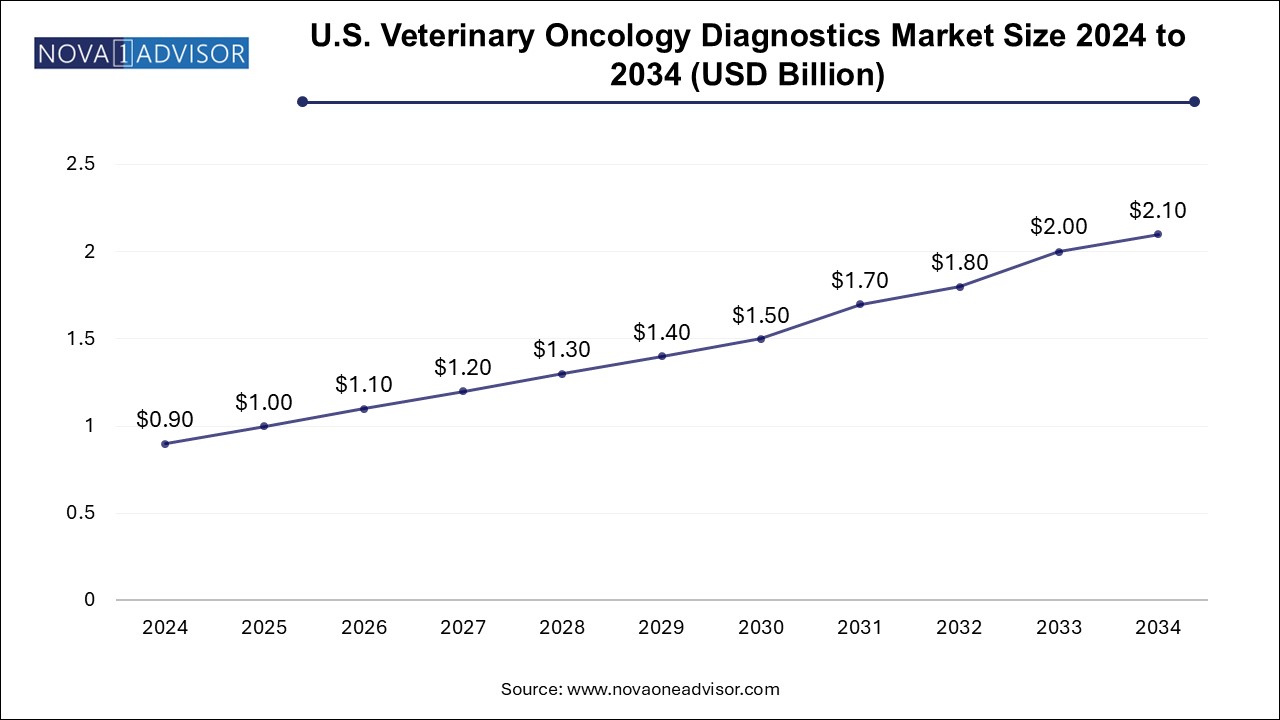
The veterinary oncology diagnostics market size was exhibited at USD 2.34 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 5.29 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.5% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
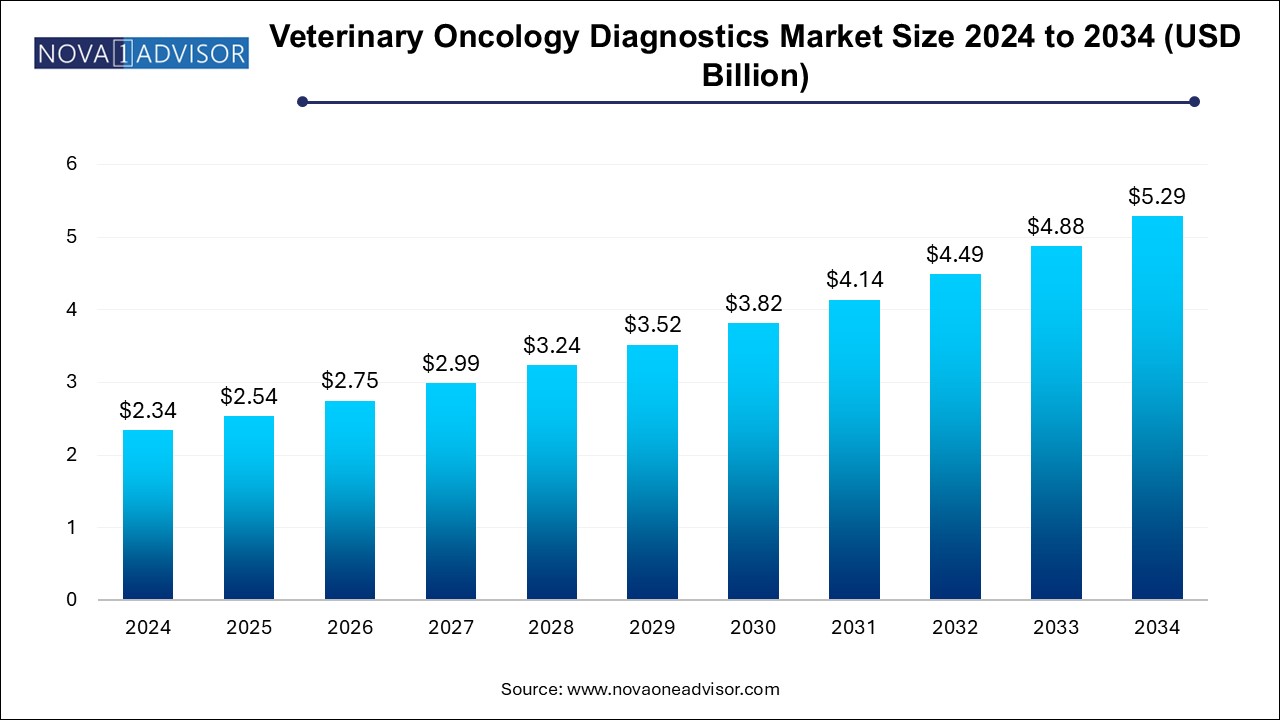
The U.S. veterinary oncology diagnostics market size is evaluated at USD 0.90 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 2.1 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.0% from 2025 to 2034.
North America leads the global veterinary oncology diagnostics market, driven by high pet ownership, advanced veterinary infrastructure, and strong investment in pet healthcare. The U.S., in particular, boasts a dense network of specialty oncology centers, academic institutions, and diagnostic laboratories offering sophisticated cancer testing. The presence of companies like IDEXX Laboratories, Antech Diagnostics, and PetDx underscores the region's leadership in diagnostics innovation. Additionally, the widespread use of pet insurance, high awareness among pet parents, and proactive veterinary wellness programs have contributed to a thriving oncology diagnostics market in this region.
Asia Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing market, propelled by rising disposable incomes, urban pet adoption, and growing veterinary awareness in countries like China, India, and Japan. As the veterinary infrastructure improves and specialty care becomes more accessible, demand for oncology diagnostics is rapidly increasing. Moreover, partnerships between global diagnostic providers and regional labs are expanding test availability. While currently under-penetrated, the region’s young pet-owning demographic and digital health adoption trends make it a hotspot for future growth in veterinary oncology diagnostics.
