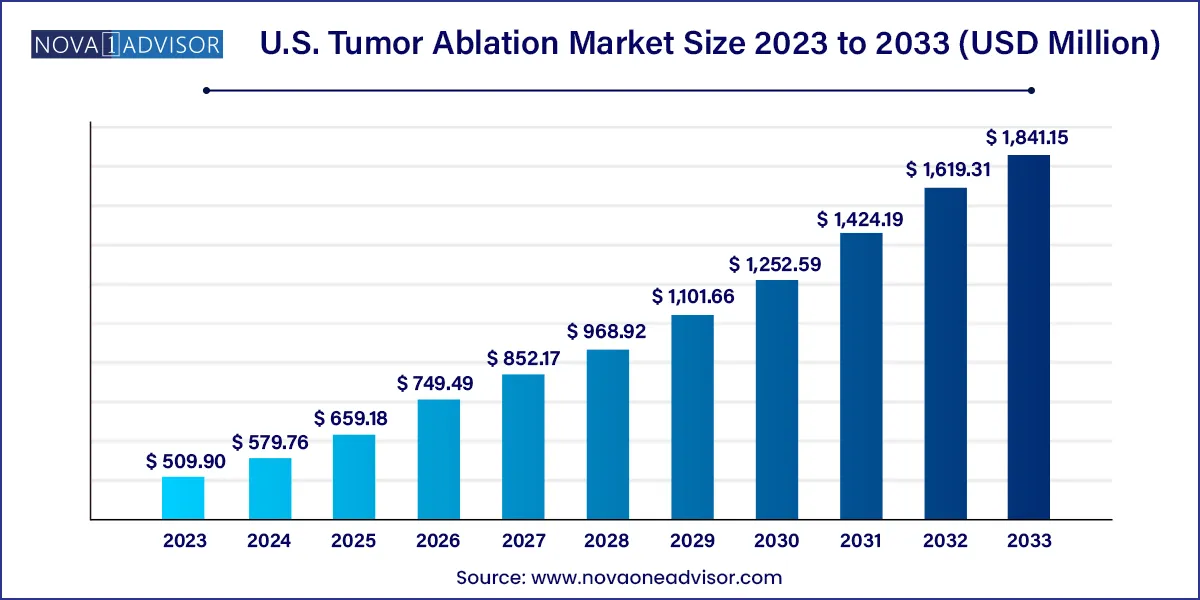
The U.S. tumor ablation market size was valued at USD 509.90 million in 2023 and is projected to surpass around USD 1,841.15 million by 2033, registering a CAGR of 13.7% over the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. tumor ablation market has emerged as a vital component in the fight against cancer, offering minimally invasive and targeted therapies for tumor management. Tumor ablation, which involves the destruction of cancerous cells through localized thermal or chemical methods, has gained substantial traction across various oncology departments. This popularity stems from its precision, lower complication rates, reduced hospital stays, and ability to treat inoperable or hard-to-reach tumors. In a healthcare environment that prioritizes cost-effectiveness, patient recovery, and advanced treatment options, tumor ablation has positioned itself as a technology of choice in both primary and adjuvant cancer care settings.
As cancer incidence continues to climb in the U.S., the need for innovative treatment approaches has intensified. According to the American Cancer Society, approximately 2 million new cancer cases are expected in the U.S. in 2025, with rising prevalence particularly in liver, kidney, prostate, and lung cancers key application areas for ablation technologies. Given these rising numbers and the growing elderly population with multiple comorbidities who may not be suitable candidates for surgery or chemotherapy, tumor ablation represents a promising alternative.
The U.S. also benefits from an advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher adoption of novel technologies, and favorable reimbursement policies for outpatient and minimally invasive procedures. Government and private funding are fueling ongoing research and clinical trials, aiming to enhance the efficacy of ablation devices and broaden their application across oncology indications. Furthermore, growing investments from med-tech giants and increasing merger and acquisition activities are accelerating innovation, thereby expanding access to next-generation ablation solutions.
Shift Toward Minimally Invasive Cancer Therapies: Ablation offers quicker recovery, reduced scarring, and fewer complications compared to traditional surgery.
Rise of Outpatient Oncology Procedures: Reimbursement and convenience drive adoption of ablation in ambulatory surgery centers and outpatient departments.
Adoption of Robotic-Assisted Ablation: Integration with navigation systems enhances precision, especially in laparoscopic and percutaneous procedures.
Emergence of Microwave Ablation (MWA) as a Preferred Technology: MWA provides faster heating and treats larger tumors compared to radiofrequency.
Application Expansion to Non-Traditional Tumors: Increasing research on ablation for breast, bone, and pancreatic cancers.
Hybrid Imaging Techniques Integration: Use of CT, MRI, and ultrasound-guided navigation for real-time visualization during ablation.
Focus on Personalized Oncology: Ablation being incorporated into personalized, multimodal cancer therapy regimens.
Private and Public Research Funding Boost: NIH and industry-sponsored trials exploring ablation efficacy in early-stage and metastatic cancers.
