U.S. Regenerative Medicine Market Size and Growth
The U.S. regenerative medicine market size was valued at USD 17.19 billion in 2023 and is projected to surpass around USD 80.74 billion by 2033, registering a CAGR of 16.73% over the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
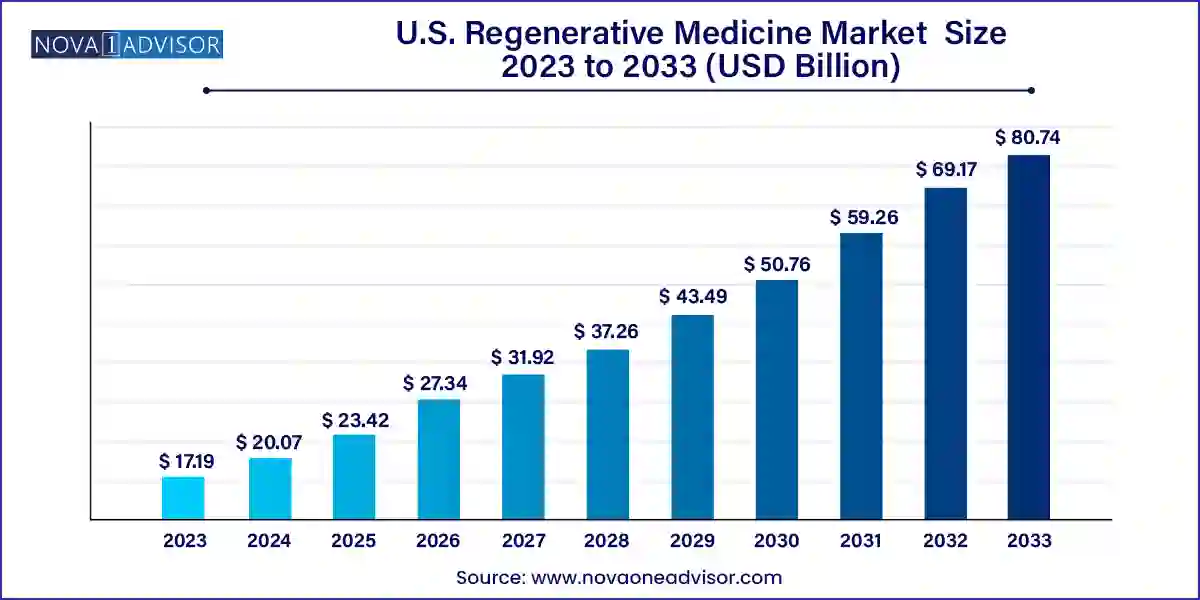
U.S. Regenerative Medicine Market Key Takeaways
- The oncology segment held the largest market share of 31.15% in 2023.
- The cardiovascular segment is expected to witness a considerable CAGR during the forecast period
- The therapeutics segment held the largest market share of 75.19% in 2023.
- The bank segment is expected to witness the fastest CAGR from 2024 to 2033
Market Overview
The U.S. regenerative medicine market represents one of the most dynamic and transformative sectors in modern healthcare. Regenerative medicine encompasses a spectrum of approaches that seek to repair, replace, or regenerate human cells, tissues, or organs to restore or establish normal function. This includes therapies utilizing stem cells, gene editing, tissue engineering, and cell-based immunotherapies, often in combination with biomaterials, growth factors, and supportive technologies.
In the United States, regenerative medicine has evolved from experimental science to clinical application. It plays a critical role in treating degenerative diseases, trauma injuries, genetic disorders, and even age-related conditions. The country's strong biomedical research ecosystem, patient access to clinical trials, favorable regulatory environment, and significant investment capital have helped position the U.S. at the forefront of global regenerative medicine innovation.
The field has seen remarkable progress across multiple fronts—from stem cell-based interventions in orthopedics and dermatology to CAR-T cell therapies for hematologic cancers and CRISPR-based gene editing tools entering clinical phases. Moreover, regenerative medicine supports minimally invasive approaches, reducing recovery times, improving long-term outcomes, and aligning with patient preferences for less disruptive treatments.