The veterinary oncology diagnostics market is becoming increasingly vital within the global veterinary healthcare landscape. As pet ownership surges and the human-animal bond deepens, pet owners are seeking advanced and personalized healthcare solutions for their animals—particularly in oncology, where early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes and quality of life. Cancer is one of the leading causes of death in companion animals, especially in older pets. With rising awareness, clinical research, and technological integration, the veterinary oncology diagnostics segment is poised for transformative growth over the coming decade.
Unlike traditional veterinary diagnostics focused largely on infectious diseases or general wellness, oncology diagnostics delve deeper into tumor detection, classification, and genetic profiling. This involves a wide spectrum of diagnostic modalities such as blood-based biomarker screening, fine needle aspiration cytology, imaging techniques (MRI, CT, ultrasound), biopsy sampling, and even next-generation genome testing. These tools are no longer confined to academic settings but are increasingly available in commercial veterinary labs and high-end clinics.
The market is largely driven by the parallel between human and veterinary oncology. The cross-over of diagnostic tools, therapies, and technologies from human medicine to veterinary care has created new opportunities. Moreover, the increase in pet insurance coverage and growing willingness of pet parents to invest in premium healthcare services have further catalyzed the adoption of advanced cancer diagnostics. Reference laboratories and specialty veterinary oncology centers are expanding their service portfolios, incorporating precision diagnostics and AI-based image interpretation.
