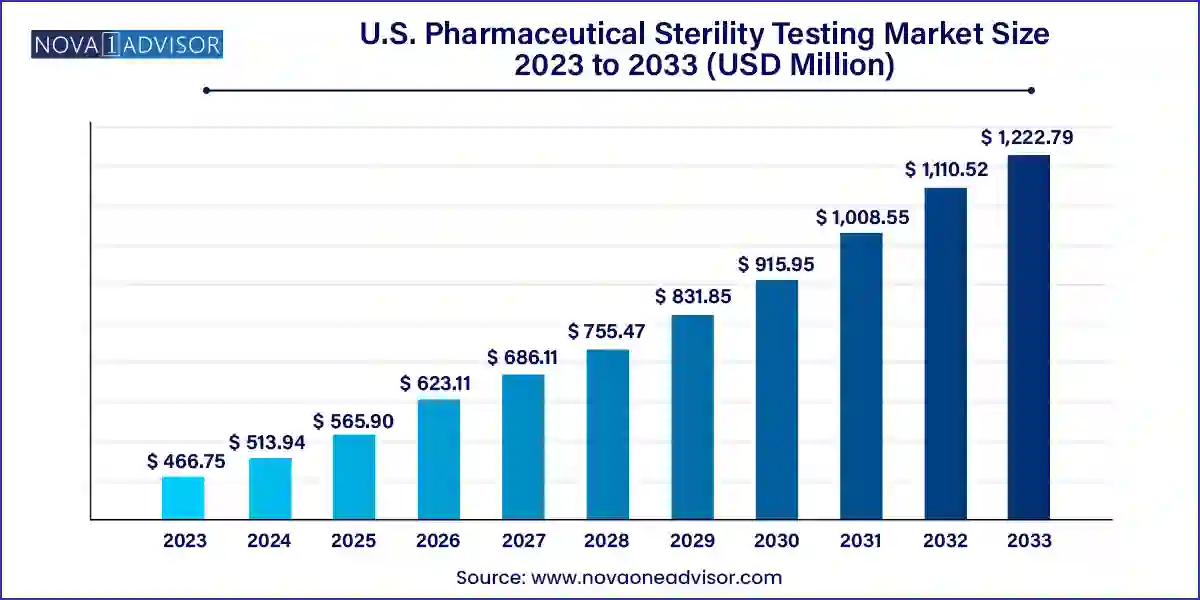
The U.S. pharmaceutical sterility testing market size was exhibited at USD 466.75 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 1,222.79 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.11% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. Pharmaceutical Sterility Testing Market serves as a cornerstone in the broader pharmaceutical quality assurance ecosystem. As one of the most regulated healthcare markets globally, the United States mandates rigorous sterility testing protocols to ensure that pharmaceuticals, biologics, and medical devices are free of viable contaminating microorganisms. The rising demand for complex biologics, personalized therapies, and parenteral drugs has significantly increased the volume and complexity of sterility testing procedures in the country.
Sterility testing is not merely a compliance function it is a vital quality control measure that protects patients from sepsis, toxic shock syndrome, and other potentially fatal infections. Whether in the manufacturing of injectable drugs, ophthalmic preparations, or implantable medical devices, sterility assurance is a non-negotiable parameter. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have laid down stringent guidelines for conducting sterility and microbial limit tests.
With a growing number of pharmaceutical product recalls linked to microbial contamination, sterility testing has gained greater visibility at the boardroom level within pharmaceutical and biopharma companies. Outsourcing, automation, and the integration of rapid microbiological methods (RMM) are key dynamics shaping this market. Moreover, the emergence of cell and gene therapies, which often require aseptic processing, has further expanded the need for validated sterility tests that are both compliant and adaptive to complex formulations.
Shift Toward Rapid Sterility Testing Technologies: Adoption of rapid microbiological methods (RMM), including ATP bioluminescence and PCR-based testing, is accelerating for faster product release.
Growth of Outsourced Testing Models: A growing number of pharmaceutical firms are outsourcing sterility testing to specialized contract research organizations (CROs) and third-party labs.
