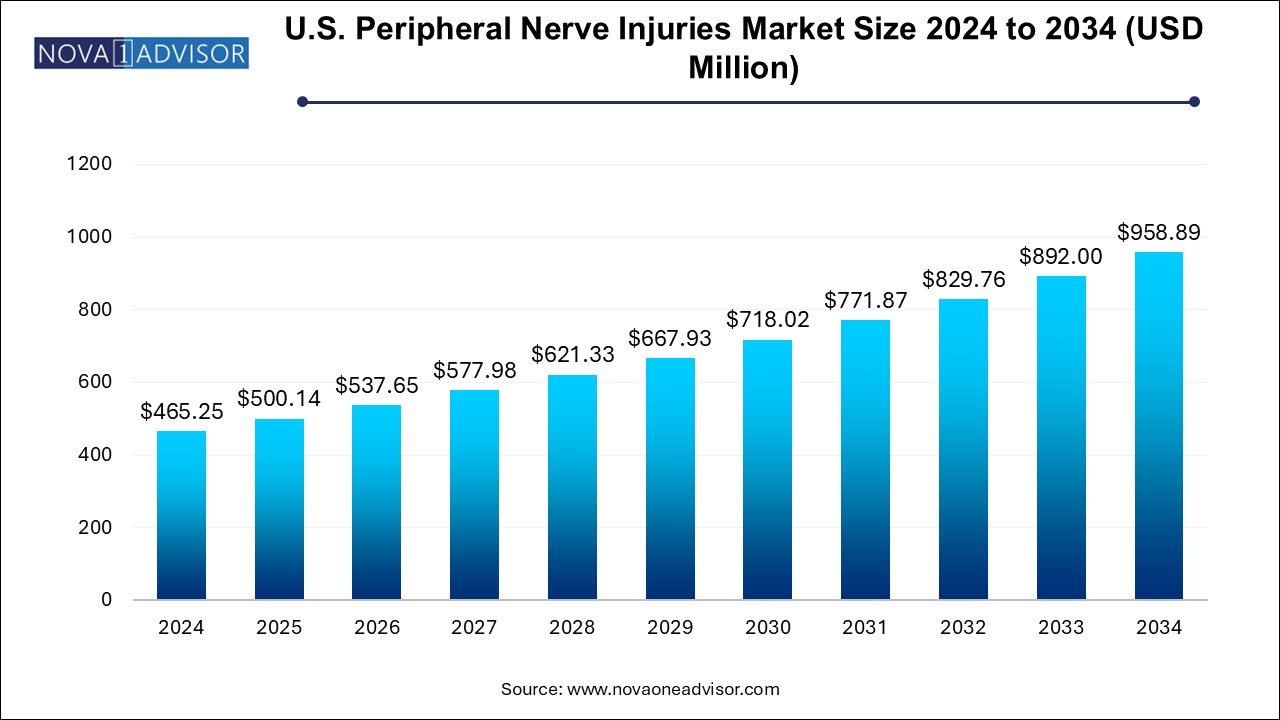
The U.S. peripheral nerve injuries market size was exhibited at USD 465.25 million in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 958.89 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period 2024 to 2034.
The U.S. Peripheral Nerve Injuries (PNI) Market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving segment of the broader neurotherapeutics and surgical devices landscape. Peripheral nerve injuries, often caused by trauma, surgical complications, repetitive strain, or medical conditions such as diabetes, result in partial or complete loss of motor, sensory, or autonomic functions. These injuries affect millions of Americans annually and demand specialized care that blends surgical intervention, regenerative technologies, and rehabilitation.
In the United States, peripheral nerve injuries range from minor compression syndromes (like carpal tunnel syndrome) to complex traumatic brachial plexus injuries. The increase in vehicular accidents, sports injuries, and surgical complications is contributing to a consistent rise in demand for effective therapeutic solutions. Meanwhile, advancements in regenerative medicine, including stem cell-based nerve regeneration, and innovations in bioengineered materials are transforming the treatment paradigm.
Surgical techniques such as direct nerve repair, nerve grafting (autografts and allografts), internal neurolysis, and neurorrhaphy remain gold standards. However, biomaterials like nerve conduits, nerve protectors, nerve wraps, and nerve connectors are increasingly being adopted due to their lower donor site morbidity and ability to facilitate axonal regrowth.
