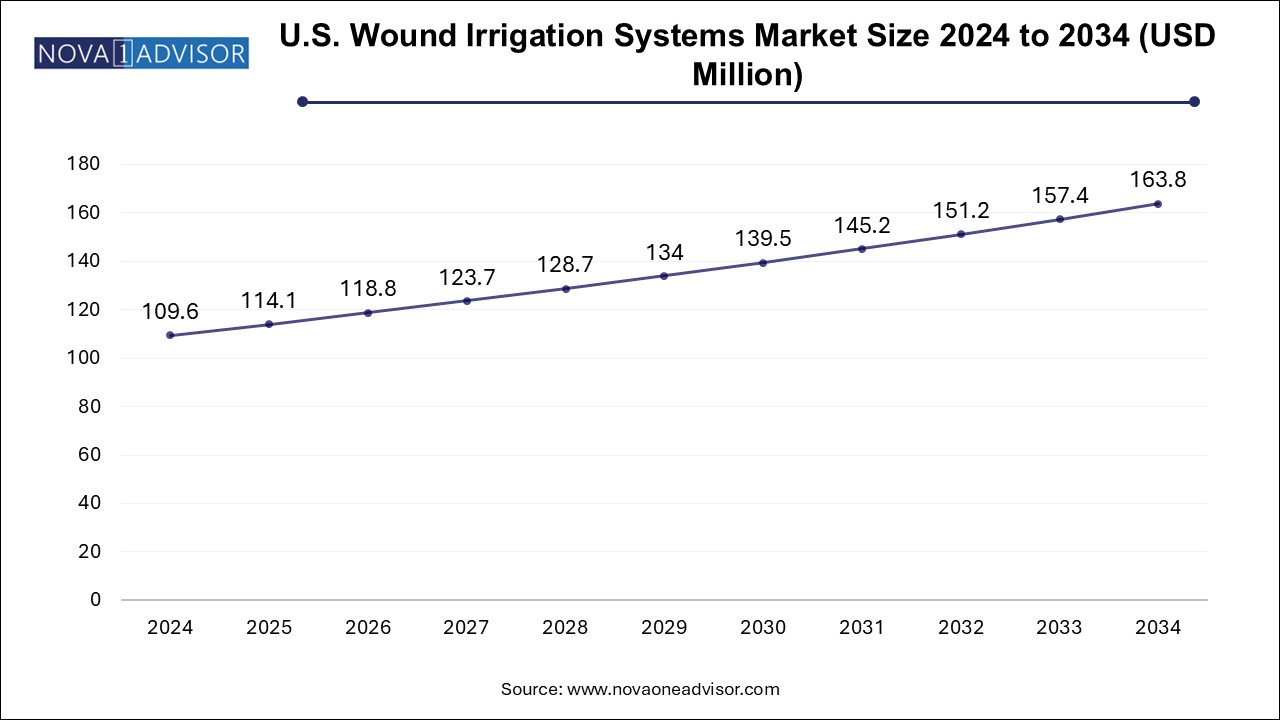
The wound irrigation systems market size was exhibited at USD 339.89 million in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 507.97 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.1% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
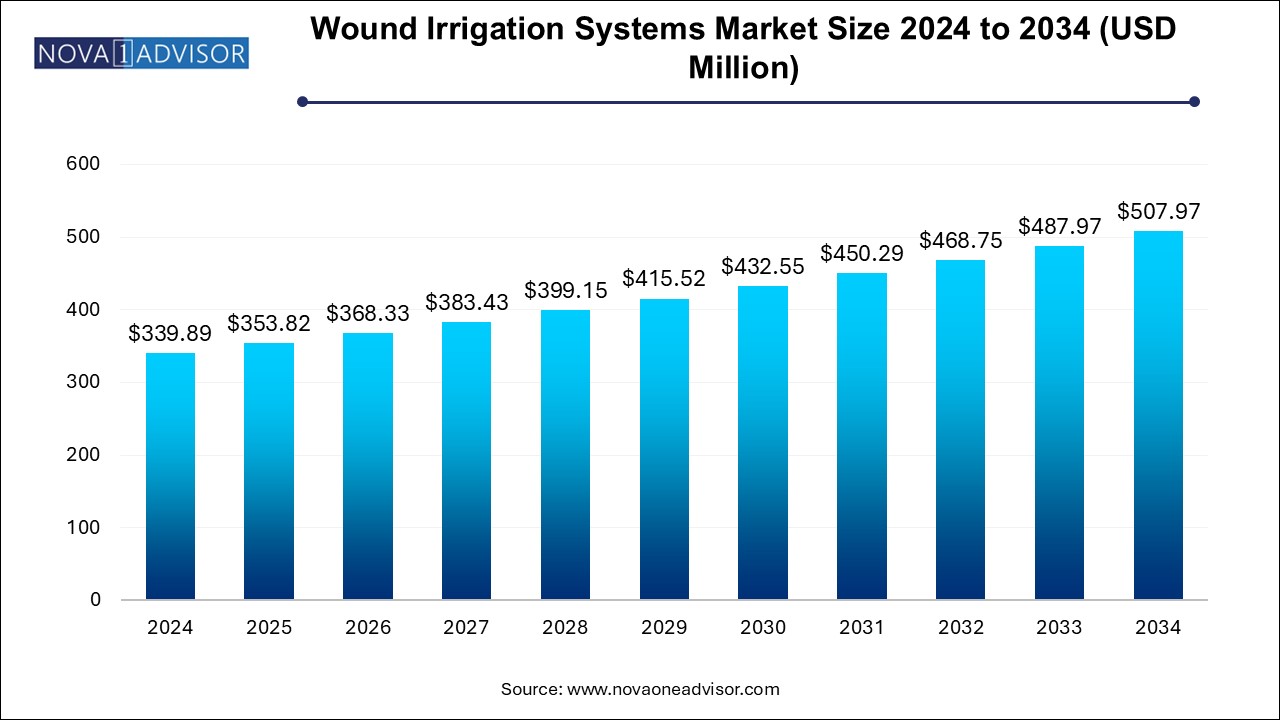
The U.S. wound irrigation systems market size is evaluated at USD 109.6 million in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 163.8 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 3.72% from 2025 to 2034.
