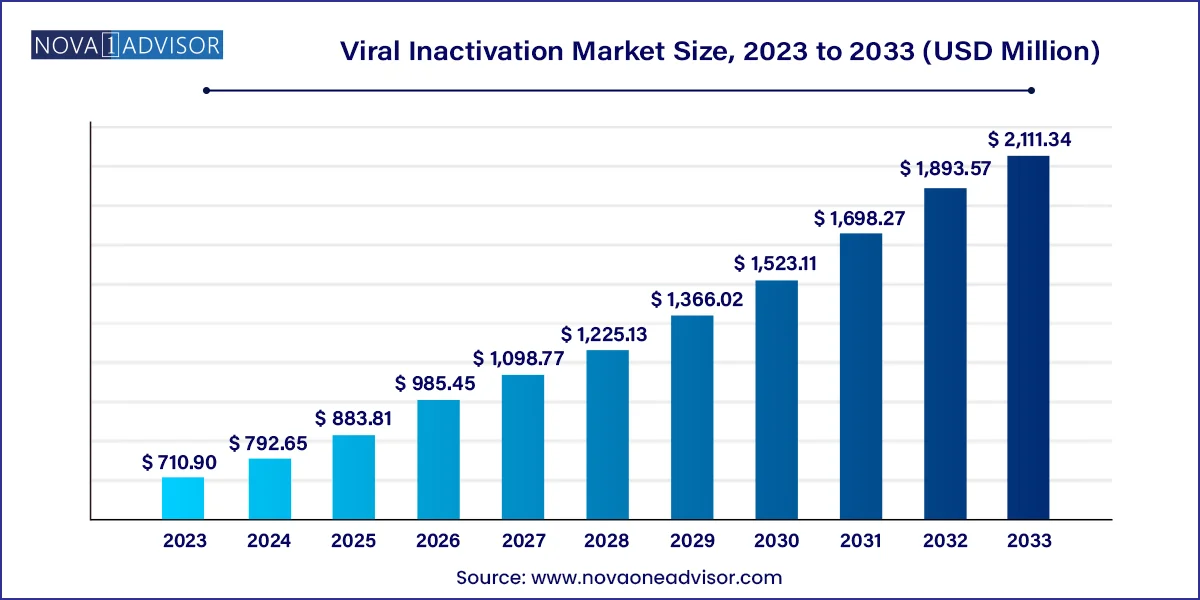
The global viral inactivation market size was valued at USD 710.90 million in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 2,111.34 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11.5% from 2024 to 2033.
The viral inactivation market plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of biopharmaceutical products, cell therapies, and blood-based therapeutics. Viral inactivation is the process by which viruses are rendered non-infectious without compromising the biological integrity of the product. This is a critical step in biomanufacturing workflows, particularly in the production of vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, plasma-derived products, and advanced therapies like gene and cell therapies.
As the global demand for biologics continues to rise, the need for robust viral safety measures has become more urgent. High-profile contamination events in the past have driven regulatory bodies like the FDA, EMA, and WHO to strengthen oversight around viral clearance. Consequently, pharmaceutical manufacturers and contract research organizations (CROs) have integrated advanced viral inactivation protocols into early stages of drug development and production pipelines.
The COVID-19 pandemic further underscored the importance of viral risk mitigation. Rapid vaccine development showcased the necessity of streamlined viral inactivation techniques that can scale efficiently. Post-pandemic, the market has witnessed increased investment in virus reduction technologies, including photochemical methods, solvent/detergent treatments, low pH inactivation, and nanofiltration.
With ongoing innovation, regulatory pressure, and rising R&D expenditures in biologics, the viral inactivation market is positioned for strong, sustained growth over the next decade.
Increased Use of Continuous Bioprocessing: Viral inactivation methods are being adapted to continuous manufacturing workflows to increase production efficiency.
Growth in Gene and Cell Therapy: The rise in advanced therapies is expanding the application of viral inactivation beyond traditional biologics.
Automation and Closed System Integration: To reduce contamination risks, companies are adopting closed systems with automated viral inactivation steps.
Development of Broad-Spectrum Inactivation Kits: Manufacturers are introducing reagents and kits effective across a wider range of enveloped and non-enveloped viruses.
Strategic Collaborations and Licensing Agreements: Biotech firms and service providers are partnering to access novel inactivation technologies and global markets.
Expansion into Emerging Markets: Viral safety protocols are being increasingly enforced in regions like Asia-Pacific and Latin America as biologics manufacturing expands.
Regulatory Advancements in Viral Safety Guidelines: Agencies like the FDA and EMA are standardizing viral inactivation validation and testing protocols.
Photon-based and Nanotechnology Inactivation: Emerging techniques using UV-C light and nanoparticles are being explored for rapid, scalable viral deactivation.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 792.65 million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 2,111.34 million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 11.5% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Product & services, application, end-use, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Charles River Laboratories, Inc., Clean Cells, Cytiva (Danaher Corporation), Merck KGaA, Mettler Toledo, Parker Hannifin Corp, Rad Source Technologies Inc, Sartorius AG, Texcell SA, Vironova AB |
One of the most powerful drivers in the viral inactivation market is the explosive growth in biologics and biosimilars. Biologics, including monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, and vaccines, are derived from living cells, making them inherently susceptible to viral contamination. As pharmaceutical companies expand their biologics pipelines, the need to ensure viral safety becomes indispensable. For instance, blockbuster drugs like Humira and Keytruda require rigorous viral clearance during production. Biosimilar manufacturers also need to follow strict viral safety standards to gain regulatory approval. This trend has led to increased demand for viral inactivation services, kits, and integrated systems across both established biopharma firms and emerging biotech players.