Automation in Sterility Testing Labs: Use of robotic sample handlers and closed system isolators is reducing human error and contamination risks.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Evolving Guidelines: USP <71> sterility testing standards and FDA audits have become more rigorous, prompting investment in compliance infrastructure.
Rise in Biopharmaceutical Product Launches: The expansion of monoclonal antibodies, biosimilars, and gene therapies has created a surge in sterility testing for complex biologics.
Sterility Testing in Personalized Medicine: Small-batch, patient-specific drugs require sterility verification within compressed timeframes.
Increased Focus on Environmental Monitoring Integration: Sterility testing is being bundled with cleanroom monitoring and risk-based validation systems.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 513.94 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 1,222.79 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 10.11% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Type, Product Type, Test Type, Sample, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope | U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled | SGS SA; Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings; Boston Analytical; Charles River Laboratories; Pacific Biolabs; STERIS; Pace Analytical; Nelson Laboratories, LLC; Infinity Laboratories; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. |
A powerful driver of the U.S. sterility testing market is the escalating demand for biologics and sterile injectable formulations. Unlike oral drugs, injectables bypass the body’s natural barriers, making sterility paramount. The rise of biopharmaceuticals—particularly monoclonal antibodies, cell therapies, vaccines, and gene-modified products—requires meticulous aseptic manufacturing and comprehensive sterility testing. According to industry data, over 60% of the pipeline drugs in the U.S. are biologics or parenterals, indicating long-term demand for sterility testing infrastructure.
Further, the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for swift and accurate sterility testing for large-scale vaccine production. Even beyond the pandemic, injectable therapies for oncology, autoimmune diseases, and diabetes are becoming mainstream, necessitating rigorous sterility validations. This has led companies like Pfizer, Amgen, and Moderna to either invest in internal microbiology labs or partner with leading CROs specializing in microbial quality control.
Despite its critical role, sterility testing is fraught with high operational costs, stringent regulatory requirements, and complex validation procedures. Unlike chemical assays, microbiological tests must prove not just accuracy but also environmental reliability and reproducibility over time. Validation for sterility testing methods—especially for new product classes like biologics or cell therapies—often requires repeated testing, stability studies, and contamination control validation, which can take months and significantly delay time to market.
In addition, laboratories must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, which include investment in cleanrooms, isolators, HEPA filtration, gowning protocols, and personnel training. Failing an FDA audit or validation test could result in product recalls, reputational damage, or even manufacturing shutdowns. Smaller biotech firms often lack the infrastructure or expertise, making them reliant on costly outsourcing services. This makes cost and operational burden a real barrier, especially for early-stage companies or startups operating under tight funding constraints.
An emerging opportunity in the U.S. market lies in the integration of AI and digital tools in sterility testing environments. Artificial intelligence can be used to track microbial growth patterns, predict contamination risks, and automate decision-making in environmental monitoring. Machine vision tools are increasingly being explored to detect early signs of turbidity or contamination in sterility testing samples thus reducing the time-to-detection compared to manual inspection.
Companies are also digitizing their Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), allowing real-time audit trails, chain-of-custody verification, and remote inspection capabilities all crucial for FDA compliance. For instance, cloud-based sterility management tools now allow contract testing labs and pharmaceutical clients to collaborate more efficiently on test results and deviations. With predictive analytics, manufacturers can forecast microbial loads and proactively adjust their cleanroom operations. These innovations promise to make sterility testing not just a reactive quality control step, but a predictive and preventive pillar of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Outsourcing dominated the U.S. pharmaceutical sterility testing market, especially among small to mid-sized pharma and biopharma companies. These firms often lack the infrastructure to maintain validated cleanroom environments and prefer to partner with contract research organizations (CROs) that offer specialized microbiological services. Outsourcing also allows for faster testing turnaround, scalability, and easier regulatory documentation. Key CROs in the space, such as Eurofins, Charles River Laboratories, and Nelson Labs, offer full-service sterility testing suites compliant with USP <71>, <85>, and FDA cGMP regulations.
