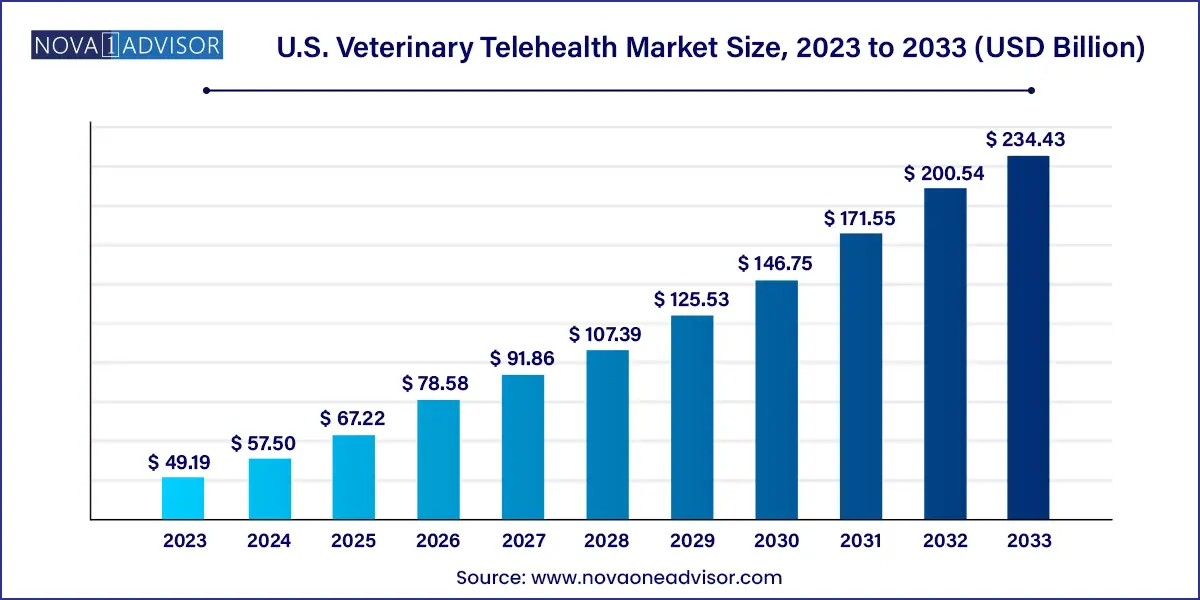
The U.S. veterinary telehealth market size reached USD 49.19 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 234.43 billion by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of 16.9% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. veterinary telehealth market has emerged as a transformative force in the field of animal healthcare, propelled by evolving pet ownership dynamics, increasing demand for remote healthcare services, and advancements in digital technology. As pet owners seek convenience, immediacy, and quality care for their animals, telehealth platforms have become pivotal in bridging the gap between veterinarians and patients. The market has witnessed steady growth due to the dual influence of increased pet humanization and the growing comfort of consumers with digital interactions, especially following the COVID-19 pandemic that catalyzed the adoption of telemedicine across healthcare verticals.
Veterinary telehealth encompasses a variety of services, including teleconsultations, telemonitoring, and diagnostic assistance, delivered through digital platforms. In a country where over 65% of households own pets, and where rural and suburban areas sometimes suffer from limited access to specialized veterinary services, telehealth offers an efficient and scalable solution. Whether it's monitoring chronic conditions in senior dogs or offering behavioral consultations for cats, veterinary telehealth is bringing flexibility to pet care.
The rise of app-based platforms has further enhanced this accessibility. Services like Vetster, Airvet, and Fuzzy have created mobile-first approaches to telehealth, enabling pet owners to connect with licensed veterinarians within minutes. In addition, the growing agricultural animal sector has also shown interest in telemonitoring solutions to manage livestock health remotely, particularly in remote ranches or large-scale operations.
As the market matures, regulatory clarity, evolving consumer behavior, and continuous technological innovation are expected to shape the next phase of growth. The integration of AI, wearables for pets, and cloud-based health records further reinforce the outlook of veterinary telehealth as a mainstay in the U.S. animal healthcare landscape.