As veterinary medicine continues to evolve from reactive care to proactive, data-driven diagnostics, the oncology segment stands out due to its complexity and potential impact on animal health outcomes. The coming years are likely to witness a surge in innovation, research collaboration, and clinical adoption, firmly positioning oncology diagnostics as a cornerstone of next-generation veterinary healthcare.
Growth in Companion Animal Cancer Registries: Veterinary institutions and oncology networks are creating structured databases to study cancer incidence, treatment outcomes, and breed-specific risks.
Rise of Molecular and Genomic Testing: Next-generation sequencing and gene expression profiling are being used to identify cancer mutations and personalize treatment.
Cross-application of Human Oncology Technologies: Innovations from human cancer diagnostics—such as liquid biopsy, AI in imaging, and digital pathology—are being adapted for veterinary use.
Increasing Use of Teleoncology Services: Veterinary oncologists are offering remote consultations and diagnosis reviews, expanding access to specialized care.
Development of Breed-Specific Diagnostic Panels: Diagnostic tests tailored for genetically predisposed breeds (e.g., Boxers for lymphoma, Golden Retrievers for hemangiosarcoma) are gaining popularity.
Point-of-Care Cancer Screening Kits: Simple in-clinic kits for preliminary screening (e.g., blood-based biomarkers) are expanding access in general veterinary practices.
AI-Assisted Imaging Analysis: Artificial intelligence is being used to analyze radiographic and histopathological images, increasing diagnostic accuracy and speed.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 2.54 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 5.29 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 8.5% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Animal Type, Test Type, Cancer Type, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | Zoetis; Antech Diagnostics, Inc. (Mars Inc.); IDEXX Laboratories, Inc.; Neogen Corporation; Gold Standard Diagnostics (Eurofins Technologies); Embark Veterinary, Inc.; VolitionRx Limited; CANCAN DIAGNOSTICS; Oncotect; PetDx |
A primary driver of the veterinary oncology diagnostics market is the combination of rising pet ownership and an aging pet population. In the U.S. alone, over 65% of households own at least one pet, with similar upward trends visible in Europe and Asia. Thanks to better nutrition, preventive healthcare, and indoor lifestyles, pets are living longer—but this longevity also increases the likelihood of chronic diseases, particularly cancer.
Older animals are significantly more susceptible to tumors, especially in organs like the lymphatic system, mammary glands, and skin. Consequently, veterinarians are encountering more cancer cases and are seeking accurate and early diagnostics to improve treatment planning. The increasing emotional and financial investment of pet parents, combined with the desire to extend healthy life years, is pushing demand for advanced diagnostics like genome testing and imaging scans. This trend is expected to deepen as veterinary care becomes more specialized and pet health is prioritized akin to human healthcare.
One of the key restraints hindering widespread adoption in the veterinary oncology diagnostics market is the high cost of advanced testing modalities. Genome sequencing, MRI scans, or biopsy interpretation by board-certified pathologists can cost hundreds to thousands of dollars—figures that may be unaffordable for a significant portion of pet owners, especially those without insurance.
While urban pet owners may have access to specialty clinics or diagnostic labs, those in rural or lower-income regions often face limited diagnostic capabilities. Additionally, many general practitioners lack the training to interpret complex oncological tests, leading to underutilization. Although pet insurance is gaining traction, it still covers a small portion of the global pet population, particularly in developing markets. This pricing barrier restricts accessibility and remains a challenge, particularly for integrating precision diagnostics into mainstream veterinary practice.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and digital pathology into veterinary oncology diagnostics presents a promising opportunity for enhancing diagnostic efficiency and reach. Traditionally, pathology interpretation in oncology requires expert review of tissue slides—a process that is time-consuming, subjective, and geographically limited. However, digitizing biopsy samples and using AI models to detect malignancy patterns can standardize diagnostics and reduce turnaround time.
AI algorithms trained on thousands of annotated images can identify tumors, grade them, and even predict their progression with impressive accuracy. These tools can be deployed across general veterinary clinics through cloud-based platforms, enabling faster referrals and second opinions from remote oncology specialists. Furthermore, AI in radiology is aiding the detection of tumors in imaging scans like X-rays, CT, or MRI. As AI tools become more validated and commercially available, they offer a scalable solution to meet the growing demand for quality oncology diagnostics in veterinary care.
Canine diagnostics dominate the veterinary oncology diagnostics market, accounting for the majority of testing volume and clinical focus. Dogs are more likely to be diagnosed with cancer compared to other pets, largely due to their genetic predisposition, longer life spans, and better access to veterinary care. Lymphoma, hemangiosarcoma, and mast cell tumors are among the most commonly diagnosed cancers in dogs. Dog owners, especially in developed markets, are increasingly willing to pursue advanced diagnostic workups, including biopsies, CT scans, and even gene testing, to guide therapeutic decisions.
