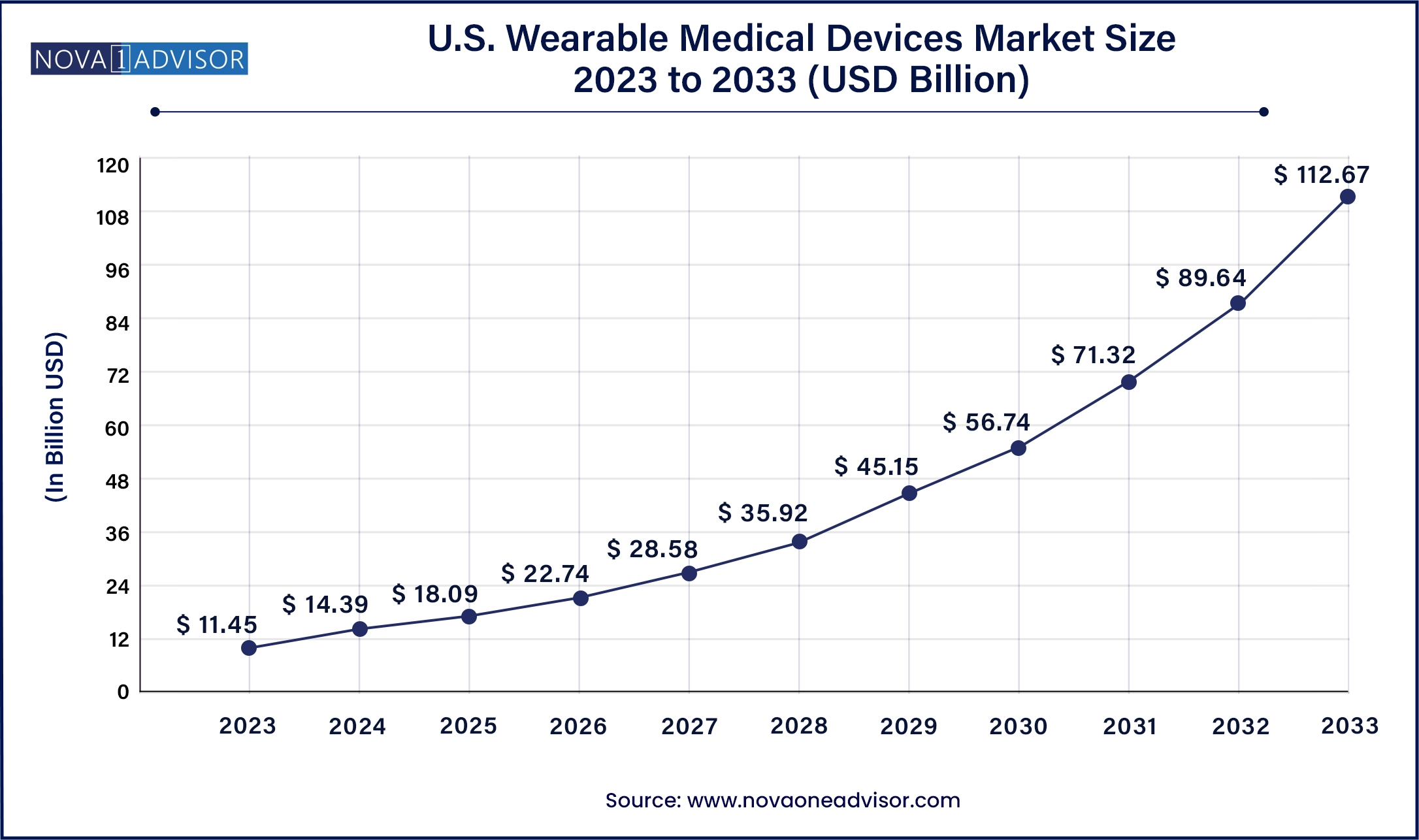
The U.S. wearable medical devices market size was valued at USD 11.45 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 112.67 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 25.69% from 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. wearable medical devices market has rapidly evolved into a pivotal component of modern healthcare delivery, driven by the intersection of technology, consumer wellness awareness, and chronic disease management needs. These devices worn on the body to continuously monitor, diagnose, or treat physiological conditions have revolutionized the concept of healthcare by enabling real-time, continuous, and remote patient monitoring. This market, once dominated by fitness wearables, has expanded to include highly sophisticated medical-grade tools used in clinical settings and at home.