Backed by the FDA’s Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation and the 21st Century Cures Act, companies developing novel regenerative treatments benefit from accelerated review pathways. At the same time, large pharmaceutical and biotech firms are actively acquiring or partnering with regenerative startups, signaling sustained commercial interest and market expansion potential.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Growing adoption of autologous and allogenic stem cell therapies in orthopedics, wound healing, and cardiovascular disorders.
-
Rapid commercialization of gene therapies, especially for rare genetic and oncology indications.
-
Increased use of cell-based immunotherapies like CAR-T and TCR therapies in hematologic malignancies.
-
Expansion of regenerative dermatological products for burns, chronic wounds, and aesthetic treatments.
-
Integration of AI and 3D bioprinting to enhance tissue engineering and scaffold design.
-
Establishment of biobanks to store stem cells, tissues, and umbilical cord blood for future personalized treatments.
-
Surge in musculoskeletal applications driven by aging population and rising prevalence of osteoarthritis.
-
Public-private partnerships and NIH-funded consortia to accelerate regenerative medicine research.
U.S. Regenerative Medicine Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 20.07 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 80.74 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 16.73% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, therapeutic category |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
AstraZeneca plc; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Integra Lifesciences Corp.; Astellas Pharma, Inc.; Cook Biotech, Inc.; Bayer AG; Pfizer, Inc.; Merck KGaA; Abbott; Vericel Corp.; Novartis AG; GlaxoSmithKline (GSK). |
Market Driver: Expanding Pipeline of Regenerative Therapies and Clinical Trials
A major driver of the U.S. regenerative medicine market is the expanding pipeline of regenerative therapeutics entering clinical development and commercialization. As of 2024, the FDA is overseeing over 1,000 investigational new drug (IND) applications for regenerative treatments, including cell-based therapies, gene therapies, and tissue-engineered products. This reflects a broadening base of evidence supporting the safety and efficacy of these interventions.
For example, autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI) for cartilage repair, stem cell injections for spinal cord injuries, and gene-modified immune cell therapies like CAR-T have gained both regulatory momentum and real-world validation. The ability to modify the genetic or cellular basis of disease, rather than simply manage symptoms, is shifting the treatment paradigm. Furthermore, FDA programs such as RMAT and Breakthrough Therapy designation have allowed developers to fast-track promising candidates through regulatory milestones. This rapid movement through clinical stages has fueled investment and stimulated adoption of regenerative solutions in both hospital settings and outpatient care.
Market Restraint: High Manufacturing Costs and Supply Chain Complexities
Despite promising clinical progress, a major challenge restraining the U.S. regenerative medicine market is the high cost and complexity associated with manufacturing, storage, and distribution. Unlike conventional pharmaceuticals, regenerative products—particularly those involving live cells require specialized production environments, including GMP-compliant cleanrooms, validated bioreactors, and cold-chain logistics systems.
Manufacturing autologous therapies requires patient-specific workflows, making them labor-intensive and difficult to scale. Even allogenic products, while more scalable, face hurdles in cell sourcing, expansion, and long-term preservation. Moreover, quality control, sterility assurance, and regulatory documentation must be rigorously maintained throughout the manufacturing pipeline.
These constraints not only increase cost per dose often exceeding $300,000 for certain gene therapies but also limit availability across geographic regions. While technological innovation is underway to address scalability and automation, cost-efficiency remains a barrier to broader accessibility and reimbursement adoption.
Market Opportunity: Integration of Regenerative Medicine into Mainstream Clinical Practice
A key opportunity for the U.S. regenerative medicine market lies in the growing integration of regenerative technologies into mainstream clinical practice, especially in orthopedics, wound care, ophthalmology, and cardiology. Physicians are increasingly adopting stem cell injections, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and gene-enhanced tissue grafts as adjuncts to traditional surgeries or pharmaceutical regimens.