Expansion of Telemedicine to Preventative Care: Veterinary telemedicine is expanding beyond emergency or follow-up consultations to include routine check-ups, dietary assessments, and behavioral therapy, widening the use case spectrum.
AI Integration for Diagnosis Support: AI-enabled tools are being integrated to assist veterinarians in diagnosing diseases through video analysis, symptoms tracking, and pattern recognition in pets’ behavior or physical appearance.
Mobile App Dominance: There’s a significant surge in mobile-first platforms that allow video consultation, medication reminders, and real-time health monitoring of pets directly through smartphones.
Veterinary Telehealth for Large Animals: Farmers and livestock owners are increasingly adopting telemonitoring systems for herd management, improving efficiency and early detection of diseases in bovine and swine populations.
Cross-State Veterinary Licensing Initiatives: Collaborative regulatory initiatives are underway to enable veterinarians to offer teleconsultation services across state lines, improving accessibility for under-served regions.
Subscription-Based Models Gaining Popularity: Services offering monthly or annual subscription models for pet care (e.g., unlimited chats or consultations) are gaining traction for their cost-effectiveness and continuous engagement.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 57.50 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 234.43 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 16.9% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Animal type, service type |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Airvet; Activ4Pets; BabelBark, Inc.; Teletails; PetHub, Inc.; VitusVet; Televet; GuardianVets; Whiskers Worldwide, LLC; Animan Technologies Inc.; Chewy, Inc.; Petzam |
One of the primary drivers propelling the U.S. veterinary telehealth market is the growing rate of pet ownership, combined with the shifting lifestyle patterns of pet owners. As more Americans, particularly millennials and Gen Z, choose to adopt pets as part of their families, there has been a heightened demand for personalized and convenient care solutions. Urban dwellers, in particular, face challenges such as limited access to veterinary clinics, rigid work schedules, and transportation issues — making telehealth a valuable solution.
For instance, a young couple living in downtown Chicago may struggle to find time for in-person vet visits due to long work hours. A teleconsultation allows them to connect with a veterinarian for a post-surgical follow-up of their dog without disrupting their daily routine. Moreover, telehealth has proven particularly effective in addressing non-emergency concerns such as dietary advice or skin allergies, reducing unnecessary clinic visits and alleviating the burden on veterinary staff.
Despite the evident benefits, the U.S. veterinary telehealth market faces substantial regulatory hurdles that hinder seamless growth. Licensing remains a significant barrier, as veterinarians are generally restricted to providing services within the state in which they are licensed. This limitation constrains the scalability of telehealth services and discourages multi-state operations for telehealth platforms.
Moreover, there are inconsistencies in the interpretation of the veterinarian-client-patient relationship (VCPR) across states. While some states allow the establishment of VCPR through virtual consultations, others mandate an initial in-person examination, which defeats the primary purpose of telehealth. This fragmented regulatory landscape increases the complexity for telehealth platforms and slows the expansion of comprehensive services nationwide. Until a more uniform legal framework is established, the full potential of veterinary telehealth may remain partially untapped.
A promising opportunity lies in the integration of veterinary telehealth services with wearable health monitoring devices for pets. Smart collars, biosensors, and GPS-enabled health trackers are gaining momentum in the pet tech space, offering real-time data on vital signs, activity levels, and behavioral changes. When linked with telehealth platforms, these devices can offer proactive care interventions and early diagnosis of health issues.
Imagine a scenario where a cat’s smart collar detects abnormal breathing patterns or irregular movement and automatically notifies a linked telehealth service, prompting a veterinarian to intervene remotely. This integration allows pet parents to address issues before they escalate, supporting chronic disease management, post-operative recovery, and general wellness monitoring.
For the livestock sector, IoT-enabled ear tags for cattle or swine can monitor body temperature, detect illness early, and alert veterinarians through a central dashboard. The fusion of telehealth and wearable tech could revolutionize preventive veterinary care in both companion and production animals.