In the United States, several socio-demographic and systemic factors contribute to this market’s growth. The country’s aging population, rising incidence of chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disorders, and increasing preference for home healthcare services have all amplified demand. Coupled with the advent of Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, and mobile health platforms, wearable medical devices are becoming more accurate, multifunctional, and interconnected. From smartwatches that detect atrial fibrillation to biosensors that guide insulin therapy, these devices are now being used not just for wellness but for lifesaving interventions.
Government initiatives such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) expanding reimbursement policies for remote monitoring and private insurers embracing digital health are further accelerating adoption. As U.S. healthcare continues shifting toward value-based models, wearable devices are positioned at the forefront of proactive, preventive, and personalized care. The result is a market that blends medical rigor with consumer-grade convenience poised to transform patient engagement, clinical workflows, and long-term health outcomes.
Consumerization of medical devices, with smartwatches and rings evolving into diagnostic tools beyond wellness tracking.
Integration of AI and machine learning, enabling predictive insights, anomaly detection, and personalized treatment alerts.
Miniaturization and design innovations, making devices more comfortable, stylish, and wearable 24/7 without lifestyle disruption.
Expansion of telemedicine and RPM (Remote Patient Monitoring) platforms that incorporate wearable data into virtual care workflows.
Increased focus on chronic disease management, especially in diabetes, respiratory, and cardiac care, with data-driven therapeutic wearables.
Regulatory clarity and FDA approvals for clinical-grade wearables, supporting their use in hospitals and insurance-covered programs.
Interoperability with EHRs (Electronic Health Records), allowing real-time clinician access to biometric data.
Rise in insurance reimbursements for connected devices, encouraging patient compliance and physician recommendation.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 14.39 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 112.67 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 25.69% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product, site, application, grade type, distribution channel |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Koninklijke Philips N.V.; Apple Inc.; Fitbit; Basis Science; Garmin; Medtronic; Omron Corp.; Withings; Vital Connect; Polar Electro; Everist Genomics; Intelesens Ltd.; Sotera Wireless; AbbVie Inc. |
Diagnostic Devices Dominated the Market
Diagnostic devices form the backbone of the U.S. wearable medical devices market, accounting for the largest revenue share due to their widespread application across wellness, chronic disease management, and clinical diagnostics. Among these, heart rate monitors and activity trackers have become nearly ubiquitous among consumers, especially those using smartwatches and fitness bands. However, more sophisticated devices like wearable ECGs, blood pressure monitors, and pulse oximeters are also seeing increased use, particularly for clinical-grade monitoring in patients with cardiac and respiratory conditions.
Additionally, sleep monitoring devices including wrist actigraphs and polysomnographs are gaining popularity as sleep health becomes a growing public concern. The surge in sleep apnea diagnoses has fueled demand for smart CPAP-integrated sleep trackers, further blurring the lines between diagnostics and therapeutics. With continual innovation improving sensor accuracy, form factor comfort, and battery life, diagnostic wearables will continue to lead the product category in both volume and value.
Therapeutic Devices Are the Fastest-Growing Product Segment
While diagnostic devices lead in usage, therapeutic wearables are the fastest-growing category, thanks to technological advancements and growing patient comfort with self-managed treatment tools. Devices like neurostimulation patches for pain management, insulin pumps for diabetes, and portable ventilators and CPAP machines for respiratory therapy are revolutionizing chronic care delivery outside hospital walls. These tools not only provide treatment but can automatically adjust dosing or output based on real-time feedback enabling closed-loop care models.
In particular, insulin delivery systems, including automated insulin pumps and patch-based injectors, are seeing exponential adoption due to rising diabetes rates in the U.S. Similarly, wearable rehabilitation devices including accelerometers and sensing sleeves used post-stroke or injury are transforming home-based physical therapy. As these devices gain FDA clearance and insurance support, therapeutic wearables will continue to close the gap between hospital-level care and at-home convenience.
