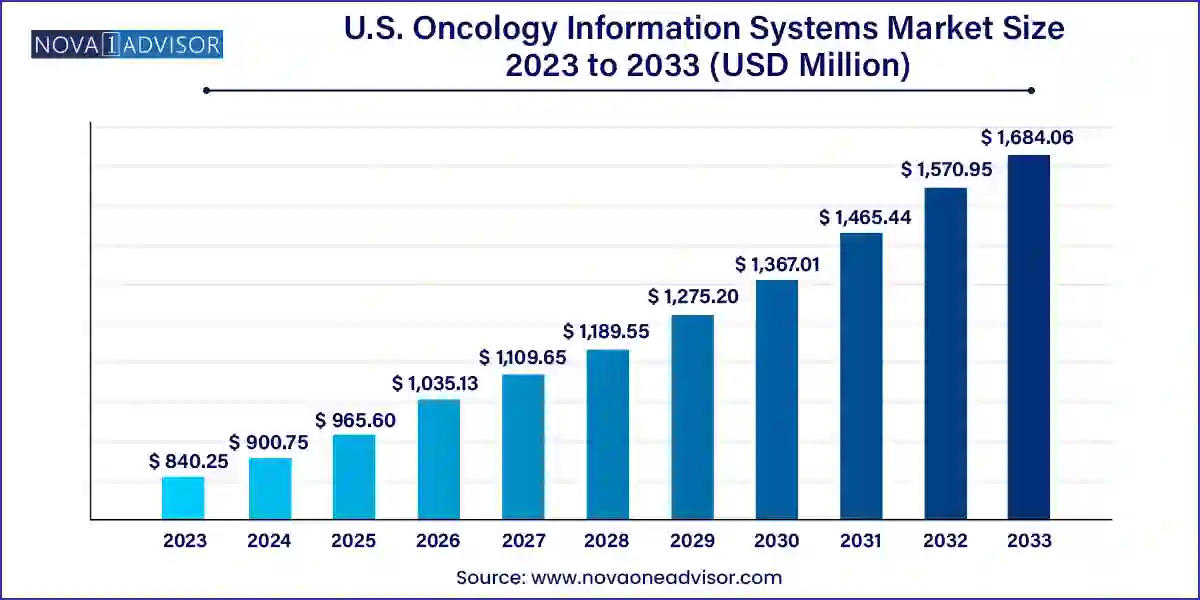
The U.S. oncology information systems market size was exhibited at USD 840.25 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 1,684.06 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. Oncology Information Systems (OIS) Market represents a critical element in the continuum of cancer care, playing a transformative role in how oncologists, radiologists, and surgeons manage patient data, coordinate care, and streamline decision-making. Oncology Information Systems are specialized healthcare IT solutions designed to collect, manage, and analyze patient information across the oncology treatment lifecycle. These systems support functions such as treatment planning, medical record documentation, clinical decision support, and patient engagement. With cancer remaining the second leading cause of death in the United States, the demand for efficient, integrated oncology care solutions is more urgent than ever.
In recent years, the U.S. healthcare landscape has shifted toward value-based care, prompting a surge in demand for health IT systems that offer not only automation and efficiency but also quality improvement. As hospitals and cancer centers strive to manage increasingly complex cases and multidisciplinary treatment plans, Oncology Information Systems are stepping in as vital enablers of coordination, compliance, and clinical excellence.
The adoption of OIS has grown in tandem with the increasing volume of cancer cases. According to the American Cancer Society, it is estimated that over 1.9 million new cancer cases will be diagnosed in the United States in 2025. Managing this caseload demands tools that enable real-time decision-making, automate documentation, support teleoncology, and integrate with electronic health records (EHRs) and diagnostic equipment. As a result, oncology information systems are no longer optional tools—they are foundational pillars in modern cancer care infrastructure.
Integration of AI and Predictive Analytics: AI-powered tools are being integrated into OIS to assist in predictive modeling, early cancer detection, treatment customization, and patient monitoring.
Cloud-Based Oncology Platforms: Cloud-based OIS solutions are witnessing increased adoption for their scalability, ease of access, and ability to facilitate remote monitoring and cross-site collaboration.
Interoperability with Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Enhanced interoperability with EHRs is becoming standard, ensuring smoother information flow between departments and reducing duplicate testing or errors.
Personalized Oncology Care Through Genomic Data: Integration of genomic data and biomarkers into OIS allows for more personalized treatment approaches based on patient-specific cancer biology.
Teleoncology Integration: Post-pandemic growth in telehealth has encouraged OIS providers to embed telemedicine features within their platforms to ensure continuity of care remotely.
Regulatory Compliance Enhancements: Vendors are increasingly focusing on making systems compliant with evolving regulatory frameworks like HIPAA and ONC certification requirements.
Automation in Radiation Planning: Automation tools are being built into treatment planning systems to reduce manual errors and enhance precision in radiation dosage.