On the other hand, feline diagnostics are the fastest-growing segment, driven by increased awareness among cat owners and improvements in feline-specific diagnostic tools. Historically, cats were underdiagnosed due to their subtle symptom presentation and resistance to clinical handling. However, with improved sedation protocols and non-invasive diagnostic options such as blood biomarkers and ultrasound imaging, more cancers are being detected in felines—especially lymphoma and mammary gland tumors. The rise of feline-specific oncology panels is contributing to more accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment, supporting this segment's growth trajectory.
Biopsy remains the gold standard and the dominant diagnostic modality in veterinary oncology, as it allows for histopathological evaluation and definitive diagnosis. It helps determine tumor grade, margin status, and treatment feasibility. Fine needle aspiration and core biopsies are widely used by veterinary oncologists, often followed by immunohistochemistry or molecular characterization. Despite the invasiveness of the procedure, biopsies remain indispensable for treatment planning, particularly for solid tumors in dogs and cats.
However, genome testing is the fastest-growing test type, reflecting a paradigm shift toward personalized veterinary oncology. With increasing understanding of the genetic drivers of animal cancers, commercial labs are offering genomic panels that detect mutations, identify drug targets, and provide prognostic insights. This is especially valuable in complex cases or rare cancers where conventional diagnostics fall short. As genome testing becomes more affordable and integrated into specialty care protocols, it is expected to play a pivotal role in the future of veterinary oncology.
Reference laboratories hold the largest market share, as most advanced oncology diagnostics—particularly histopathology, genome testing, and immunohistochemistry—are performed in centralized facilities. These labs are equipped with high-throughput analyzers, skilled pathologists, and integrated digital reporting systems. Veterinary clinics and specialty hospitals routinely send samples to these labs, leveraging their expertise and broader test menus. Market leaders in this segment offer courier services, cloud portals, and AI-supported analysis, enhancing turnaround and quality.
Conversely, veterinary hospitals and clinics are the fastest-growing end-use segment, reflecting the decentralization of diagnostics and increased in-house capabilities. Clinics are investing in ultrasound machines, point-of-care cytology tools, and even small-scale pathology labs. This shift allows for quicker diagnosis and treatment initiation, enhancing clinical outcomes and customer satisfaction. As diagnostic equipment becomes more compact and affordable, more practices will expand their in-clinic oncology testing capabilities.
Lymphoma represents the largest segment by cancer type, being one of the most common cancers in both dogs and cats. Its prevalence, especially among certain breeds like Boxers and Golden Retrievers, has led to a high volume of diagnostic testing. Blood tests, cytology, and imaging are commonly employed to detect lymph node involvement and stage the disease. Ongoing research into canine lymphoma has also made it a benchmark model for comparative oncology studies, further driving investment in accurate diagnostic approaches.
In contrast, skin cancers are the fastest-growing cancer type segment, due to increased recognition and diagnostic capability at general practices. With higher awareness of unusual skin lesions, dermatological biopsies and digital imaging have become routine tools in veterinary clinics. Melanomas, mast cell tumors, and squamous cell carcinomas are frequently identified and require precise staging for effective management. The increasing use of dermatoscopy, cytology, and image-sharing platforms for skin tumor evaluation is supporting the segment’s rapid growth.
In March 2025, PetDx launched OncoK9 Express, a blood-based liquid biopsy panel for early cancer detection in dogs, designed for general veterinary practices and mobile clinics.
IDEXX Laboratories, in January 2025, introduced AI-enhanced cytology screening for faster tumor classification, integrated within its reference lab network across the U.S. and Canada.
Antech Diagnostics, in February 2025, announced a strategic partnership with the Veterinary Cancer Society to develop breed-specific cancer registries and diagnostic panels.
In December 2024, Zoetis expanded its oncology diagnostics portfolio through the acquisition of a U.K.-based genomic testing firm specializing in canine lymphoma markers.
Scopio Labs, an AI-based digital pathology startup, launched its VetScope platform in October 2024, enabling real-time slide analysis for veterinary clinics through cloud infrastructure.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the veterinary oncology diagnostics market
By Animal Type
By Test Type
By Cancer Type
By End-use
By Regional