North America currently dominates the wound irrigation systems market, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong reimbursement policies, and high awareness of wound management best practices. The U.S. accounts for the majority of regional revenue, owing to the high prevalence of chronic wounds, especially among elderly and diabetic populations. The presence of major market players such as Stryker, Medline Industries, and Becton Dickinson further strengthens the region’s position.
The region also benefits from established wound care centers, extensive training programs for clinicians, and continuous technological innovation. For example, several U.S.-based institutions have integrated wound irrigation systems into electronic wound care documentation platforms, enabling better tracking of outcomes and treatment adjustments. Moreover, the expansion of value-based care models incentivizes hospitals to invest in effective tools like wound irrigation systems to reduce readmissions and improve healing rates.
Asia Pacific is witnessing the fastest growth in the wound irrigation systems market, fueled by a combination of rising chronic disease prevalence, improved healthcare access, and government investment in wound care infrastructure. Countries like India, China, and Japan are experiencing a surge in diabetic and geriatric populations—two major drivers of chronic wound incidence. Simultaneously, the establishment of specialized wound clinics and training programs is fostering better wound care practices across the region.
Furthermore, the region is attracting investment from global manufacturers looking to tap into large patient pools and unmet needs. For example, the partnership between local distributors and global wound care firms in Southeast Asia is accelerating product availability. Additionally, the increasing popularity of home healthcare and the shift toward community-based wound management in countries like Australia and South Korea contribute to the market’s rapid growth.
The wound irrigation systems market is undergoing a significant transformation, propelled by the growing global burden of acute and chronic wounds, the aging population, rising healthcare expenditure, and increased focus on infection control protocols. Wound irrigation—an essential component of wound management—involves the controlled delivery of fluid to remove debris, pathogens, and necrotic tissue from the wound bed. It not only aids in decontamination but also prepares the wound for healing, reduces the risk of infection, and facilitates better clinical outcomes.
As clinical practices evolve to emphasize minimally invasive, patient-centered care, the demand for efficient, sterile, and easy-to-use irrigation devices has witnessed notable growth. Manual and battery-operated wound irrigation systems are increasingly being adopted in hospitals, surgical centers, ambulatory care settings, and home care environments. Particularly in the context of chronic conditions like diabetic foot ulcers and pressure sores, wound irrigation plays a pivotal role in curbing complications and lowering hospital readmissions.
The market is shaped by continuous innovation in device ergonomics, fluid delivery precision, and portability. Moreover, increased awareness regarding proper wound care protocols, especially in post-operative and burn care settings, has further broadened the application base of wound irrigation systems. As healthcare systems worldwide prioritize cost-effective and outcome-driven wound care strategies, the wound irrigation systems market is poised for robust expansion through 2034.
Rising Adoption of Battery-Operated and Automated Irrigation Devices for Enhanced Efficiency
Integration of Antimicrobial and Antiseptic Solutions in Irrigation Protocols
Growing Focus on Infection Prevention in Post-Surgical Wound Management
Shift Toward Home-Based Wound Care and Portable Device Development
Increased Use of Wound Irrigation Systems in Burn Units and Emergency Rooms
Emphasis on Single-Use and Disposable Devices to Minimize Cross-Contamination
Expansion of Wound Care Guidelines and Training in Developing Regions
Mergers and Acquisitions Aimed at Expanding Product Portfolios in Wound Management
Technological Advancements in Pressure Regulation and Flow Control Mechanisms
Growing Investments in Research on Chronic Wound Healing and Irrigation Efficacy
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 353.82 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 507.97 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 4.1% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Application, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled | Zimmer Biomet; Stryker; Medline Industries, LP; Essity Aktiebolag (publ); CooperSurgical Inc.; BD; Bionix LLC.; Irrisept. |
A primary driver of the wound irrigation systems market is the increasing incidence of chronic wounds, particularly among the aging population and patients with comorbid conditions such as diabetes, vascular diseases, and immobility. Chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers are notoriously difficult to manage and often require prolonged care. These wounds are prone to infections and biofilm formation, which complicates healing and increases the need for frequent and efficient debridement and irrigation.