Subscription-Based Software Models: The shift toward SaaS and subscription-based pricing models is making OIS more accessible for smaller oncology practices and clinics.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 900.75 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 1,684.06 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 7.2% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Products and Services, Application |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | Elekta AB; Accuray Incorporated; Varian Medical Systems(Siemens Healthineers); RaySearch Laboratories; Cerner Corporation (Oracle Corporation); BrainLab; Philips Healthcare; Prowess, Inc.; DOSIsoft S.A.; ViewRay Inc.; MIM Software and Flatiron |
The most prominent driver of the U.S. Oncology Information Systems market is the rising cancer burden and the increasing complexity of oncology treatment pathways. The cancer treatment journey typically involves multiple specialists, diagnostic evaluations, treatment planning, ongoing monitoring, and long-term follow-up. Managing this intricate continuum manually or through disjointed systems often leads to inefficiencies, errors, and suboptimal outcomes.
Oncology Information Systems centralize patient records, imaging results, treatment histories, and decision pathways into a unified platform, ensuring timely access and holistic visibility for providers. For example, in multi-modality care where a patient may receive chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation the coordination of care can be streamlined through an OIS, reducing redundancy and enhancing patient outcomes.
In a setting where an oncologist might be managing dozens of complex patients daily, an OIS equipped with clinical decision support can flag potential drug interactions, suggest evidence-based protocols, and automate documentation for insurance compliance. This improves both operational efficiency and patient safety, making OIS adoption a strategic necessity for modern oncology centers.
Despite the promise of improved care delivery, the high upfront costs associated with implementing oncology information systems remain a notable barrier to widespread adoption particularly among small to mid-sized oncology practices. These costs include not just the software licensing fees, but also expenses for hardware upgrades, integration with existing EHRs, staff training, data migration, and ongoing maintenance.
Moreover, implementing OIS requires specialized IT infrastructure and professionals familiar with oncology workflows and clinical informatics. Smaller clinics or rural cancer centers may lack both the capital and technical manpower to deploy and maintain such systems effectively. Interoperability issues and resistance from healthcare staff accustomed to traditional documentation methods further delay implementation timelines.
This financial and technical hurdle can lead to a digital divide in cancer care, with top-tier academic hospitals and urban cancer centers benefiting from state-of-the-art OIS while community-based facilities continue to rely on fragmented or outdated systems.
One of the most compelling opportunities in the U.S. Oncology Information Systems market lies in the integration of precision medicine and personalized oncology care. As treatment paradigms shift away from “one-size-fits-all” models toward targeted therapies based on genetic, proteomic, and biomarker data, the demand for OIS platforms capable of capturing and interpreting this data is surging.
For example, OIS platforms that can store genomic sequencing data and link it to actionable treatment guidelines will be critical in the decision-making process. Providers like Flatiron Health have already started leveraging real-world oncology data to inform treatment outcomes and guide therapy selection. Such capabilities not only improve treatment efficacy but also reduce adverse reactions by enabling tailored therapeutic regimens.
Furthermore, the incorporation of AI-driven insights from big data helps in identifying trends across similar patient populations, refining protocols, and supporting clinical trial recruitment. Companies that invest in building OIS modules supporting personalized care pathways are likely to benefit significantly from this growing niche.
Radiation oncology represents the largest application segment, largely due to the highly technical nature of radiation therapy that necessitates detailed treatment planning and dose management. Radiation oncology departments rely heavily on OIS platforms to ensure precision, from imaging-based simulation and contouring to plan generation and treatment delivery verification. Moreover, quality assurance modules embedded in OIS software reduce the risk of misadministration of radiation, thereby improving patient safety and treatment outcomes. Integration with imaging modalities like CT, PET, and MRI is essential for real-time planning adjustments, making OIS an operational backbone for radiation therapy centers.
Medical oncology is emerging as the fastest-growing application area, particularly as cancer drug therapy becomes more personalized and complex. Chemotherapy regimens, immunotherapies, and targeted biologics demand precise dosage calculations, toxicity tracking, and cycle monitoring tasks made more efficient by OIS platforms. With the rising use of outpatient infusion centers and increasing efforts toward reducing hospital stays, OIS systems enable continuity of care through real-time patient records, remote monitoring, and integrated adverse event alerts. Furthermore, many OIS platforms now incorporate AI tools for treatment outcome predictions, fueling growth in the medical oncology segment.
Software dominates the U.S. oncology information systems market, owing to its crucial role in data management, treatment planning, and workflow integration across oncology care teams. Within software, treatment planning systems are indispensable tools for radiation oncology departments. These systems allow oncologists to design personalized treatment protocols that target tumor sites with high precision while minimizing exposure to surrounding tissues. Advanced software enables 3D modeling, real-time dosage adjustment, and integration with linear accelerators, which is vital for ensuring treatment accuracy. Additionally, patient information systems allow for seamless communication across care teams and help in meeting regulatory documentation requirements, reducing human error and improving patient safety.