The U.S. healthcare system’s robust infrastructure, coupled with significant investment in medical R&D and the presence of leading medtech companies, makes it a hub for PNI treatment innovation. With increasing awareness, favorable reimbursement frameworks, and growing demand for improved functional recovery post-injury, the market is projected to witness steady growth through 2030 and beyond.
Rise of Bioengineered Nerve Repair Devices: Bioabsorbable nerve conduits, connectors, and wraps are replacing traditional nerve grafts in many clinical settings.
Advancements in Stem Cell Therapy: Stem-cell-based nerve regeneration is moving from experimental to clinical stages, offering new hope for chronic injury management.
Minimally Invasive Nerve Repair Techniques: Surgeons and medical device firms are developing techniques that reduce recovery time and scarring.
Digital Intraoperative Nerve Monitoring: Electrophysiological mapping and nerve stimulators are being integrated into surgical procedures to reduce intraoperative risk.
Increased Use of Allografts: Processed human allografts offer an off-the-shelf alternative to autografts, reducing operative time and complications.
Carpal Tunnel Release Innovations: Endoscopic and ultrasonic techniques are gaining ground as less invasive options for common entrapment neuropathies.
Integration of AI in Surgical Planning: AI and machine learning are being used to predict recovery outcomes and optimize surgical strategies.
Bundled Care Models and Reimbursement Incentives: Value-based care initiatives are encouraging bundled payments and long-term recovery tracking in nerve injury cases.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 500.14 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 958.89 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 7.5% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Product/therapies, Surgery, Application, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Key Companies Profiled | Axogen Corporation; Stryker/Collagen Matrix/Polyganics BV; Integra Lifesciences Corporation; Toyobo Co., Ltd.; Alafair Bioscience; Synovis Micro Companies Alliance, Inc. (Baxter International, Inc.) |
A major driver of the U.S. Peripheral Nerve Injuries Market is the rising incidence of traumatic and iatrogenic nerve damage, spurred by vehicular accidents, sports injuries, combat-related trauma, and postoperative complications. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, peripheral nerve injuries affect over 200,000 people in the U.S. each year, many of whom experience functional impairment for months or even years.
Surgical interventions such as hip and knee replacements, hernia repairs, and cancer resections carry an inherent risk of nerve damage, especially in complex cases or re-operations. Additionally, chronic compression syndromes due to repetitive strain—common among workers in construction, technology, and manufacturing are contributing to the case volume. As the population ages and life expectancy increases, the likelihood of comorbid conditions (e.g., diabetes) that heighten nerve injury risk is also on the rise.
This escalating demand has created a pressing need for faster, more effective, and minimally invasive nerve repair technologies. The U.S. market, with its broad reimbursement infrastructure and presence of specialized neuro-orthopedic centers, is at the forefront of responding to this need with innovation and clinical excellence.
A notable restraint in the market is the limited access to regenerative therapies and challenges surrounding insurance reimbursement for novel treatment approaches. While technologies like stem cell therapy, processed nerve allografts, and nerve conduits offer promising outcomes, they often come with high costs and inconsistent payer support.
Many regenerative products are still considered investigational or fall outside traditional reimbursement codes, especially when used off-label. Furthermore, smaller hospitals and outpatient centers may lack the surgical expertise or capital to adopt newer, costlier technologies. This creates disparities in care, with advanced treatments concentrated in urban academic medical centers or private institutions.
Additionally, patients with complex injuries may require multiple surgeries and long-term rehabilitation, which further strains insurer willingness to cover comprehensive nerve repair. These financial and systemic barriers limit equitable access to state-of-the-art solutions, hindering broader market penetration.
A compelling opportunity lies in the expansion of outpatient surgical centers and integrated rehabilitation models for nerve injury management. Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs), which offer same-day surgical procedures at lower costs, are increasingly equipped with minimally invasive tools and intraoperative imaging systems suitable for peripheral nerve repairs.
As Medicare and private payers push for site-of-service optimization, procedures like carpal tunnel release, superficial nerve decompressions, and small-scale graft repairs are increasingly being shifted to ASCs. This shift not only reduces costs but improves patient convenience and operational efficiency.
Moreover, integrated recovery models that combine surgery, physical therapy, electrostimulation, and digital recovery tracking are being piloted across health systems. These models enhance functional outcomes and reduce readmission rates—making them attractive under value-based care programs. Companies and providers that build solutions for outpatient and post-acute care environments are well-positioned to capitalize on this opportunity.