Conversely, in-house sterility testing is the fastest-growing sub-segment, particularly among large pharmaceutical companies and vertically integrated biopharma firms. Giants like Pfizer and Merck have invested heavily in internal sterility testing labs to gain more control over product release timelines and intellectual property. Moreover, companies developing personalized therapies or autologous cell-based products are building in-house capacity to comply with short testing windows and patient-specific workflows. While outsourcing remains cost-effective, the rising need for speed and IP security is driving a shift toward internal capability development.
Kits and reagents accounted for the largest share in 2024, as they are essential consumables used across both in-house and outsourced testing environments. From nutrient media to sterility indicators, filtration membranes, and rinse solutions, kits form the backbone of repeatable testing protocols. These products offer standardization, validation, and compliance with USP guidelines. Companies like Merck KGaA (MilliporeSigma) and Thermo Fisher Scientific dominate this category, supplying validated kits for membrane filtration and direct inoculation tests.
Services, however, are the fastest-growing product type, driven by the increasing demand for third-party expertise, particularly in sterility and bacterial endotoxin testing. These services include method development, validation, and lot release testing. As FDA scrutiny grows around aseptic manufacturing, service providers offer not just test execution but also documentation support, deviation investigation, and audit preparation. This “testing-as-a-service” model is especially attractive for emerging biotechs and CDMOs that need scalable yet compliant sterility assurance.
Sterility testing using membrane filtration dominated this segment, as it is the preferred method for aqueous and filterable products. This technique allows for greater sensitivity and is more applicable to parenterals, eye drops, and biologics, which require comprehensive sterility validation. Membrane filtration is particularly effective in detecting low levels of contamination and is easily adapted for both manual and automated workflows. The method also allows for rinse testing and simulation studies, making it highly versatile for pharmaceutical manufacturers.
Bioburden testing is the fastest-growing test type, due to its growing relevance in upstream manufacturing and environmental monitoring. Bioburden tests are increasingly used as predictive tools to assess raw material microbial loads, which helps in setting sterilization parameters and validating cleanroom practices. These tests are crucial for biologics, where product viability is often sensitive to excessive heat or radiation. With biopharma firms seeking to minimize over-processing, bioburden assessments offer a balance between safety and efficacy.
Pharmaceuticals dominated the market in 2024, driven by the vast volume of small-molecule and generic injectables that must pass sterility testing as part of batch release. Parenteral drugs, IV fluids, ophthalmics, and surgical irrigations are subject to FDA sterility requirements before they can be released to the market. Companies like Teva, Sandoz, and Baxter have extensive sterility testing pipelines for both new and legacy pharmaceutical products.
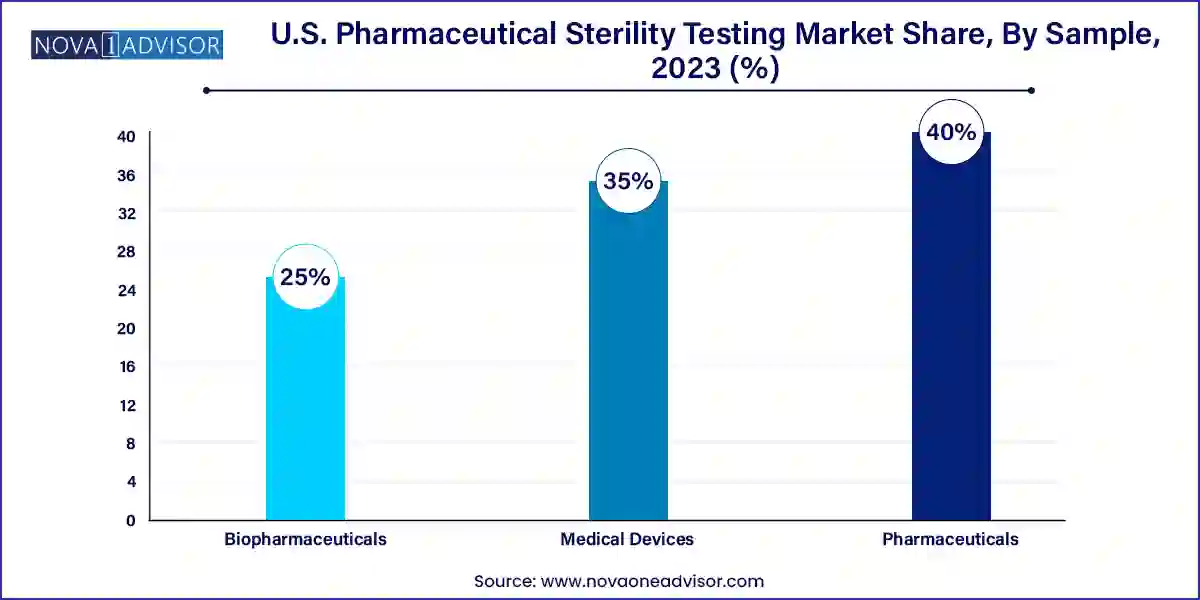