Growth in Geriatric Oncology: Older patients who are unfit for surgery increasingly opting for ablation treatments.
Improved Thermal Monitoring and Feedback: Smart probes and thermal sensors enhance safety and efficiency during ablation procedures.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 579.76 million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 1,841.15 million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 13.7% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Technology, treatment, application |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Medtronic; Boston Scientific Corp.; Johnson & Johnson Service Inc. (Ethicon, Inc.); AngioDynamics; Bioventus Inc. (Misonix Inc.); EDAP TMS; Chongqing Haifu Medical Technology Co., Ltd.; Mermaid Medical; HealthTronics, Inc.; H.S. Hospital Service S.p.A. |
One of the primary drivers of the U.S. tumor ablation market is the rapidly growing cancer population, paired with a notable preference for less invasive treatments. The increase in diagnosis of early-stage cancers, largely due to advancements in imaging and screening programs, has led clinicians to seek alternative modalities that offer effective tumor control with minimal trauma. Tumor ablation is uniquely positioned in this regard, offering targeted tumor destruction without extensive tissue removal.
For instance, patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), who may not qualify for surgery due to liver dysfunction or age, benefit from radiofrequency or microwave ablation. According to clinical data, these methods yield comparable survival rates to surgical resection in select patient groups. In addition, the fast turnaround time, often as short as a day, makes it attractive to both patients and healthcare providers aiming to reduce hospitalization costs and improve turnover rates in oncology departments.
Despite its growing adoption, one of the key restraints in the tumor ablation market is its limited efficacy for treating larger or multiple tumors. Most ablation techniques are currently recommended for tumors smaller than 3–5 cm in diameter. Treating larger lesions often requires multiple overlapping ablations or combination therapy, which increases the complexity, duration, and risk of the procedure. In addition, ablation may not achieve complete necrosis in larger tumors, increasing the risk of recurrence.
This limitation poses a significant barrier, especially for cancers such as renal cell carcinoma or metastatic colorectal cancer where larger tumor sizes are common at diagnosis. Moreover, tumor proximity to vital structures such as bile ducts, blood vessels, or nerves can limit the application of thermal ablation, as it may damage surrounding tissues. While advances in non-thermal techniques such as irreversible electroporation (IRE) offer hope, their adoption remains limited due to high costs and insufficient long-term data.
A compelling growth opportunity in the U.S. tumor ablation market lies in its integration with precision medicine and artificial intelligence (AI)-guided oncology. As healthcare shifts toward tailored treatment protocols based on a patient’s genomic profile, ablation is being increasingly incorporated into multi-disciplinary care pathways. AI and machine learning tools now assist in identifying ideal ablation candidates by analyzing tumor size, location, heat-sink effect, and risk factors.
Advanced software platforms are also being used to simulate heat distribution during thermal ablation or electric field spread in IRE procedures, ensuring optimal tumor coverage. For example, AI-guided image segmentation is helping radiologists define tumor margins more accurately during liver or lung ablation procedures. Additionally, ablation is increasingly being paired with real-time biopsy and molecular diagnostics, enabling simultaneous treatment and tissue characterization. These innovations are paving the way for more precise, efficient, and personalized ablation therapies.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) dominated the technology segment in the U.S. tumor ablation market due to its long-standing clinical use, established safety profile, and affordability. RFA devices generate localized heat to destroy tumor cells and are commonly used for liver, kidney, and lung cancers. Given its widespread availability in hospitals and ambulatory centers, RFA continues to be the go-to technology, especially in smaller community hospitals. Moreover, robust data from over two decades of use has cemented its role in standard treatment guidelines across multiple cancer types.
On the other hand, microwave ablation (MWA) is emerging as the fastest growing segment, driven by its superior performance characteristics. MWA delivers higher temperatures, treats larger tumors, and requires shorter procedure times compared to RFA. Recent device innovations such as multi-probe systems and cooled-shaft designs have enhanced procedural safety and flexibility. The increasing use of MWA in outpatient liver and lung tumor cases illustrates its rising prominence. Companies like Medtronic and Johnson & Johnson have also released next-generation MWA systems, supporting its rapid adoption.
Percutaneous ablation procedures currently dominate the treatment segment, reflecting the shift toward minimally invasive, image-guided interventions. These procedures are usually performed under local anesthesia using CT or ultrasound guidance, reducing patient risk and enabling same-day discharge. Commonly used for liver and kidney tumors, percutaneous ablation avoids open incisions and is increasingly preferred for older or frail patients. The growing use of fusion imaging systems and robotic needle placement has also improved precision and reduced complication rates.
However, laparoscopic ablation is growing at a faster pace, especially in cases where direct visualization of tumor sites offers improved safety such as in certain colorectal liver metastases or gynecologic cancers. Laparoscopic approaches combine the benefits of minimal invasion with the ability to perform adjunctive procedures, such as biopsies or lymph node removal. Surgeons are also using ablation during laparoscopic resections as part of a hybrid technique to ensure complete tumor destruction, further boosting growth in this segment.
