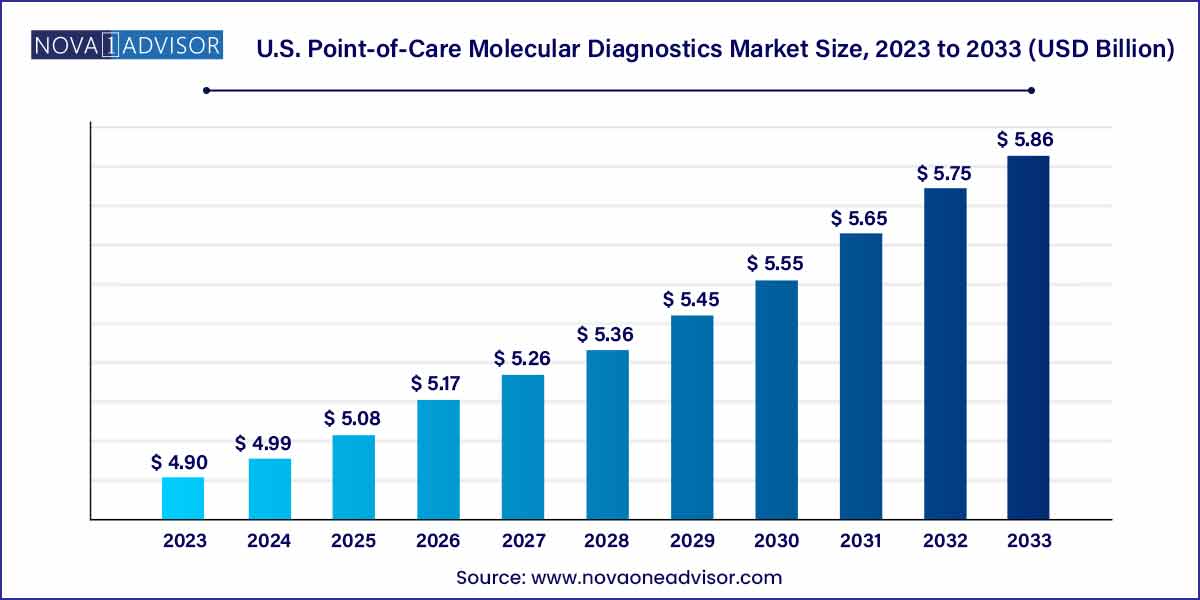
The U.S. point-of-care molecular diagnostics market size was estimated at USD 4.90 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 5.86 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 1.8% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. Point-of-Care (POC) Molecular Diagnostics Market is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by the increasing need for rapid, accurate, and decentralized diagnostic solutions. Point-of-care molecular diagnostics (POC-MDx) combine the speed of traditional POC testing with the sensitivity and specificity of molecular techniques such as PCR and genetic sequencing. These platforms allow for the on-site detection of pathogens, genetic markers, and disease biomarkers, often in under an hour, thereby eliminating delays associated with centralized laboratory testing.
The U.S. healthcare system is increasingly focusing on early detection, rapid treatment initiation, and decentralized patient care. This shift is particularly relevant in infectious diseases, oncology, prenatal care, and chronic disease monitoring—areas where POC molecular tests offer tremendous clinical and economic value. The success of rapid COVID-19 molecular testing, particularly at pharmacies and urgent care centers, demonstrated the scalability and public acceptance of POC-MDx platforms.
Major players in this space include Abbott, Cepheid (Danaher), Roche, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and a host of emerging startups developing compact, cartridge-based platforms. The U.S. market is supported by a favorable regulatory landscape, ongoing FDA approvals for CLIA-waived molecular assays, and growing demand from both public health agencies and retail health providers.
Miniaturization and Portability: Development of handheld, battery-operated molecular testing devices for use in rural clinics, home care, and emergency services.
Integration with Digital Health Platforms: Cloud-connected devices enabling remote data analysis, results sharing, and longitudinal patient tracking.
Multiplex Assay Expansion: Simultaneous testing for multiple pathogens (e.g., flu/COVID/RSV panels) is becoming standard in respiratory diagnostics.
