end angiography suites, stocking advanced devices, and conducting physician training makes them the primary customer base for device manufacturers. Additionally, the presence of robust hospital-based research and clinical trial networks contributes to early adoption of next-generation neurothrombectomy devices, reinforcing the hospital segment's leadership.
.webp)
Ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) represent the fastest-growing end-use segment, supported by regulatory shifts and payer interest in lower-cost intervention settings. ASCs are now beginning to integrate neurointerventional capabilities, especially in metropolitan regions, where outpatient treatment pathways are being optimized for stroke and TIA (transient ischemic attack) patients.
Driven by demand for convenience, rapid response, and efficient resource utilization, ASCs offer patients a faster return to normal activity, shorter procedural scheduling times, and greater flexibility. As neurothrombectomy technologies become more compact and user-friendly, their deployment in ASCs is expected to increase, particularly in partnership models with larger hospital systems or stroke networks.
The U.S. is uniquely positioned as the global epicenter of neurothrombectomy innovation due to a combination of factors: a well-funded healthcare system, high awareness of stroke symptoms, rapid EMS (Emergency Medical Services) response protocols, and robust reimbursement frameworks for neurointerventional procedures. National campaigns like “FAST” (Face, Arms, Speech, Time) have improved public knowledge, helping patients seek care within treatment windows.
Most major cities are now equipped with multiple designated stroke centers, while air ambulance networks support patient transport from rural areas. Federal agencies, such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH), actively fund stroke research and device innovation, giving rise to new startups and academic-industry collaborations. Private insurers have also evolved their policies to cover neurothrombectomy procedures extensively, recognizing their cost-effectiveness in reducing post-stroke disability and long-term rehabilitation costs.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. neurothrombectomy devices market
Product
End-use