Nerve grafting remains the dominant therapy in the peripheral nerve injury treatment landscape, especially for larger gap repairs where tensionless coaptation is not possible. Autografts, harvested from the patient’s own body (often the sural nerve), are considered the gold standard due to their immunocompatibility and intrinsic regenerative properties. Despite donor site morbidity and increased operative time, many surgeons continue to favor autografts for their high success rates, especially in complex brachial plexus injuries.
However, biomaterial-based therapies are the fastest-growing segment, driven by innovations in synthetic and biological scaffolds that promote axonal regrowth without requiring donor tissue. Nerve conduits made of collagen or polyglycolic acid, nerve wraps, and connectors are increasingly preferred for short-gap injuries or adjunctive repair. Companies like Axogen, Polyganics, and Integra LifeSciences have developed FDA-approved products that offer reliable alternatives to autografts, with reduced surgical morbidity and improved workflow efficiency. These biomaterials are gaining acceptance not just in academic centers but also among private surgeons and outpatient centers.
Carpal tunnel release is the most commonly performed surgical intervention within the peripheral nerve repair market, accounting for a significant share of procedural volume. As one of the most prevalent entrapment neuropathies, carpal tunnel syndrome affects over 3 million people annually in the U.S., and surgical release remains a highly effective treatment when conservative management fails. Both open and minimally invasive endoscopic approaches are widely used, with the latter gaining favor for faster recovery and reduced scarring.
Stem cell therapy is emerging as the fastest-growing surgical adjunct, particularly in academic trials and advanced clinical settings. Autologous mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), bone marrow-derived stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are being explored to enhance axonal regeneration, modulate inflammation, and improve long-term outcomes. While currently limited to pilot studies and experimental use, stem cell-enhanced nerve conduits and injectables are showing early promise in accelerating functional recovery. Companies that can validate efficacy through clinical trials and navigate regulatory pathways may unlock a transformative new segment.
Upper extremities dominate the market by application, encompassing high-incidence areas such as the hands, arms, and shoulders. These regions are more frequently involved in traumatic injuries, repetitive stress syndromes, and iatrogenic damage. Surgeries like ulnar nerve decompression, digital nerve repairs, and brachial plexus reconstruction account for the majority of nerve injury cases. Moreover, the functional priority of the upper limbs in daily life often drives earlier diagnosis, referral, and intervention.
Lower extremity nerve repair is gaining momentum, fueled by increased recognition of sports-related injuries, diabetic neuropathies, and surgical complications involving the peroneal, tibial, or femoral nerves. Peripheral neuropathies affecting gait and balance significantly reduce quality of life in older adults and diabetics. As podiatric surgery and orthopedic trauma programs adopt biomaterials and advanced imaging, the demand for targeted lower limb nerve interventions is growing. Additionally, emerging interest in neuromodulation for chronic pain in lower extremities supports future market growth in this segment.
Hospitals remain the primary setting for nerve injury treatment, particularly for complex trauma cases and surgeries requiring microsurgical expertise. Tertiary hospitals and academic medical centers lead in volume for brachial plexus repair, tumor-related neurolysis, and research trials involving nerve regeneration. These institutions have the necessary infrastructure microscopes, imaging, specialist teams to manage high-risk or multi-organ injury cases.