Strap, Clip, and Bracelet-Based Wearables Dominated Usage
Wearable medical devices worn on the wrist or clipped onto the body dominate the market due to user comfort, familiarity, and ease of use. These include devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, ECG bands, and insulin pump clips. The popularity of wrist-based devices stems from decades of consumer habit (e.g., wristwatches), making these devices natural extensions of daily attire. Their visibility also encourages consistent use and user engagement.
Bracelet-based formats offer sufficient space for sensors, batteries, and Bluetooth modules, making them ideal for continuous vital monitoring. As innovation introduces multi-sensor wrist wearables combining heart rate, oxygen saturation, sleep, temperature, and ECG in a single device—this segment is set to retain dominance.
Shoe Sensors and Headbands Are Emerging Rapidly
Among newer formats, shoe sensors and headbands are experiencing fast growth, particularly in applications such as neurological monitoring and gait analysis. Shoe sensors are used in Parkinson’s, stroke recovery, and fitness rehabilitation to track steps, balance, and fall risk. Similarly, EEG-integrated headbands are becoming popular in mental health research and sleep studies. They allow for unobtrusive brainwave monitoring, facilitating insights into cognitive disorders, stress, or sleep quality.
These less conventional formats offer targeted applications and have the potential to open up new markets especially as design advances make them lighter and more fashionable. Their growth also reflects the expanding diversity of use cases across healthcare and wellness.
Remote Patient Monitoring Dominates the Application Landscape
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is the dominant application for wearable medical devices in the U.S., driven by systemic healthcare trends toward value-based care, reduced hospital readmissions, and patient-centered outcomes. Wearables used in RPM enable clinicians to track vital signs, glucose levels, heart rhythms, and respiratory data in real time—helping patients stay home while still receiving medical-grade supervision. This is particularly valuable for patients with heart failure, COPD, or post-surgical recovery needs.
RPM's expansion is further enabled by CMS's endorsement of remote monitoring services, allowing providers to bill for time spent reviewing wearable data. As health systems invest in care-at-home programs, wearable RPM tools are becoming standard issue in chronic care pathways, cementing their dominant role in the application segment.
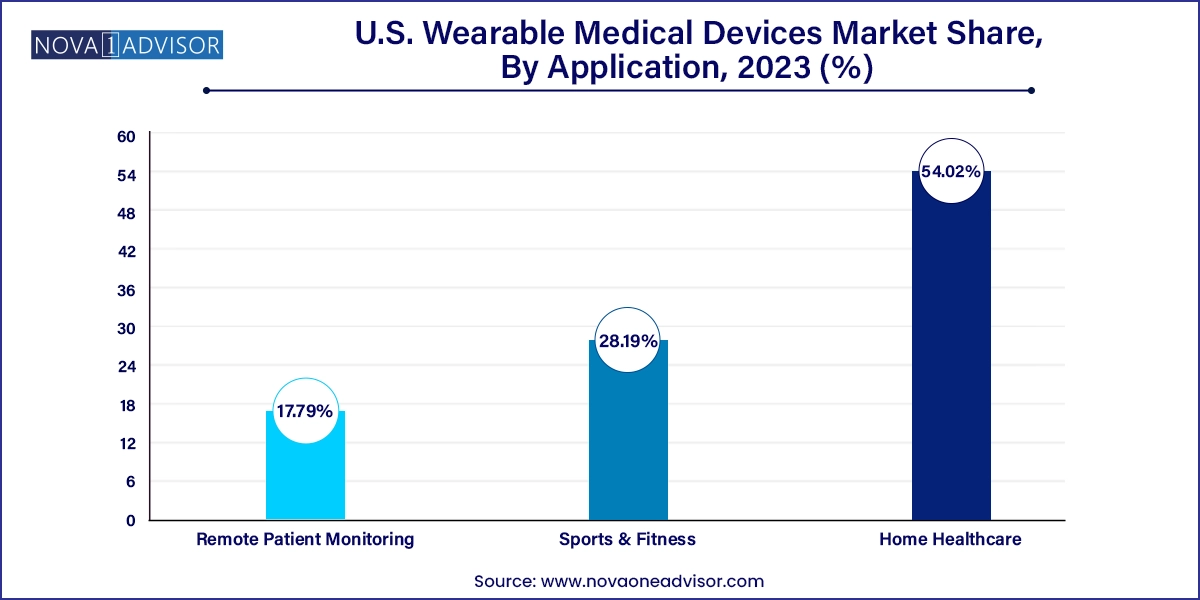
Sports and Fitness Remain the Fastest-Growing Consumer Segment
While RPM leads in clinical use, sports and fitness applications are the fastest-growing, particularly among younger, tech-savvy demographics. Fitness trackers, heart rate monitors, and recovery tools like wearable EMG patches and hydration sensors are increasingly popular in recreational and professional sports settings. These devices help users optimize training, prevent injury, and monitor biometric thresholds like lactate buildup or fatigue levels.