According to the American Diabetes Association, over 11% of the U.S. population has diabetes, and nearly 15–25% of them are expected to develop diabetic foot ulcers during their lifetime. Wound irrigation systems are integral in managing such ulcers, as they help remove slough, exudate, and infectious agents. Hospitals and outpatient wound care clinics are increasingly incorporating advanced irrigation systems into standard treatment regimens to ensure wound bed preparation and faster recovery. This trend is anticipated to continue with the global rise in chronic disease prevalence.
Despite the growing recognition of wound irrigation in optimal wound management, the market faces constraints related to the lack of skilled healthcare personnel and standardized usage protocols—particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Proper use of irrigation systems requires training in pressure regulation, wound assessment, and fluid dynamics to avoid tissue trauma or ineffective cleansing.
In many healthcare settings, especially in rural regions, wound care is delegated to undertrained personnel who may lack access to or understanding of modern irrigation technologies. Moreover, the absence of global consensus on the ideal irrigation fluid, pressure settings, or device choice leads to variability in clinical outcomes. This variation often discourages procurement decision-makers from adopting newer systems, especially in resource-constrained environments. Thus, market expansion is hampered in some regions despite the evident clinical need.
An emerging opportunity lies in the expansion of home healthcare and outpatient wound care services, especially in the post-pandemic era where hospital resources are being preserved for critical care. With chronic wound patients requiring frequent interventions, there’s a growing preference for treatment in non-acute settings such as outpatient clinics and even at home, provided adequate tools and training are available.
Battery-operated wound irrigation systems, particularly those designed with lightweight, user-friendly features, are increasingly being deployed in home care environments. These devices allow caregivers and patients to manage wound cleansing without the need for specialized facilities. Companies are tapping into this trend by developing compact systems with pre-filled sterile solutions, disposable components, and intuitive operation. As healthcare systems globally aim to reduce hospital-acquired infections and overall treatment costs, enabling wound management at home offers both clinical and commercial value.
Based on products, the manual wound irrigation system segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 56.0% in 2024. These systems typically consist of a syringe or gravity-fed system used to flush the wound with sterile solutions. They are extensively used in emergency departments, surgical units, and home care environments where electric or battery-powered devices may not be feasible. Manual systems are particularly favored in low-resource settings for their affordability and minimal technical complexity.
The battery-operated wound irrigation segment is anticipated to experience the fastest growth, with a CAGR of 4.3% over the forecast period. These systems offer consistent flow, adjustable pressure settings, and improved ergonomics, enabling more efficient and safer wound cleansing. They are particularly useful in surgical and burn care where precision irrigation is vital for minimizing tissue trauma and infection risks. For example, the introduction of systems like Stryker’s PulsaVac and Medline’s Advanced Wound Irrigation Systems have significantly improved irrigation outcomes in clinical settings. As technology advances and costs decrease, battery-operated devices are expected to see increased uptake across both developed and emerging markets.
Based on application, the chronic wounds segment accounted for the largest revenue share of around 35.0% in 2024. These include diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure ulcers—conditions that are often slow to heal and associated with significant morbidity. Effective irrigation is critical for debridement, infection control, and wound bed preparation in chronic wound management. Given the increasing prevalence of diabetes and obesity, healthcare systems are placing more focus on structured wound care programs that incorporate irrigation as a core intervention. For example, hospitals and outpatient clinics frequently use wound irrigation as part of integrated care pathways for patients with long-term ulcers.
In contrast, burn wounds represent the fastest-growing application segment. Burn injuries, particularly second and third-degree burns, necessitate meticulous wound care to prevent infection and support tissue regeneration. Wound irrigation is routinely used in burn centers for cleansing, pain reduction, and antimicrobial delivery. With rising burn cases from industrial accidents, domestic mishaps, and natural disasters, the demand for irrigation systems in burn care has surged. Moreover, the increasing investment in specialized burn units in Asia and Latin America is expected to fuel the adoption of wound irrigation devices tailored for high-acuity cases.
March 2025: Stryker Corporation expanded its wound management portfolio by launching a new generation of PulsaVac Plus battery-powered irrigation systems featuring enhanced ergonomic design and flow control.
February 2025: Becton Dickinson (BD) collaborated with a European wound care organization to evaluate the efficacy of its latest wound irrigation technology in managing diabetic foot ulcers across multiple clinical centers.
January 2025: Medline Industries introduced a portable wound irrigation kit for home and outpatient care settings, aiming to enhance access to sterile and efficient irrigation for chronic wound patients.
December 2024: Smith & Nephew announced its investment in R&D to develop smart wound irrigation devices equipped with feedback sensors to optimize fluid delivery and tissue protection.
November 2024: Coloplast A/S launched a new wound irrigation solution pack in Asia Pacific markets, incorporating antiseptic solutions with prefilled disposable syringes.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the wound irrigation systems market
By Product
By Application
By Regional