CLIA-Waived Molecular Test Surge: A growing number of POC-MDx tests are receiving CLIA-waived status, enabling wider usage in pharmacies and clinics.
Retail Health Channel Adoption: Pharmacies like CVS, Walgreens, and Walmart Health are offering molecular diagnostic services using compact platforms.
Decentralized Oncology Testing: Liquid biopsy and gene expression POC platforms are emerging for decentralized cancer screening.
Rise of At-Home Molecular Diagnostics: FDA-authorized kits for influenza, COVID-19, and other conditions are enabling consumer-driven testing.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 4.99 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 5.86 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 1.8% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Test location, application type, technology, end-use, states |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Abbott Laboratories; QIAGEN; Danaher; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; BD; F. Hoffman-La Roche AG; Charles River Laboratories; Quest Diagnostics Incorporated; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; Hologic Inc.; Agilent Technologies, Inc. |
A key driver of the U.S. POC-MDx market is the increasing demand for rapid diagnosis of infectious diseases a need that was dramatically highlighted during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rapid and accurate detection is critical for diseases like influenza, RSV, strep throat, and tuberculosis, where immediate treatment decisions impact outcomes and transmission risk.
Molecular diagnostics at the point of care offer superior sensitivity and specificity compared to antigen-based tests, which have higher false negative rates. The ability to confirm a diagnosis within 30–60 minutes using a nasal swab or blood sample is game-changing in settings like emergency rooms, urgent care centers, nursing homes, and schools.
This shift is not limited to COVID-19. Influenza and sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, are increasingly diagnosed through rapid molecular assays, improving treatment timelines and reducing follow-up burdens. The CDC’s emphasis on test-and-treat protocols has further fueled adoption across public health channels.
Despite their clinical value, POC molecular diagnostics often come with higher costs than traditional lab-based methods or antigen tests. Cartridge-based molecular platforms, while convenient, can be expensive on a per-test basis, and their upfront equipment costs may deter adoption by small clinics and home healthcare providers.
Additionally, reimbursement remains inconsistent, particularly for newer or multiplexed tests. Payers may not fully reimburse newer assays unless they are bundled into larger diagnostic protocols or recommended by authoritative bodies like the CDC or USPSTF. Coding and billing variations across payers and state programs further complicate matters, especially in assisted living and long-term care environments.
Unless pricing models become more accessible or test costs are offset by improved health outcomes and shorter treatment cycles reimbursement concerns may limit broader market penetration.
The most exciting opportunity lies in the expansion of home-based molecular diagnostics, which blend consumer convenience with clinical accuracy. Post-pandemic, consumers are more willing to test themselves at home, especially for respiratory infections and chronic disease markers.
Companies like Lucira Health and Cue Health have introduced FDA-authorized molecular test kits for at-home use. These tests are smartphone-integrated, offer digital results within 30 minutes, and can be used to initiate telehealth consults. As FDA policies become more flexible, more applications—such as STD testing, prenatal screening, and pharmacogenomics—are moving into the home-testing model.
Moreover, partnerships with online pharmacies and telemedicine providers are creating ecosystems where a test, diagnosis, and prescription can occur entirely outside traditional clinical settings, enhancing access and convenience for the U.S. population.
POC (point-of-care) settings dominate the market, including decentralized hospital labs, urgent care, physician offices, and pharmacies. These locations require rapid, actionable results that allow healthcare providers to make immediate clinical decisions. Molecular diagnostics in POC settings are especially vital during flu seasons or STD outbreaks, enabling real-time response. Companies like Cepheid have positioned themselves well with modular testing platforms like GeneXpert, commonly deployed in hospitals and walk-in centers.
OTC (over-the-counter) testing is the fastest-growing segment, catalyzed by consumer demand and policy support during the COVID-19 era. Home molecular tests are being approved for influenza, COVID-19, and RSV. The entry of consumer tech firms into the diagnostics space for example, Amazon’s acquisition of One Medical and entry into at-home health points to broader consumerization of molecular diagnostics in the coming years.