Liver cancer remains the leading application segment in the U.S. tumor ablation market, owing to the high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastases. Ablation is often recommended for early-stage liver tumors and in patients who are not suitable for resection or transplantation. Techniques like RFA and MWA are widely used due to the liver’s accessibility and tolerance to thermal injury. Recent studies have shown ablation to be a cost-effective first-line therapy for small solitary liver lesions, supporting its continued dominance.
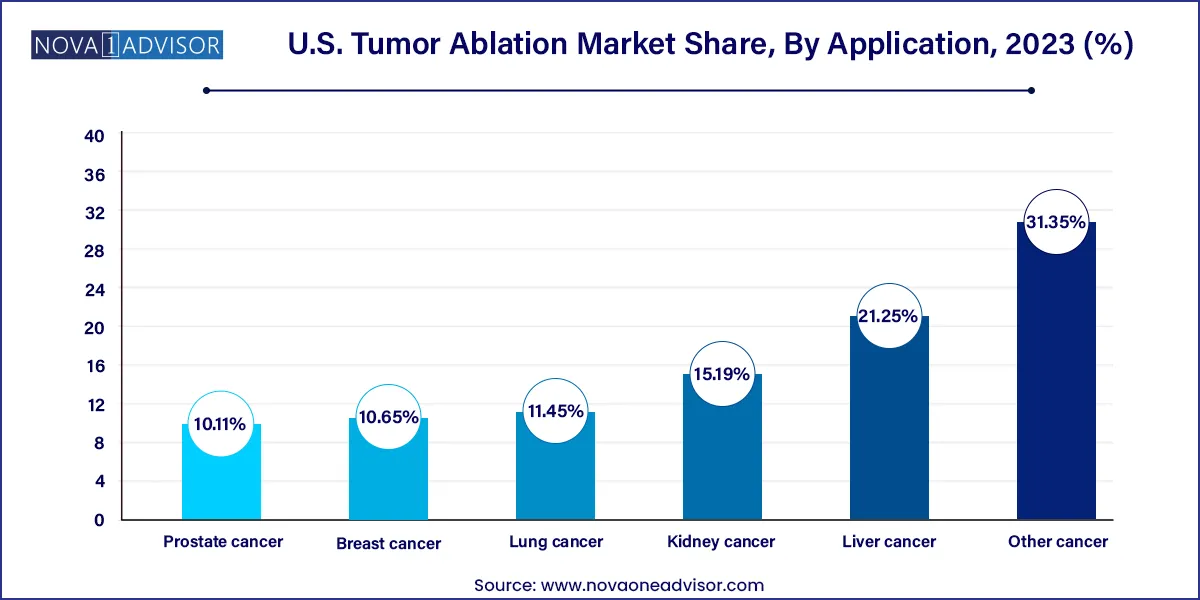
In contrast, lung cancer is the fastest-growing application area, with tumor ablation offering a non-surgical option for patients with inoperable or metastatic lung tumors. The availability of high-resolution CT imaging, advancements in percutaneous access tools, and the reduced need for general anesthesia are enabling ablation in pulmonary oncology. Microwave and cryoablation technologies are particularly suitable for lung tissue due to their ability to operate under air-filled conditions. The growing elderly population and smoking-related morbidities are expected to fuel further growth in this segment.
In the U.S., the tumor ablation market is driven by a combination of technological leadership, high cancer awareness, and specialized oncology infrastructure. States such as California, Texas, New York, and Florida see the highest procedure volumes due to the concentration of cancer centers, academic hospitals, and med-tech hubs. Many of these states also participate in NIH-funded clinical trials, accelerating the adoption of novel ablation platforms.
Moreover, Medicare and private insurers are offering favorable reimbursement for outpatient ablation procedures, which is particularly influencing practice patterns in ambulatory care settings. The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and integrated health systems like Kaiser Permanente have also incorporated ablation into their standard cancer treatment protocols, especially for liver and kidney cancer patients.
Telemedicine integration and remote ablation planning, supported by cloud-based imaging review systems, are further enhancing accessibility across rural and underserved regions. Coupled with the growing availability of mobile ablation units and remote robotic-assisted technologies, the U.S. market stands as a model of innovation and accessibility in oncologic ablation.
March 2025: Medtronic received FDA clearance for its next-generation Emprint™ Ablation System with Thermosphere™ technology, enhancing microwave ablation control for liver tumors.
February 2025: Boston Scientific announced a new clinical study in collaboration with MD Anderson Cancer Center evaluating cryoablation for metastatic lung tumors.
January 2025: AngioDynamics expanded its oncology portfolio with the launch of the NanoKnife® 4.0 IRE system, featuring improved real-time feedback for prostate and pancreatic tumor ablation.
December 2024: Johnson & Johnson’s Ethicon unit launched a clinical trial for combining microwave ablation with immunotherapy in breast cancer patients.
November 2024: IceCure Medical received U.S. FDA Breakthrough Device designation for its ProSense™ Cryoablation System targeting early-stage breast cancer in high-risk patients.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. Tumor Ablation market.
By Technology
By Treatment
By Application