Despite the growing need for viral inactivation, the cost-intensive nature of implementation poses a barrier, especially for smaller biotechnology companies and academic institutes. Setting up virus clearance infrastructure involves purchasing high-end systems, validating processes, and training personnel—all of which are expensive and time-consuming. Furthermore, each biopharmaceutical product may require a unique inactivation strategy, necessitating multiple validation studies for different viruses under specific conditions. This level of customization adds complexity and cost, often deterring adoption in early-stage research and smaller-scale operations.
The growing adoption of cellular and gene therapies is opening new frontiers for viral inactivation technologies. These therapies often use viral vectors like lentiviruses and adeno-associated viruses (AAV) to deliver genetic material, creating a higher risk of viral contaminants during production. Regulatory bodies now mandate that manufacturers implement robust viral clearance strategies, even for therapies produced at small scales. This creates a substantial opportunity for companies offering compact, flexible inactivation systems and reagents tailored to gene therapy workflows. Startups and CDMOs (Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations) are especially interested in integrated platforms that can be quickly deployed for early-stage GMP manufacturing.
Kits and reagents dominate the viral inactivation market, primarily due to their widespread use in standardized and flexible laboratory workflows. These include solvent/detergent reagents, photochemical agents, and pH modifiers that enable quick and validated viral inactivation. Companies like Merck and Sartorius offer proprietary reagents tailored for specific biologics and therapeutic classes. The popularity of kits is fueled by their ease of integration into both batch and continuous processing environments, enabling high throughput and consistent viral clearance.
Services are the fastest-growing segment, especially among pharmaceutical firms and gene therapy startups outsourcing viral clearance studies. Contract testing organizations and CROs provide customized validation studies using a wide array of model viruses, shortening time to regulatory submission. These services cover experimental design, execution, and full documentation, and are increasingly in demand due to their scalability and regulatory alignment. For example, Charles River Laboratories has expanded its viral clearance services portfolio to meet growing client needs across North America and Europe.
Vaccines and therapeutics represent the largest application segment, owing to the large-scale production of biologics that must meet stringent viral safety requirements. Both prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines undergo multi-step virus removal and inactivation procedures to ensure safety and efficacy. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated demand in this segment, with companies seeking rapid yet validated solutions to meet emergency timelines. Additionally, mAbs (monoclonal antibodies) dominate biologics pipelines and require consistent viral clearance as part of regulatory submission packages.
Cellular and gene therapy is the fastest-growing application, driven by increasing FDA approvals and pipeline expansions in regenerative medicine. These therapies are manufactured using virus-based vectors and are often patient-specific, which demands robust and flexible viral safety strategies. In 2024, several CDMOs announced investments in modular viral inactivation suites to support customized therapies, further driving innovation and adoption in this niche yet high-potential segment.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies dominate the end-use segment, given their central role in developing biologics, vaccines, and advanced therapies. These companies rely heavily on validated inactivation steps as part of regulatory compliance, especially during BLA (Biologics License Application) submissions. Industry leaders like Pfizer, Genentech, and Gilead integrate inactivation solutions from providers such as Sartorius, Merck, and Danaher into their core manufacturing frameworks. This segment also drives innovation by collaborating with suppliers to develop new virus deactivation technologies tailored to emerging therapeutic modalities.
CROs are the fastest-growing end-users, reflecting the growing trend of outsourcing non-core functions such as viral safety testing. CROs cater to a broad range of customers—from emerging biotech to large pharmaceutical players—by offering virus inactivation and clearance validation studies on a contract basis. These service providers are expanding their capabilities with advanced biosafety labs, trained personnel, and simulation platforms. Charles River, SGS, and Texcell are prominent CROs making strategic investments to meet this rising demand.
North America dominates the global viral inactivation market, fueled by a well-established biopharmaceutical industry, advanced research infrastructure, and strict regulatory frameworks. The United States, in particular, leads in the development and manufacturing of biologics and advanced therapies, with numerous FDA-approved facilities requiring validated viral safety processes. The presence of key market players like Charles River, Thermo Fisher, Merck (MilliporeSigma), and Danaher further boosts the region's technological leadership. Additionally, federal funding for biologics R&D and pandemic preparedness has reinforced the importance of viral inactivation capabilities.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with countries like China, South Korea, India, and Japan heavily investing in biologics manufacturing infrastructure. Government-backed initiatives to establish domestic vaccine and biosimilar production hubs have prompted pharmaceutical companies to upgrade their viral safety protocols. CDMOs in the region are rapidly expanding their service portfolios to include viral clearance and inactivation solutions, making Asia-Pacific an attractive destination for international biotech firms looking for cost-effective and scalable manufacturing options.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Viral Inactivation market.
By Product & Services
By Application
By End-use
By Region