Infectious diseases dominate the application landscape, accounting for the largest share of POC molecular diagnostics. Within this segment, Influenza/Flu POC and RSV POC are seeing robust demand, particularly with the emergence of co-circulation of viruses and the need for differential diagnosis. HIV POC and TB POC testing continue to play a major role in public health initiatives, especially in underserved communities. The use of multiplex respiratory panels (e.g., COVID-19, flu, RSV) has gained traction among pediatricians and geriatric care providers.
Oncology is the fastest-growing application, with decentralized testing platforms for certain biomarkers entering clinical workflows. Liquid biopsies, circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), and gene expression analysis are being developed for use in oncology clinics and eventually in home care. POC platforms capable of detecting EGFR mutations or HER2 expressions in near-patient settings can radically reduce the time from diagnosis to treatment planning.
PCR-based molecular diagnostics remain the backbone of the U.S. POC testing market. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) offers the highest sensitivity and specificity and is widely used for respiratory viruses, STIs, and TB. Portable real-time PCR devices like Abbott’s ID NOW and Roche’s Cobas Liat are gold standards in clinical POC settings.
Genetic sequencing-based tests are emerging as the fastest-growing technology, particularly in oncology, pharmacogenomics, and prenatal diagnostics. Portable NGS platforms and CRISPR-based molecular diagnostics are also gaining attention for rapid mutation detection, drug resistance monitoring, and precision medicine applications. As sequencing costs decline, their integration into routine POC workflows becomes increasingly feasible.
Hospitals dominate the end-use landscape, especially emergency departments, surgical units, and inpatient wards that require fast diagnostic confirmation for critical cases. Most major U.S. hospitals have integrated POC-MDx into their workflows, especially for sepsis, respiratory infections, and hospital-acquired infections like MRSA.
Home-care and assisted living healthcare facilities are the fastest-growing end-use segments, driven by aging demographics and the need for decentralized chronic disease management. Molecular tests for influenza, UTIs, and pneumonia in these settings can reduce hospital transfers and improve patient outcomes. Portable testing devices and telehealth platforms further enhance these settings by supporting remote diagnostic workflows.
The U.S. point-of-care molecular diagnostics market is the global leader in terms of innovation, regulatory infrastructure, and adoption. The presence of key global players, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and a proactive public health system enables faster uptake of new diagnostic technologies.
U.S. policy agencies such as the FDA, CMS, and CDC actively shape the regulatory and reimbursement landscape, often granting Emergency Use Authorizations (EUAs) and CLIA-waivers to accelerate the deployment of critical diagnostics. Public-private partnerships have further advanced the market, such as NIH’s RADx initiative that funded innovative diagnostic startups during the pandemic.
In addition to hospitals and clinical labs, the U.S. has a well-developed retail healthcare model, allowing for walk-in testing at pharmacies and clinics—an ecosystem that is rapidly integrating POC-MDx platforms. Telemedicine's rise has further reinforced the demand for rapid and remote diagnostics, creating a fertile environment for innovation.
April 2025 – Cepheid received FDA approval for its new multiplex test for COVID-19, influenza A/B, and RSV, compatible with its GeneXpert system.
March 2025 – Cue Health announced the expansion of its at-home molecular testing platform to include influenza and strep throat, in addition to COVID-19.
February 2025 – Lucira Health launched a new CRISPR-based at-home test kit for HPV detection, receiving Breakthrough Device designation from the FDA.
January 2025 – Abbott unveiled a next-gen version of its ID NOW platform with a broader test menu, targeting emergency rooms and urgent care centers.
December 2024 – Roche Diagnostics partnered with a major U.S. pharmacy chain to pilot decentralized POC-MDx kiosks for respiratory and STD testing.
Some of the key players operating in the U.S. point-of-care molecular diagnostics market include Abbott Laboratories; QIAGEN; F. Hoffman-La Roche Ltd; bioMerieux; and BD. Numerous key players are undertaking strategic initiatives such as expansion, product introductions, mergers, and acquisitions, while also focusing on increasing product reach in the U.S. Several market participants are investing in research and development initiatives, making the market susceptible to further growth.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. Point-of-Care Molecular Diagnostics market.
By Test Location
By Application Type
By Technology
By End-use