Canine segment dominated the U.S. veterinary telehealth market in 2024, accounting for the largest revenue share. Dogs are the most commonly owned pets in the U.S., and dog owners typically demonstrate a high willingness to invest in digital health solutions. Conditions such as skin infections, arthritis, and gastrointestinal issues are frequently addressed through teleconsultation. The high awareness of veterinary telehealth among dog owners, combined with the availability of tailored services for canine behavioral training and dietary consultation, continues to drive segment growth. Startups like Airvet and Pawp report that over 60% of their consultations cater to dog owners, highlighting this demographic’s contribution to market expansion.
The feline segment is projected to be the fastest-growing during the forecast period. Cats are often less cooperative with travel and clinical settings, making them ideal candidates for remote veterinary services. Telehealth reduces stress for both the cat and its owner by enabling consultations in the comfort of home. Moreover, emerging telemonitoring technologies that help identify signs of chronic kidney disease or behavioral issues in cats are gaining popularity. Companies offering feline-specific care guidance through chatbots and live sessions are creating a niche within the broader telehealth ecosystem, further fueling this segment’s expansion.
Telemedicine segment led the service category, dominating the U.S. veterinary telehealth market owing to its wide range of applications from diagnostics to follow-up care. Pet owners frequently use telemedicine platforms to assess symptoms, seek second opinions, or manage post-operative care without traveling. The convenience of digital prescriptions and real-time access to veterinarians makes telemedicine a highly preferred service type. Especially during the pandemic years, telemedicine proved to be an essential tool to maintain continuity of care for chronic cases, vaccinations, and dermatological conditions. Today, it remains the backbone of most veterinary telehealth platforms.
Meanwhile, telemonitoring is anticipated to grow at the fastest pace, driven by its application in chronic disease management, particularly for aging pets and livestock. Wearables and sensors that transmit data such as heart rate, temperature, and mobility patterns allow veterinarians to continuously track an animal's condition. For instance, livestock farmers in Texas are using wearable tags integrated with telemonitoring dashboards to oversee herd health without being physically present in the fields. Similarly, diabetic dogs or epileptic cats can be remotely monitored at home, enhancing the quality of life while reducing hospital visits. As technology becomes more sophisticated and affordable, the telemonitoring segment is likely to attract significant investment and innovation.
The United States, being the birthplace of many leading veterinary telehealth platforms, has set the tone for how digital pet care can be scaled successfully. With over 80 million pet dogs and more than 60 million cats, the country's sheer pet population offers a fertile ground for telehealth services. Urban hubs such as New York, Los Angeles, and San Francisco have demonstrated early adoption, driven by tech-savvy populations and high pet ownership rates. These cities also host some of the largest pet tech and veterinary innovation conferences, indicating a robust innovation pipeline.
Rural America presents a different but equally critical use case. In states like Montana and Nebraska, where veterinary clinics may be hours apart, teleconsultations have become indispensable. Furthermore, academic institutions such as the University of California, Davis, and Texas A&M Veterinary School are collaborating with tech startups to integrate telehealth training into veterinary curricula a move that will likely solidify the long-term growth of this model in the country.
February 2025 – Airvet, a leading U.S.-based veterinary telehealth company, launched a new subscription plan offering unlimited 24/7 access to licensed vets for $19.99 per month. The service is particularly targeted at new pet parents adopting from shelters.
November 2024 – Fuzzy Pet Health rolled out a beta version of their AI-powered health assistant that can screen symptoms and recommend next steps before a video consultation.
September 2024 – Vetster announced a partnership with Petco to integrate telehealth appointments with in-store product recommendations, creating an omnichannel experience for pet owners.
June 2024 – Banfield Pet Hospital, part of Mars Veterinary Health, piloted a remote monitoring system for diabetic dogs using continuous glucose monitoring patches, with data feeding directly into teleconsultation platforms.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. Veterinary Telehealth market.
By Animal Type
By Service Type