Biopharmaceuticals are the fastest-growing sample category, due to the complex and contamination-sensitive nature of biologics, including monoclonal antibodies, gene therapies, and autologous cell products. Biologics manufacturing involves multiple aseptic processing stages, each requiring sterility validation. The emergence of personalized therapies such as CAR-T cells has created demand for ultra-rapid, patient-specific sterility tests that can be turned around within days, not weeks.
Pharmaceutical companies dominated the end-use segment, owing to the large-scale production of injectables, biologics, and ophthalmic solutions that require rigorous sterility testing for every batch. These companies either conduct in-house testing or work closely with contract labs to meet FDA compliance and ensure product integrity. The high volume of products and the frequency of audits make sterility testing a critical line item in pharmaceutical quality control budgets.
Medical device companies are emerging as the fastest-growing end-users, as devices such as surgical implants, catheters, and IV sets are subject to sterility standards before being marketed. The FDA’s increased focus on combination products (drug-device hybrids) has further elevated sterility testing requirements for device manufacturers. Whether for FDA 510(k) clearance or PMA submissions, companies are expanding their microbiology testing capabilities or outsourcing to firms specializing in ISO 11737 sterility protocols.
In the United States, the sterility testing landscape is shaped by a unique confluence of regulatory rigor, advanced manufacturing infrastructure, and a diversified pharmaceutical pipeline. The U.S. FDA mandates sterility testing under Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21 Part 211, supported by USP <71> and <85>. From Boston and San Francisco to Raleigh-Durham and San Diego, the country hosts biotechnology clusters with both in-house and outsourced sterility capabilities.
Several pharmaceutical hubs like New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Indiana host not only drug manufacturers but also testing facilities, CDMOs, and reagent suppliers. Additionally, the rise in federal funding for biopharma innovation through BARDA and NIH grants is encouraging sterility validation investments, particularly for pandemic preparedness and national defense stockpiles. In the context of increasing clinical trial activity and global drug supply chains, the U.S. remains the epicenter of sterility testing innovation, quality assurance, and regulation.
In March 2025, Charles River Laboratories announced the expansion of its sterility testing capabilities in its Ohio facility to accommodate biopharma clients engaged in cell and gene therapy development.
In February 2025, MilliporeSigma (Merck KGaA) launched its new Steritest™ Symbio Pump, an automated system designed to streamline membrane filtration sterility testing with integrated data management.
In January 2025, Nelson Labs received FDA recognition for its automated endotoxin detection platform, reducing manual intervention and improving test reproducibility for parenteral products.
In December 2024, Thermo Fisher Scientific introduced a digital platform integrating sterility testing data with quality management systems (QMS) for pharmaceutical manufacturers.
In November 2024, Eurofins Scientific acquired a specialized microbiology CRO in Pennsylvania, expanding its sterility and bioburden testing footprint in the U.S. market.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2023 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. pharmaceutical sterility testing market
Type
Product Type
Test Type
Sample
End-use