In addition, sports-based wearables are now integrating biofeedback features—providing vibration cues or app-based alerts for posture correction, breathing rhythm, or real-time performance coaching. As Americans increasingly adopt fitness-focused lifestyles and participate in wearable challenges, this segment will continue its high-growth trajectory, supported by influencers, athlete endorsements, and fitness app ecosystems.
Consumer-Grade Devices Lead the Market in Volume
Consumer-grade wearable medical devices dominate the market in terms of volume, thanks to the widespread adoption of smartwatches, rings, and fitness trackers by health-conscious users. These devices often serve as entry points for health engagement tracking steps, heart rate, sleep, and more. Though not always FDA-approved, many consumer devices now offer clinically relevant metrics, especially as sensor precision improves. They are also significantly cheaper and more aesthetically appealing than clinical alternatives.
Clinical-Grade Devices Are Gaining Speed as Healthcare Embraces Digital Monitoring
Clinical-grade devices, though fewer in number, are growing quickly in adoption and regulatory acceptance. Devices used in hospitals, remote care, or prescribed by physicians for chronic conditions like wearable ECGs or smart insulin patches—are undergoing FDA clearance and proving their value in trials. Clinical-grade wearables offer higher accuracy, better integration with EHRs, and clear medical outcomes, making them more likely to be covered by insurance. As clinicians gain trust in these tools and prescribe them more frequently, this segment will experience exponential growth.
Online Channels Dominate and Redefine Sales
Online channels dominate distribution, not only due to convenience but also because of the shift toward direct-to-consumer medical device marketing. Wearables are increasingly purchased via brand websites, third-party platforms (like Amazon), or telehealth partners bundling devices with subscriptions. Online reviews, influencer endorsements, and social media campaigns play a critical role in product discovery and brand loyalty in this channel.
Pharmacies Remain Critical for Clinical and Reimbursable Devices
However, pharmacies continue to be essential for FDA-approved and reimbursable devices, such as glucose monitors and CPAP equipment. Patients trust their pharmacists for device training, warranty assistance, and supply management. As retail pharmacies expand into primary care and chronic management roles (e.g., CVS Health, Walgreens), they may become key players in wearable distribution and data collection.
The U.S. remains the global epicenter of wearable medical device innovation, adoption, and commercialization. With a robust healthcare infrastructure, a dynamic tech sector, and a consumer base willing to invest in health tech, the country is ideally positioned to lead this market. The presence of leading academic hospitals, tech incubators, and health insurers has led to rapid innovation cycles—from concept to FDA approval and clinical use.
The U.S. is also home to favorable reimbursement policies and public-private programs promoting preventive care and digital health. Medicare and Medicaid are increasingly covering RPM services, and many employers offer wearables through wellness programs. Urban centers like San Francisco, Boston, and New York serve as testbeds for pilot programs involving AI wearables, remote monitoring, and cloud-based care delivery.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. Wearable Medical Devices market.
By Product
By Site
By Application
By Grade Type
By Distribution Channel