For instance, orthopedic surgeons are using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to treat degenerative joint conditions and support tissue repair after trauma. Cardiologists are investigating stem cell-based regeneration following myocardial infarctions. Dermatologists are exploring skin regeneration for burn victims and patients with diabetic ulcers. These non-systemic, localized applications offer faster recovery, fewer side effects, and higher patient satisfaction.
The continued development of outpatient-friendly regenerative protocols and CMS reimbursement support will enhance the accessibility of these technologies. This creates fertile ground for innovation in tools, services, and supporting platforms that bridge clinical delivery with regenerative science.
U.S. Regenerative Medicine Market By Therapeutic Category Insights
Musculoskeletal applications were the leading therapeutic category in 2024, as the aging U.S. population drives a significant increase in degenerative joint conditions, spinal disorders, and sports injuries. Orthopedic surgeons are using autologous stem cells, PRP injections, and cell-enhanced scaffolds to promote healing and tissue regeneration. These therapies often reduce the need for invasive surgery and are compatible with outpatient delivery models, increasing their appeal across healthcare providers.
Oncology is the fastest-growing therapeutic category, fueled by the rapid adoption of cell-based immunotherapies such as CAR-T and T-cell receptor (TCR) therapies. These regenerative immunotherapies are increasingly being used in hematological malignancies and are expanding into solid tumors. The development of "off-the-shelf" allogenic cell therapies and the integration of gene editing for immune modulation are pushing oncology to the forefront of regenerative medicine. Companies are investing heavily in scalable GMP facilities, clinical trial infrastructure, and advanced analytics to support the deployment of these next-generation treatments.
U.S. Regenerative Medicine Market By Product Insights
Therapeutics dominated the U.S. regenerative medicine market in 2024, with cell- and gene-based therapies contributing the majority share of total market revenue. Within therapeutics, stem cell and progenitor cell-based treatments are widely used for orthopedic, dermatological, and cardiovascular conditions. These include both autologous and allogenic formats. The increasing number of FDA-approved therapies and clinical trial activities in cell-based immunotherapies such as CAR-T and NK cell therapies has further fueled demand for therapeutic regenerative solutions.
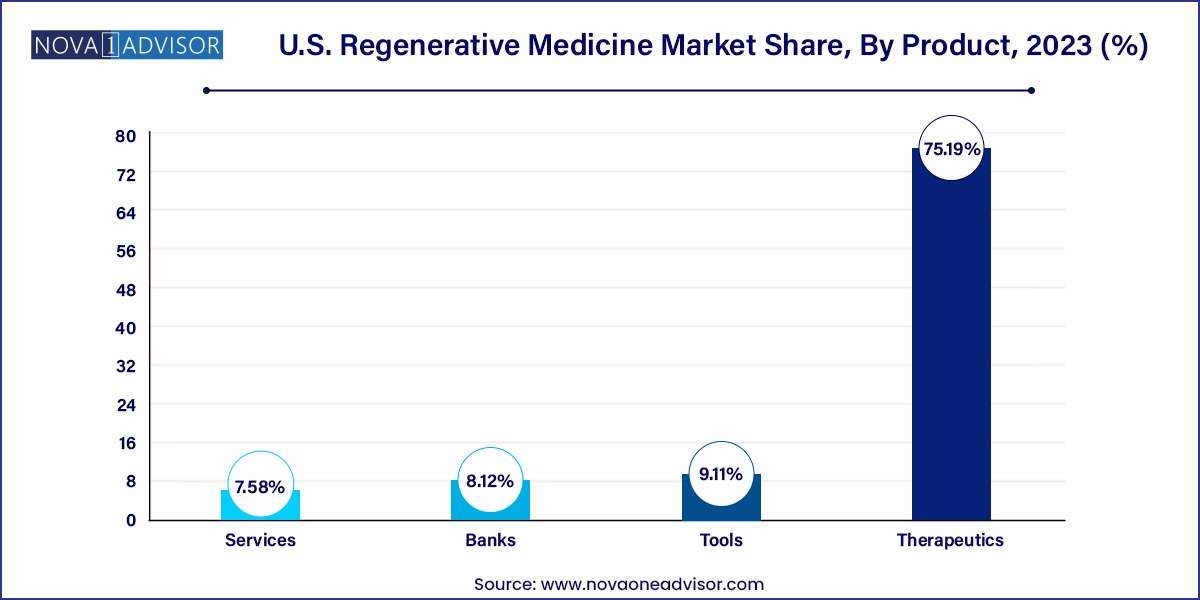
Gene therapies are the fastest-growing subsegment, supported by technological breakthroughs in CRISPR and viral vector delivery. Recent FDA approvals of therapies like Zolgensma for spinal muscular atrophy and Luxturna for retinal dystrophy have set the stage for a new wave of commercial gene therapies. Their ability to deliver long-term or curative outcomes makes them attractive despite their high upfront costs. Several U.S.-based biotech firms are scaling up their in-house and outsourced capabilities for plasmid DNA, AAV, and lentiviral vector manufacturing to meet growing demand.