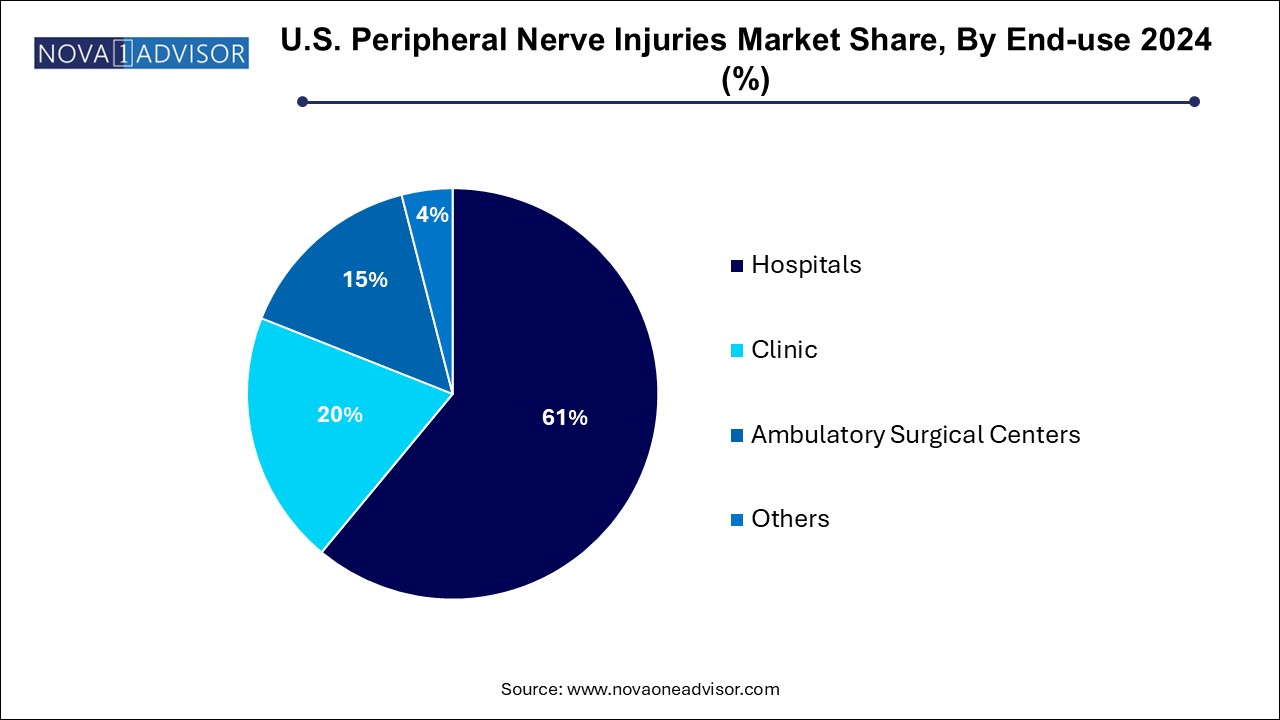
Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs) are the fastest-growing end-use segment, thanks to the migration of elective and minimally invasive procedures to outpatient settings. Many ASCs now perform carpal tunnel release, nerve decompression, and short-gap repairs using bioresorbable conduits. Their cost-effectiveness, shorter wait times, and ease of scheduling are attractive to both patients and insurers. Companies developing portable nerve repair kits and minimally invasive tools tailored for ASC use are tapping into a high-growth opportunity.
In the United States, the peripheral nerve injuries market is characterized by high clinical demand, regulatory rigor, and innovation-friendly infrastructure. The U.S. FDA has established clear pathways for Class II and Class III devices, fostering rapid yet safe commercialization of nerve repair products. Furthermore, Medicare and commercial insurers provide structured reimbursement for many PNI procedures, particularly when performed in credentialed settings.
The country’s high incidence of traumatic injuries, aging population, and rising diabetes prevalence contribute to consistent case volume. Military veterans, athletes, and workers in high-risk jobs are especially prone to nerve injuries, making U.S. demand both demographically and occupationally diverse.
The presence of specialized centers such as the Mayo Clinic, Johns Hopkins, and Cleveland Clinic also supports adoption of new therapies and devices. These institutions often lead multicenter trials and act as innovation incubators. As outpatient infrastructure expands and digital health merges with surgical planning, the U.S. is poised to remain the global leader in nerve injury treatment innovation and utilization.
March 2024 – Axonics Inc. announced the FDA clearance of a new peripheral nerve repair implant designed for ulnar and radial nerve regeneration, with early clinical trials showing a 25% improvement in sensory recovery.
February 2024 – Checkpoint Surgical launched its next-generation nerve stimulator for intraoperative use, allowing surgeons to map and protect nerves during complex repairs.
January 2024 – Polyganics began U.S. distribution of its synthetic nerve conduit, Neurocap®, targeting short-gap digital nerve injuries through ASC partnerships.
December 2023 – Integra LifeSciences published real-world data demonstrating superior outcomes using its collagen-based nerve wrap in post-operative scarring reduction and axon guidance.
October 2023 – ReNerve Bio initiated a Phase 2 trial for its stem-cell-enhanced nerve conduit designed for peroneal nerve injuries in diabetic neuropathy patients.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. peripheral nerve injuries market
Products/Therapies
Surgery
Application
End-use