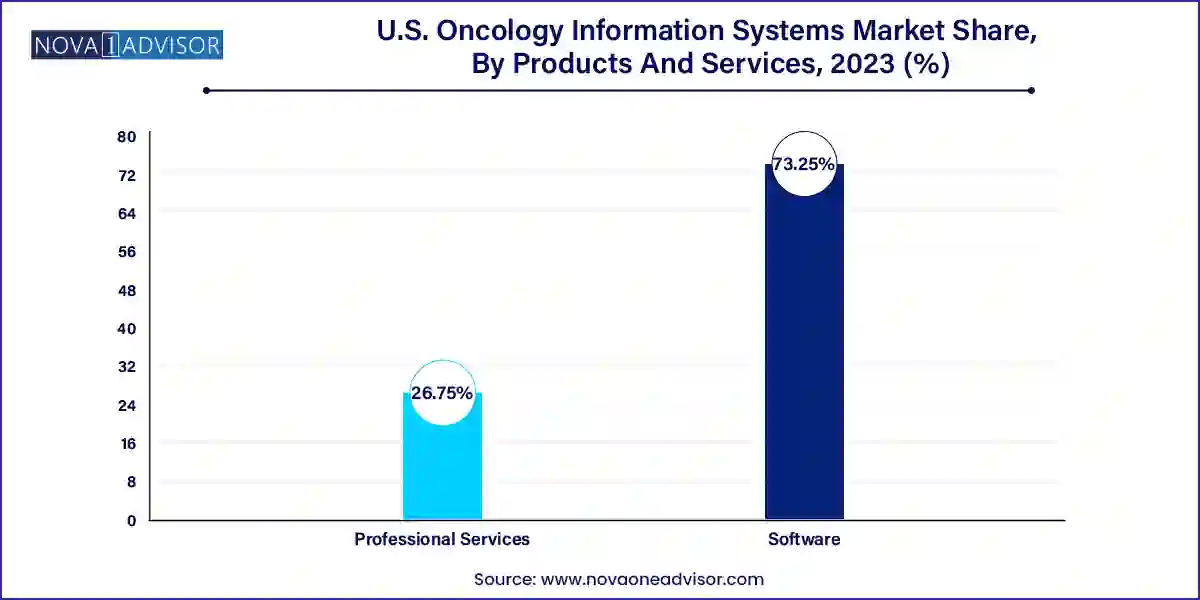
Professional services are the fastest-growing sub-segment in this category due to the increasing complexity of OIS deployment. Services such as system implementation, training, customization, and ongoing support are essential for the successful functioning of these platforms. Many hospitals rely on third-party experts to tailor the software to their specific workflows, manage system interoperability, and ensure data security. The surge in demand for cloud migrations and cybersecurity services in the post-COVID landscape has also accelerated the growth of professional services, as cancer centers seek to future-proof their IT infrastructure.
The United States, being one of the most technologically advanced healthcare markets globally, serves as both a demand generator and innovation hub for Oncology Information Systems. The presence of major cancer care networks such as MD Anderson Cancer Center, Memorial Sloan Kettering, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute drives demand for highly sophisticated OIS solutions that support integrated, multidisciplinary care. These institutions often act as early adopters, setting benchmarks for functionality, interoperability, and compliance.
Federal initiatives such as the Cancer Moonshot Program and 21st Century Cures Act have also played a pivotal role in encouraging digital health adoption, data sharing, and real-world evidence collection in oncology. The increased emphasis on value-based care models under Medicare and Medicaid has incentivized the use of analytics-driven OIS to demonstrate treatment outcomes, reduce readmission rates, and support clinical documentation for reimbursement.
Moreover, the U.S. is home to a growing ecosystem of oncology startups and health tech firms that are pushing the envelope in terms of cloud infrastructure, AI integration, and population health analytics—further enriching the market landscape. These conditions collectively create a highly fertile environment for OIS vendors to innovate and expand their offerings in the U.S. healthcare sector.
Varian, a Siemens Healthineers company (January 2025), launched ARIA OIS 18.5, featuring enhanced AI integration and a redesigned interface to improve usability for radiation oncology teams. The upgrade emphasizes automated documentation and compliance tracking.
Elekta (February 2025) announced partnerships with major U.S. cancer centers to pilot its next-generation Elekta ONE OIS platform, emphasizing interoperability with imaging and EHR systems and aiming to support personalized oncology workflows.
Flatiron Health (March 2025) rolled out a real-world evidence module within its oncology software to support clinical research and value-based care contracts, facilitating collaboration between academic centers and pharmaceutical companies.
Cerner (now part of Oracle Health, December 2024) began beta testing of oncology-specific updates to its PowerChart Oncology module, focusing on streamlined navigation for infusion therapy and improved cross-department communication tools.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. oncology information systems market
Products And Services
Application