Services are also witnessing steady growth, particularly for CDMO partnerships, logistics, and cold chain management tailored to regenerative products. Companies offering end-to-end services including donor screening, cell harvesting, expansion, cryopreservation, and GMP manufacturing are playing an increasingly critical role in enabling biotech firms to commercialize complex regenerative products.
Country-Level Analysis
The United States is the global epicenter of regenerative medicine research, development, and commercialization. Its leadership is underpinned by the presence of top-tier academic institutions, world-renowned hospitals, biopharma hubs in regions like Boston, San Diego, and San Francisco, and proactive regulatory agencies like the FDA.
The U.S. has fostered innovation through public-private partnerships, including funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Department of Defense (DoD), and patient advocacy foundations. The 21st Century Cures Act and Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation have accelerated access to promising therapies, promoting an environment conducive to innovation.
Additionally, the country hosts some of the most advanced CDMOs, cell banks, and logistics providers focused on regenerative therapeutics. This supply chain integration has enabled faster transition from lab to clinic. Growing consumer awareness, favorable reimbursement pathways (especially for life-saving gene therapies), and digital platforms supporting remote monitoring and therapy delivery are helping embed regenerative medicine into the broader U.S. healthcare system.
U.S. Regenerative Medicine Market Recent Developments
-
March 2025 – Vertex Pharmaceuticals reported positive Phase II trial results for its gene therapy candidate targeting Type 1 diabetes, using a CRISPR-based platform in collaboration with CRISPR Therapeutics.
-
February 2025 – BlueRock Therapeutics (a Bayer subsidiary) initiated Phase I trials for its induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived therapy for Parkinson’s disease in U.S. patients.
-
January 2025 – Astellas Pharma completed its acquisition of Iveric Bio to expand its U.S. pipeline in regenerative ophthalmology, targeting age-related macular degeneration.
-
December 2024 – Sana Biotechnology announced the expansion of its Seattle-based manufacturing facility to support commercial-scale gene and cell therapy production.
-
November 2024 – Fate Therapeutics began clinical testing of a novel off-the-shelf NK cell therapy for hematologic malignancies, marking a shift toward scalable allogeneic platforms.
U.S. Regenerative Medicine Market Top Key Companies:
- AstraZeneca plc
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Integra Lifesciences Corp.
- Astellas Pharma, Inc.
- Cook Biotech, Inc.
- Bayer AG
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Merck KGaA
- Abbott
- Vericel Corp.
- Novartis AG
- GlaxoSmithKline (GSK)
U.S. Regenerative Medicine Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. Regenerative Medicine market.
By Product
- Therapeutics
- Primary Cell-based Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Musculoskeletal
- Surgical
- Dental
- Others
- Stem Cell & Progenitor Cell-based Therapeutics
- Autologous
- Allogenic
- Others
- Cell-based Immunotherapies
- Gene Therapies
- Tools
- Banks
- Services
By Therapeutic Category
- Dermatology
- Musculoskeletal
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Oncology
- Cardiovascular
- Ophthalmology
- Others


